|
Biennial Bearing
Biennial bearing (or alternate) bearing is a term used in pomology to refer to trees that have an irregular crop load from year to year. In the "on" year too much fruit is set, leading to small fruit size. Excess weight in the main branches can be too much for their mechanical resistance, causing them to break. Another major consequence is that flower induction will be lower, and the subsequent year will be "off" year (too little fruit). The behavior could be due to plant hormones, particularly gibberellins produced in excess in the "on" years in the embryos of the young fruit. It could also be caused by depletion of carbohydrate reserves in the tree. Biennial bearing is more common in certain fruit crops like mango, apple, pear, apricot and avocado, and is almost nonexistent in grapes. Biennial bearing is a regular feature of Arabica coffee production in Ethiopia and East Africa, and indeed throughout the coffee-growing world. In Biennial bearing a good or excellent (bumper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomology
Pomology (from Latin , "fruit", + , "study") is a branch of botany that studies fruits and their cultivation. Someone who researches and practices the science of pomology is called a pomologist. The term fruticulture (from Latin , "fruit", + , "care") is also used to describe the agricultural practice of growing fruits in orchards. Pomological research is mainly focused on the development, enhancement, cultivation, and physiological studies of fruit trees. The goals of fruit tree improvement include enhancement of fruit quality, regulation of production periods, and reduction of production costs. History Middle East In ancient Mesopotamia, pomology was practiced by the Sumerians, who are known to have grown various types of fruit, including dates, grapes, apples, melons, and figs. While the first fruits cultivated by the Egyptians were likely indigenous, such as the palm date and sorghum, more fruits were introduced as other cultural influences were introduced. Grapes and wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Kenya to the south, South Sudan to the west, and Sudan to the northwest. Ethiopia covers a land area of . , it has around 128 million inhabitants, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, thirteenth-most populous country in the world, the List of African countries by population, second-most populous in Africa after Nigeria, and the most populous landlocked country on Earth. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African Plate, African and Somali Plate, Somali tectonic plates. Early modern human, Anatomically modern humans emerged from modern-day Ethiopia and set out for the Near East and elsewhere in the Middle Paleolithi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Terminology
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in the cities. While humans started gathering grains at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers only began planting them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs, and cattle were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. In the 20th century, industrial agriculture based on large-scale monocultures came to dominate agricultural output. , small farms produce about one-third of the world's food, but large farms are prevalent. The largest 1% of farms in the world are greater than and operate more than 70% of the world's farmland. Nearly 40% of agricultural land is found on farms larger than . However, five of every six far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering. Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propagated using the movements of humans and other animals in a symbiotic relationship that is the means for seed dispersal for the one group and nutrition for the other; humans, and many other animals, have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Consequently, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings. In common language and culinary usage, ''fruit'' normally means the seed-associated fleshy structures (or produce) of plants that typically are sweet (or sour) and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. In botanical usage, the term ''fruit'' als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowers
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, modified leaves; corolla, the petals; androecium, the male reproductive unit consisting of stamens and pollen; and gynoecium, the female part, containing style and stigma, which receives the pollen at the tip of the style, and ovary, which contains the ovules. When flowers are arranged in groups, they are known collectively as inflorescences. Floral growth originates at stem tips and is controlled by MADS-box genes. In most plant species flowers are heterosporous, and so can produce sex cells of both sexes. Pollination mediates the transport of pollen to the ovules in the ovaries, to facilitate sexual reproduction. It can occur between different plants, as in cross-pollination, or between flowers on the same plant or even the same flowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thinning
In agricultural sciences, thinning is the removal of some plants, or parts of plants, to make room for the growth of others. Selective removal of parts of a plant such as branches, buds, or roots is typically known as '' pruning''. In forestry, thinning is the selective removal of trees, primarily undertaken to improve the growth rate or health of the remaining trees. Overcrowded trees are under competitive stress from their neighbors. Thinning may be done to increase the resistance of the stand to environmental stress such as drought, insect infestation, extreme temperature, or wildfire. In forestry Tree thinning may be practised in forestry to make a stand more profitable in an upcoming final felling, or to advance ecological goals such as increasing biodiversity or accelerating the development of desired structural attributes such as large diameter trees with long tree crowns. Early thinning, e.g. after 20 years, rather than late thinning, e.g. after 50 years, has dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultivars
A cultivar is a kind of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and which retains those traits when propagated. Methods used to propagate cultivars include division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture, or carefully controlled seed production. Most cultivars arise from deliberate human manipulation, but some originate from wild plants that have distinctive characteristics. Cultivar names are chosen according to rules of the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP), and not all cultivated plants qualify as cultivars. Horticulturists generally believe the word ''cultivar''''Cultivar'' () has two meanings, as explained in '' Formal definition'': it is a classification category and a taxonomic unit within the category. When referring to a taxon, the word does not apply to an individual plant but to all plants that share the unique characteristics that define the cultivar. was coined as a term meaning "cultivated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
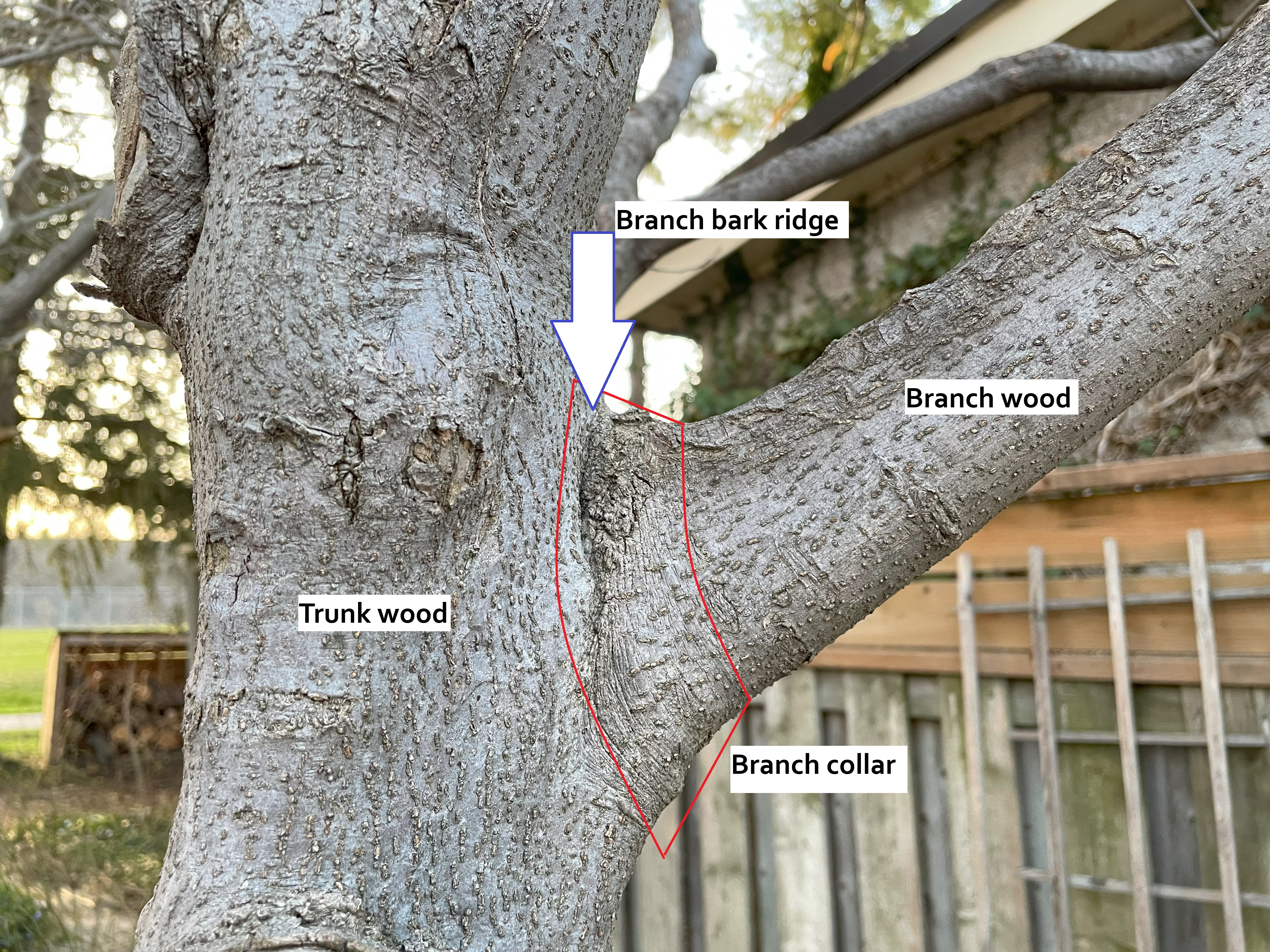
Pruning
Pruning is the selective removal of certain parts of a plant, such as branches, buds, or roots. It is practiced in horticulture (especially fruit tree pruning), arboriculture, and silviculture. The practice entails the targeted removal of diseased, damaged, dead, non-productive, structurally unsound, or otherwise unwanted plant material from crop and landscape plants. In general, the smaller the branch that is cut, the easier it is for a woody plant to compartmentalize the wound and thus limit the potential for pathogen intrusion and decay. It is therefore preferable to make any necessary formative structural pruning cuts to young plants, rather than removing large, poorly placed branches from mature plants. Woody plants may undergo a process referred to as ''self-pruning'', where they will drop twigs or branches which are no longer producing more energy than they require. It is theorized that this process can also occur in response to lack of water, in order to reduce the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stipe (botany)
In botany, a stipe is a stalk that supports some other structure. The precise meaning is different depending on which taxonomic group is being described. file:Helicteres-Yucatán-Flowers.jpg, The long stipe of a '' Helicteres'' flower. file:Helicteres-Yucatán-Fruits.jpg, remains as each flower forms a fruit. In the case of ferns, the stipe is only the petiole from the rootstock to the beginning of the leaf tissue, or lamina. The continuation of the structure within the lamina is then termed a rachis. In flowering plants, the term is often used in reference to a stalk that sometimes supports a flower's ovary. In orchids, the stipe or caudicle is the stalk-like support of the pollinia. It is a non-viscid band or strap connecting the pollinia with the viscidium (the viscid part of the rostellum or beak). A stipe is also a structure found in organisms that are studied by botanists but that are no longer classified as plants. It may be the stem-like part of the thallus of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crop Yield
In agriculture, the yield is a measurement of the amount of a crop grown, or product such as wool, meat or milk produced, per unit area of land. The seed ratio is another way of calculating yields. Innovations, such as the use of fertilizer, the creation of better farming tools, and new methods of farming and improved crop varieties have improved yields. The higher the yield and more intensive use of the farmland, the higher the productivity and profitability of a farm; this increases the well-being of farming families. Surplus crops beyond the needs of subsistence agriculture can be sold or bartered. The more grain or fodder a farmer can produce, the more draft animals such as horses and oxen could be supported and harnessed for labour and production of manure. Increased crop yields also means fewer hands are needed on farm, freeing them for industry and commerce. This, in turn, led to the formation and growth of cities, which then translated into an increased demand for foodst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. In other words, a crop is a plant or plant product that is grown for a specific purpose such as food, Fiber, fibre, or fuel. When plants of the same species are cultivated in rows or other systematic arrangements, it is called crop field or crop cultivation. Most crops are harvested as food for humans or fodder for livestock. Important non-food crops include horticulture, floriculture, and industrial crops. Horticulture crops include plants used for other crops (e.g. fruit trees). Floriculture crops include bedding plants, houseplants, flowering garden and pot plants, cut cultivated greens, and cut flowers. Industrial crops are produced for clothing (fiber crops e.g. cotton), biofuel (energy crops, algae fuel), or medicine (medicinal plants). Production There was an increase in global production of primary crops by 56% between 2000 and 2022 to 9.6 billion tonnes, which represents a 0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the region is recognized in the United Nations Statistics Division United Nations geoscheme for Africa, scheme as encompassing 18 sovereign states and 4 territories. It includes the Horn of Africa to the North and Southeastern Africa to the south. Definitions In a narrow sense, particularly in English-speaking contexts, East Africa refers to the area comprising Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda, largely due to their shared history under the Omani Empire and as parts of the British East Africa Protectorate and German East Africa. Further extending East Africa's definition, the Horn of Africa—comprising Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia—stands out as a distinct geopolitical entity within East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |