 |
Blasts
In cell biology, precursor cells—also called blast cells—are partially differentiated, or intermediate, and are sometimes referred to as progenitor cells. A precursor cell is a stem cell with the capacity to differentiate into only one cell type, meaning they are unipotent stem cells. In embryology, precursor cells are a group of cells that later differentiate into one organ. However, progenitor cells are considered multipotent. Due to their contribution to the development of various organs and cancers, precursor and progenitor cells have many potential uses in medicine. There is ongoing research on using these cells to build heart valves, blood vessels, and other tissues by using blood and muscle precursor cells. Cytological types *Oligodendrocyte precursor cell *Myeloblast *Thymocyte *Meiocyte *Megakaryoblast *Promegakaryocyte *Melanoblast *Lymphoblast *Bone marrow precursor cells * Normoblast *Angioblast (endothelial precursor cells) *Myeloid precursor cells *Plasmablast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
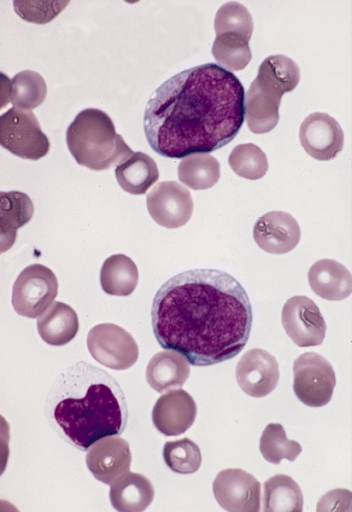
Megakaryoblast
A megakaryoblast () is a precursor cell to a promegakaryocyte. During thrombopoiesis, the promegakaryocyte matures into the form of a megakaryocyte. From the megakaryocyte, platelets are formed. The megakaryoblast is the beginning of the thrombocytic series or platelet forming series. Megakaryoblasts typically have a large oval-shaped nucleus or a nucleus that is lobed with many nuclei. The megakaryoblast resembles the myeloblast or lymphoblast morphologically; however the megakaryoblast varies in phenotype and the structure viewed with electron microscopy. Increased amounts of megakaryoblasts in the bone marrow may indicate a disease state. An example of this is acute megakaryoblastic leukemia, which occurs when the level of megakaryoblasts in the bone marrow exceeds 20%. Development The megakaryocyte develops through the following lineage: : CFU-Meg (hematopoietic stem cell/hemocytoblast) → megakaryoblast → promegakaryocyte → megakaryocyte The megakaryoblast is deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Unipotency
Cell potency is a cell's ability to differentiate into other cell types. The more cell types a cell can differentiate into, the greater its potency. Potency is also described as the gene activation potential within a cell, which like a continuum, begins with totipotency to designate a cell with the most differentiation potential, pluripotency, multipotency, oligopotency, and finally unipotency. Totipotency Totipotency () is the ability of a single cell to divide and produce all of the differentiated cells in an organism. Spores and zygotes are examples of totipotent cells. In the spectrum of cell potency, totipotency represents the cell with the greatest differentiation potential, being able to differentiate into any embryonic cell, as well as any extraembryonic tissue cell. In contrast, pluripotent cells can only differentiate into embryonic cells. A fully differentiated cell can return to a state of totipotency. The conversion to totipotency is complex and not fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
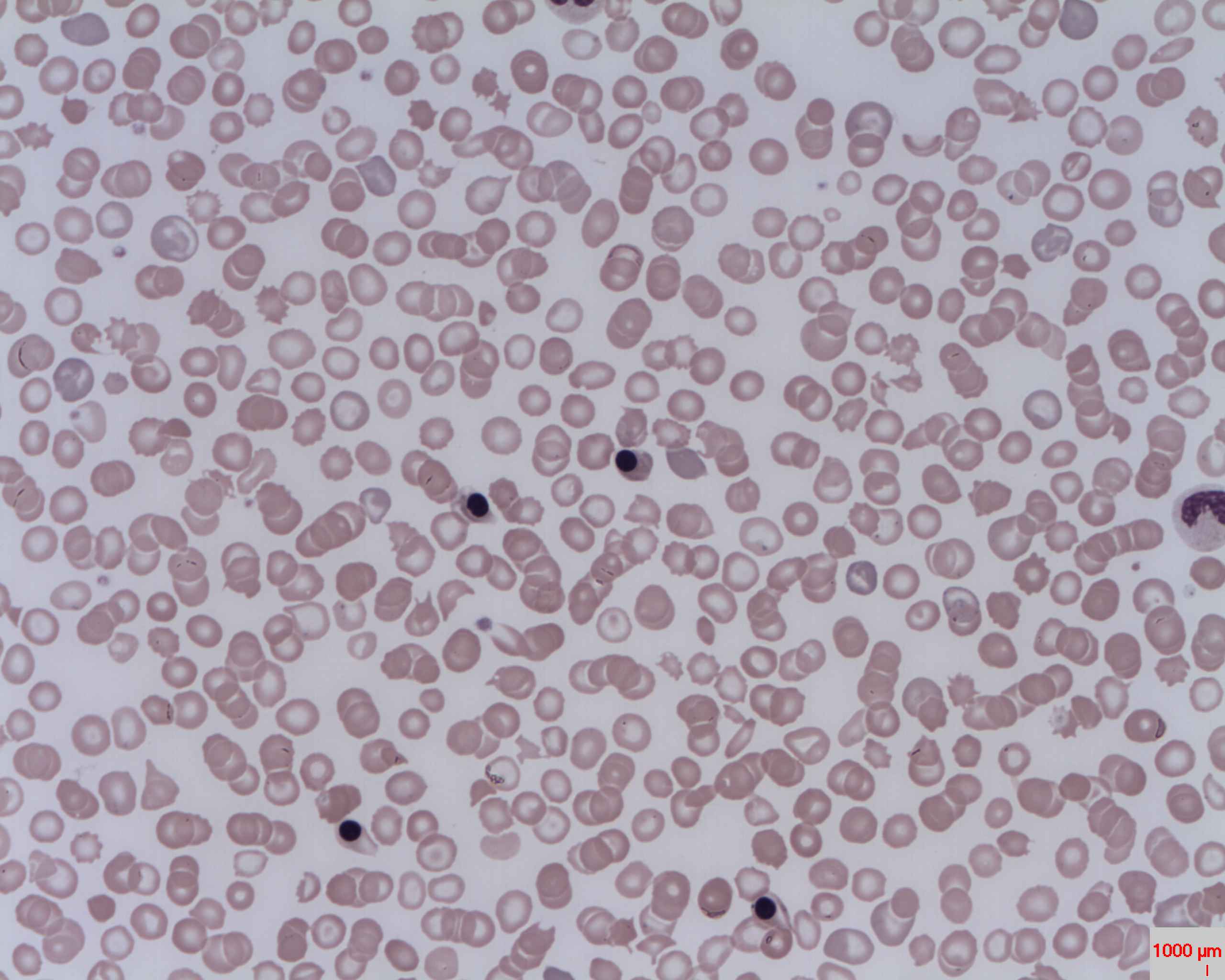 |
Normoblast
A nucleated red blood cell (NRBC), also known by several other names, is a red blood cell that contains a cell nucleus. Almost all vertebrate organisms have hemoglobin-containing cells in their blood, and with the exception of mammals, all of these red blood cells are nucleated. In mammals, NRBCs occur in normal development as precursors to mature red blood cells in erythropoiesis, the process by which the body produces red blood cells. NRBCs are normally found in the bone marrow of humans of all ages and in the blood of fetuses and newborn infants. After infancy, RBCs normally contain a nucleus only during the very early stages of the cell's life, and the nucleus is ejected as a normal part of cellular differentiation before the cell is released into the bloodstream. The presence of circulating NRBCs in adults occurs in situations of hematopoietic stress such as severe infection, massive hemorrhage, marrow infiltration, or extramedullary hematopoiesis. That is, if NRBCs are ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Multipotency
Cell potency is a cell's ability to differentiate into other cell types. The more cell types a cell can differentiate into, the greater its potency. Potency is also described as the gene activation potential within a cell, which like a continuum, begins with totipotency to designate a cell with the most differentiation potential, pluripotency, multipotency, oligopotency, and finally unipotency. Totipotency Totipotency () is the ability of a single cell to divide and produce all of the differentiated cells in an organism. Spores and zygotes are examples of totipotent cells. In the spectrum of cell potency, totipotency represents the cell with the greatest differentiation potential, being able to differentiate into any embryonic cell, as well as any extraembryonic tissue cell. In contrast, pluripotent cells can only differentiate into embryonic cells. A fully differentiated cell can return to a state of totipotency. The conversion to totipotency is complex and not fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Myeloblast
The myeloblast is a unipotent white blood cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation and cell survival. Structure Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords. Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval nucleus composed of very fine nonaggregated chromatin and possessing 3 or more nucleoli. The cytoplasm has a basophilic character an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Lymphoblast
__NOTOC__ A lymphoblast is a modified naive lymphocyte with altered cell morphology. It occurs when the lymphocyte is activated by an antigen and increased in volume by nucleus and cytoplasm growth as well as new mRNA and protein synthesis. The lymphoblast then starts dividing two to four times every 24 hours for three to five days, with a single lymphoblast making approximately 1000 clones of its original naive lymphocyte, with each clone sharing the originally unique antigen specificity. Finally the dividing cells differentiate into effector cells, known as plasma cells (for B cells), cytotoxic T cells, and helper T cells. Lymphoblasts can also refer to immature cells which typically differentiate to form mature lymphocytes. Normally, lymphoblasts are found in the bone marrow, but in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), lymphoblasts proliferate uncontrollably and are found in large numbers in the peripheral blood. The size is between 10 and 20 μm. Although commonly lymphoblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Angioblast
Angioblasts (or vasoformative cells) are embryonic cells from which the endothelium of blood vessels arises. They are derived from embryonic mesoderm. Blood vessels first make their appearance in several scattered vascular areas ( blood islands) that are developed simultaneously between the endoderm and the mesoderm of the yolk-sac, i. e., outside the body of the embryo. Here a new type of cell, the angioblast, is differentiated from the mesoderm. These cells as they divide form small, dense syncytial masses, which soon join with similar masses by means of fine processes to form plexuses. They form capillaries through vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Angioblasts are one of the two products formed from hemangioblasts (the other being multipotential hemopoietic stem cells). See also *List of human cell types derived from the germ layers This is a list of Cell (biology), cells in humans derived from the three embryonic germ layers – ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Cells d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Progenitor Cell
A progenitor cell is a biological cell that can differentiate into a specific cell type. Stem cells and progenitor cells have this ability in common. However, stem cells are less specified than progenitor cells. Progenitor cells can only differentiate into their "target" cell type. The most important difference between stem cells and progenitor cells is that stem cells can replicate indefinitely, whereas progenitor cells can divide only a limited number of times. Controversy about the exact definition remains and the concept is still evolving. The terms "progenitor cell" and "stem cell" are sometimes equated. Properties Most progenitors are identified as oligopotent. In this point of view, they can compare to adult stem cells, but progenitors are said to be in a further stage of cell differentiation. They are "midway" between stem cells and fully differentiated cells. The kind of potency they have depends on the type of their "parent" stem cell and also on their niche. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and splitting, but processes such as coalescent angiogenesis, vessel elongation and vessel cooption also play a role. Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors, and from neovascularization, although discussions are not always precise (especially in older texts). The first vessels in the developing embryo form through vasculogenesis, after which angiogenesis is responsible for most, if not all, blood vessel growth during development and in disease. Angiogenesis is a normal and vital process in growth and development, as well as in wound healing and in the formation of granulation tissue. However, it is also a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
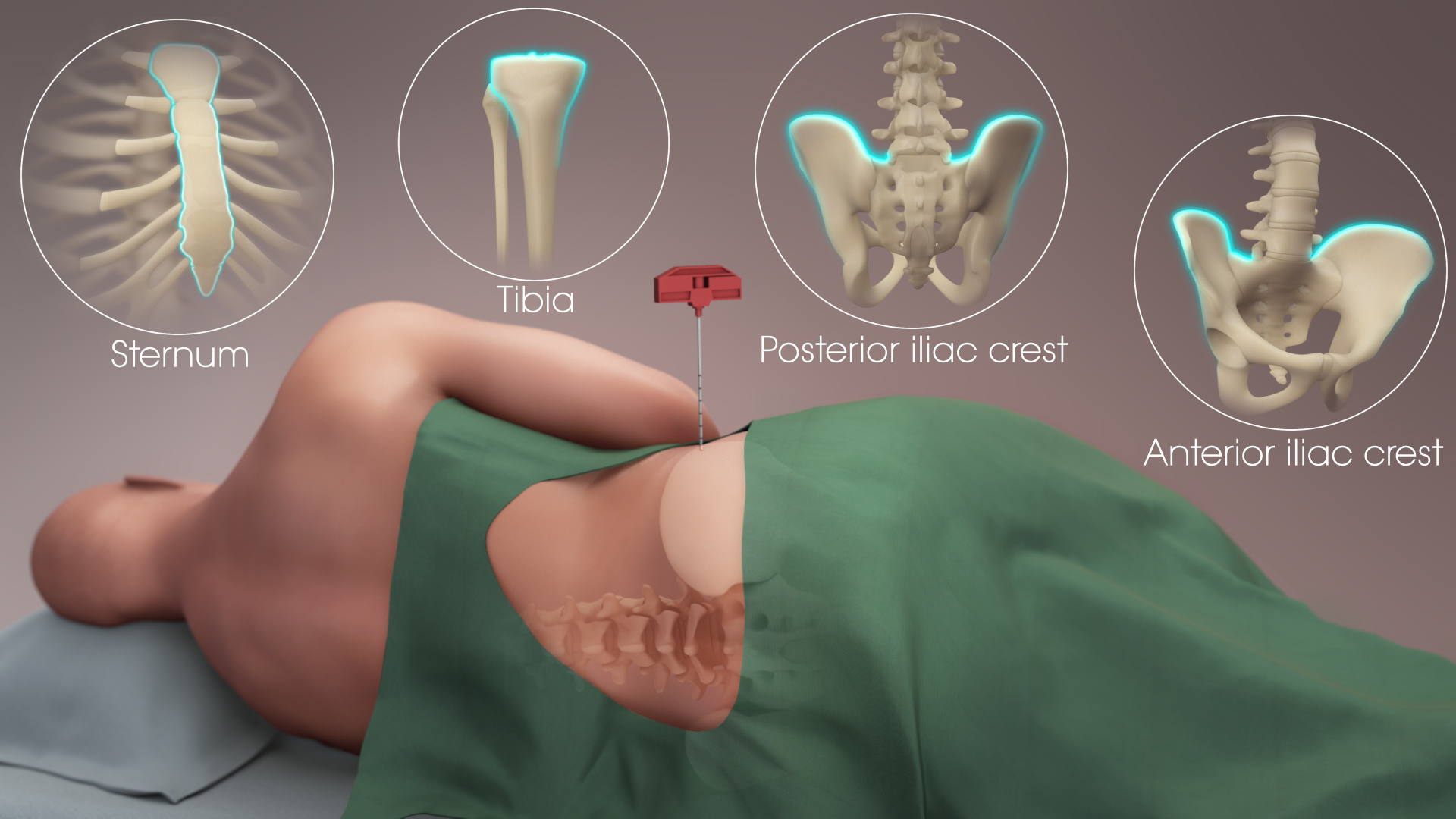 |
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of Blood cell, hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the Rib cage, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and Pelvis, bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a person weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the Circulatory system, systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of Hematopoietic cell, hematopoietic cells, including both Myeloid tissue, myeloid and Lymphocyte, lymphoid lineages, are create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |