|
Bishop Of Viterbo
The Diocese of Viterbo () is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in central Italy. From the 12th century, the official name of the diocese was the Diocese of Viterbo e Tuscania. In 1986, several dioceses were combined, and the title was changed to "Diocese of Viterbo, Acquapendente, Bagnoregio, Montefiascone, Tuscania and San Martino al Monte Cimino"; in 1991 the name was shortened to "Diocese of Viterbo"."Diocese of Viterbo" ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved January 2, 2017. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viterbo Cathedral
Viterbo Cathedral (, or ''Cattedrale di San Lorenzo'') is a Roman Catholic cathedral, and the principal church of the city of Viterbo, Lazio, central Italy. It is the seat of the Bishop of Viterbo and is dedicated to Saint Lawrence. The church is an imposing Romanesque architecture, Romanesque structure situated high on the hill which the city climbs, but it lacks much of the spectacular decoration with which it was originally adorned, thanks to an ill-advised sixteenth-century reconstruction. History Site According to legend, the cathedral was built on the site of an Etruscan mythology, Etruscan temple of Hercules. Etruscan and Ancient Rome, Roman foundations can be seen on several of the buildings facing the Piazza di San Lorenzo where the cathedral is situated. Before the 12th century, a parish church dedicated to Saint Lawrence had occupied the site of the cathedral. Even as this church was constructed, the town was already spreading northwards down the hill, leaving t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
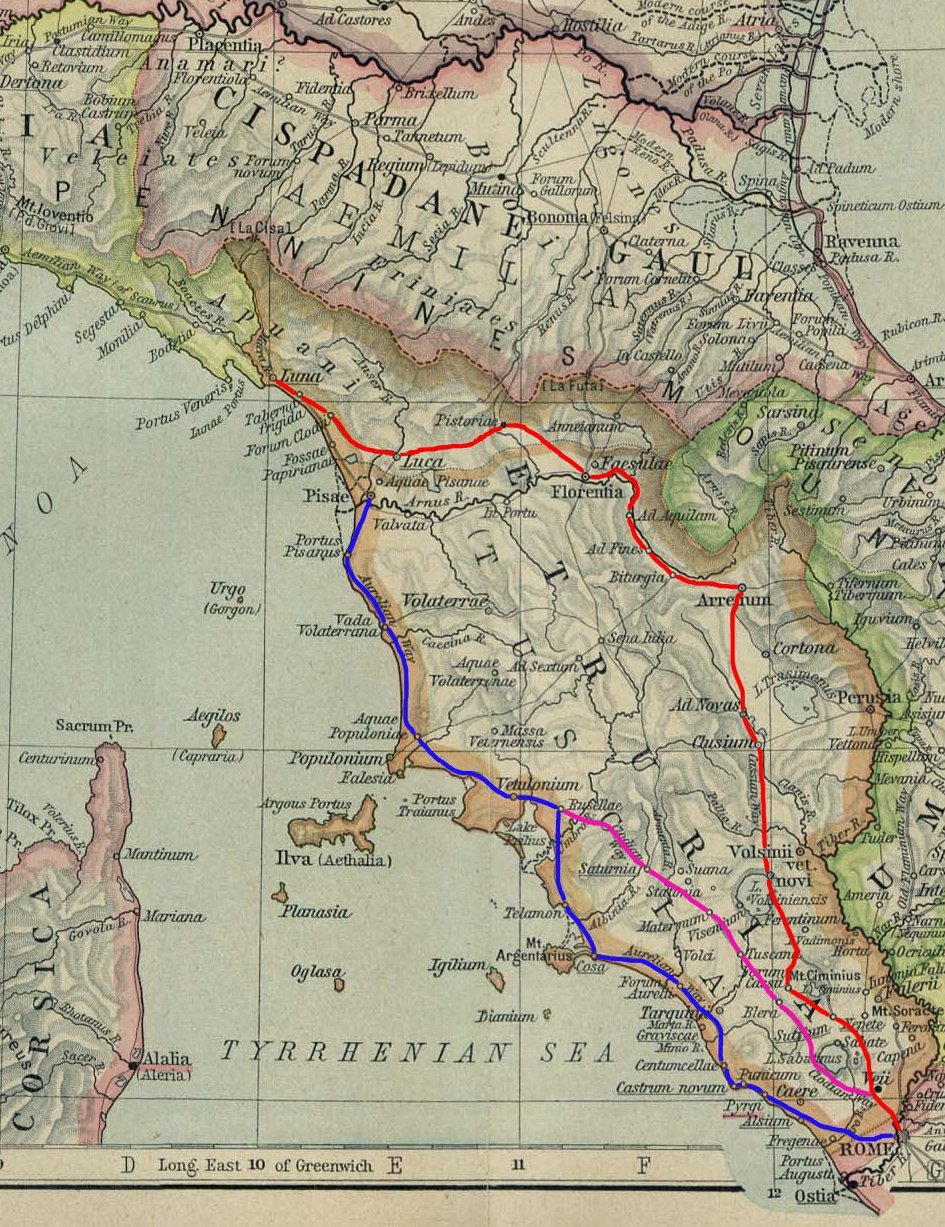
Via Cassia
The Via Cassia () was an important Roman road striking out of the Via Flaminia near the Milvian Bridge in the immediate vicinity of Rome and, passing not far from Veii, traversed Etruria. The ''Via Cassia'' passed through Baccanae, Sutrium, Volsinii, Clusium, Arretium, Florentia, Pistoria, and Luca, joining the Via Aurelia at Luna. The Via Cassia intersected other important roads. At mile 11 the Via Clodia diverged north-north-west. At Sette Vene, another road, probably the Via Annia, branched off to Falerii. In Sutrium, the '' Via Ciminia'' split off and later rejoined. The date of its construction is uncertain: it cannot have been earlier than 187 BC, when the consul Gaius Flaminius constructed a road from Bononia to Arretium, which must have coincided with a portion of the later Via Cassia. It is not mentioned by any ancient authorities before the time of Cicero, who in 45 BC speaks of the existence of three roads from Rome to Mutina: the Flaminia, the Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1268–1271 Papal Election
The 1268–71 papal election (from 1 December 1268 to 1 September 1271), following the death of Pope Clement IV, was the longest papal election in the history of the Catholic Church. This was due primarily to political infighting between the cardinals. The election of Teobaldo Visconti as Pope Gregory X was the first example of a papal election by "compromise", that is, by the appointment of a committee of six cardinals agreed to by the other ten. (This method was attempted once before, in the 1227 papal election, but the choice of the committee refused the honor and the full group of cardinals proceeded to elect the pope.) The election occurred more than a year after the magistrates of Viterbo locked the cardinals in, reduced their rations to bread and water, and removed the roof of the Palace of the Popes in Viterbo where the election took place.Bower, Archibald. 1766. ''The History of the Popes: From the Foundation of the See of Rome to the Present Time''. p. 283-284. As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Clement V
Pope Clement V (; – 20 April 1314), born Raymond Bertrand de Got (also occasionally spelled ''de Guoth'' and ''de Goth''), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 5 June 1305 to his death, in April 1314. He is remembered for suppressing the order of the Knights Templar and allowing the execution of many of its members. A Frenchman by birth, Clement moved the Roman Curia, Papacy from Rome to Avignon, ushering in the period known as the Avignon Papacy. Early career Raymond Bertrand was born in Villandraut, Vilandraut, Aquitaine, the son of Bérard, Lord of Villandraut. Bertrand studied the arts at Toulouse and canon and civil law at Orléans and Bologna. He became Canon (priest), canon and sacristan of the Cathedral of Saint-André in Bordeaux, then vicar-general to his brother Bérard de Got, the Archbishop of Lyon, who in 1294 was created Cardinal-Bishop of Albano and papal legate to France. He was then made Bishop of St-Bertrand-de-Comminges, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathars
Catharism ( ; from the , "the pure ones") was a Christian quasi- dualist and pseudo-Gnostic movement which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France, between the 12th and 14th centuries. Denounced as a heretical sect by the Catholic Church, its followers were attacked first by the Albigensian Crusade and later by the Medieval Inquisition, which eradicated the sect by 1350. Around 1 million were slaughtered, hanged, or burnt at the stake. Followers were known as Cathars or Albigensians, after the French city Albi where the movement first took hold, but referred to themselves as Good Christians. They famously believed that there were not one, but two Godsthe good God of Heaven and the evil god of this age (). According to tradition, Cathars believed that the good God was the God of the New Testament faith and creator of the spiritual realm. Many Cathars identified the evil god as Satan, the master of the physical world. The Cathars believe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Tuscanella
The Diocese of Tuscanella (Latin: Tuscaniensis) was a Latin Church residential bishopric of the Catholic Church, in existence by the 7th century. Even at the time of the Lombard invasions, it belonged to the Duchy of Rome and was immediately subject to the Pope. The seat of the bishop was originally in the church of S. Maria, then in the church of S. Pietro, and after 1592 in the church of S. Giacomo. On 22 February 852 Pope Leo IV, in the bull ''Convenit apostolico'', addressed to Bishop Virbono, confirmed the jurisdiction of the bishop over the churches and possessions of his diocese. This document is revealing, because it not only describes the towns and parishes dependent on the bishop (including Montalto, Tarquinia and Viterbo), but also details the boundaries of the diocese. From 1192 the diocese of Tuscanella and the diocese of Viterbo were in personal union ('' aeque principaliter''). The diocese was suppressed in 1986. The name, though not the diocesan structure, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Celestine III
Pope Celestine III (; c. 1105 – 8 January 1198), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 30 March or 10 April 1191 to his death in 1198. He had a tense relationship with several monarchs, including Emperor Henry VI, King Tancred of Sicily, and King Alfonso IX of León. Early career Giacinto Bobone was born into the noble Orsini family in Rome. He was appointed as cardinal-deacon in 1144 by Celestine II or Lucius II. Considered by the Roman Curia as an expert on Spain, Bobone conducted two legatine missions to Spain in (1154–55) and (1172–75) as the Cardinal-Deacon of Santa Maria in Cosmedin. Pontificate Celestine was elected on 29/30 March 1191 and ordained a priest 13 April 1191. He crowned Emperor Henry VI a day or two after his ordination. In 1192, Celestine recognized Tancred as king of Sicily, despite Henry VI's wife's claim. He threatened to excommunicate Henry VI for wrongfully keeping King Richard I of England imprison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Blera
The Diocese of Viterbo () is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in central Italy. From the 12th century, the official name of the diocese was the Diocese of Viterbo e Tuscania. In 1986, several dioceses were combined, and the title was changed to "Diocese of Viterbo, Acquapendente, Bagnoregio, Montefiascone, Tuscania and San Martino al Monte Cimino"; in 1991 the name was shortened to "Diocese of Viterbo"."Diocese of Viterbo" ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved January 2, 2017. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipope Clement III
Guibert or Wibert of Ravenna (8 September 1100) was an Italian prelate, archbishop of Ravenna, who was elected pope in 1080 in opposition to Pope Gregory VII and took the name Clement III. Gregory was the leader of the movement in the church which opposed the traditional claim of European monarchs to control ecclesiastical appointments, and this was opposed by supporters of monarchical rights led by the Holy Roman Emperor. This led to the conflict known as the Investiture Controversy. Gregory was felt by many to have gone too far when he excommunicated the Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV and supported a rival claimant as emperor, and in 1080 the pro-imperial Synod of Brixen pronounced that Gregory was deposed and replaced as pope by Guibert. Consecrated as Pope Clement III in Rome in March 1084, he commanded a significant following in Rome and elsewhere, especially during the first half of his pontificate, and reigned in opposition to four successive popes in the anti-imperial li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Centumcellae
The Diocese of Civitavecchia-Tarquinia () is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Lazio, Italy. It was established under this name in 1986. The diocese is immediately exempt to the Holy See and not part of an ecclesiastical province."Diocese of Civitavecchia-Tarquinia" ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved October 7, 2016"Diocese of Civitavecchia-Tarquinia" ''GCatholic.org''. Gabriel Chow. Retrieved October 7, 2016 |
Charles The Bald
Charles the Bald (; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as CharlesII, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), King of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a series of civil wars during the reign of his father, Louis the Pious, Charles succeeded, by the Treaty of Verdun (843), in acquiring the western third of the empire. He was a grandson of Charlemagne and the youngest son of Louis the Pious by his second wife, Judith of Bavaria (died 843), Judith. Struggle against his brothers He was born on 13 June 823 in Frankfurt, when his elder brothers were already adults and had been assigned their own ''regna'', or subkingdoms, by their father. The attempts made by Louis the Pious to assign Charles a subkingdom, first Alemannia and then the country between the Meuse and the Pyrenees (in 832, after the rising of Pepin I of Aquitaine, PepinI of Aquitaine) were unsuccessful. The numerous reconciliations with the rebellious Lothair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope John VIII
Pope John VIII (; died 16 December 882) was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 14 December 872 to his death. He is often considered one of the most able popes of the 9th century. John devoted much of his papacy to attempting to halt and reverse the Muslim gains in southern Italy and their march northwards. When his efforts to obtain assistance from either the Franks or the Byzantines failed, John strengthened the defences of Rome. He supported Methodius of Thessalonica in his mission to the Slavs, defended him against the Carolingian rulers and Bavarian clergy, and authorized the translation of the Bible into Old Church Slavonic. John also extended diplomatic recognition to the Duchy of Croatia and resolved the Photian schism. John's pontificate ended with his assassination, and the papacy became significantly weaker in the aftermath. Slavonic liturgy Pope Adrian II consecrated Methodius of Thessalonica as archbishop and supported his mission to the Slav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |