|
Biological Cost
In biology, the ''biological cost'' or ''metabolic price'' is a measure of the increased energy metabolism that is required to achieve a function. Drug resistance in microbiology, for instance, has a very high metabolic price, especially for antibiotic resistance Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resis .... References Metabolism {{Biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell (biology), cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple biological organisation, levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including scientific method, observation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Metabolism
Bioenergetics is a field in biochemistry and cell biology that concerns energy flow through living systems. This is an active area of biological research that includes the study of the transformation of energy in living organisms and the study of thousands of different cellular processes such as cellular respiration and the many other metabolic and enzymatic processes that lead to production and utilization of energy in forms such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules. Nelson, David L., Cox, Michael M. ''Lehninger: Principles of Biochemistry.'' New York: W.H. Freeman and Company, 2013. Sixth ed., pg. 27. That is, the goal of bioenergetics is to describe how living organisms acquire and transform energy in order to perform biological work. Nelson, David L., Cox, Michael M. ''Lehninger: Principles of Biochemistry.'' New York: W.H. Freeman and Company, 2013. Sixth ed., pg. 24. The study of metabolic pathways is thus essential to bioenergetics. Overview Bioenergetics is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
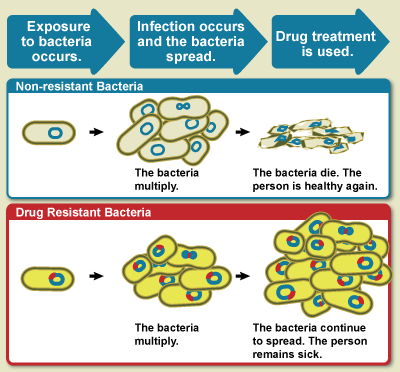
Drug Resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, resistance has evolved. Antimicrobial resistance and antineoplastic resistance challenge clinical care and drive research. When an organism is resistant to more than one drug, it is said to be multidrug-resistant. The development of antibiotic resistance in particular stems from the drugs targeting only specific bacterial molecules (almost always proteins). Because the drug is ''so'' specific, any mutation in these molecules will interfere with or negate its destructive effect, resulting in antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, there is mounting concern over the abuse of antibiotics in the farming of livestock, which in the European Union alone accounts for three times the volume dispensed to humans – leading to development of super-re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resistance), viruses (antiviral resistance), parasites (antiparasitic resistance), and fungi (antifungal resistance). Together, these adaptations fall under the AMR umbrella, posing significant challenges to healthcare worldwide. Misuse and improper management of antimicrobials are primary drivers of this resistance, though it can also occur naturally through genetic mutations and the spread of resistant genes. Antibiotic resistance, a significant AMR subset, enables bacteria to survive antibiotic treatment, complicating infection management and treatment options. Resistance arises through spontaneous mutation, horizontal gene transfer, and increased selective pressure from antibiotic overuse, both in medicine and agriculture, which accelerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |