|
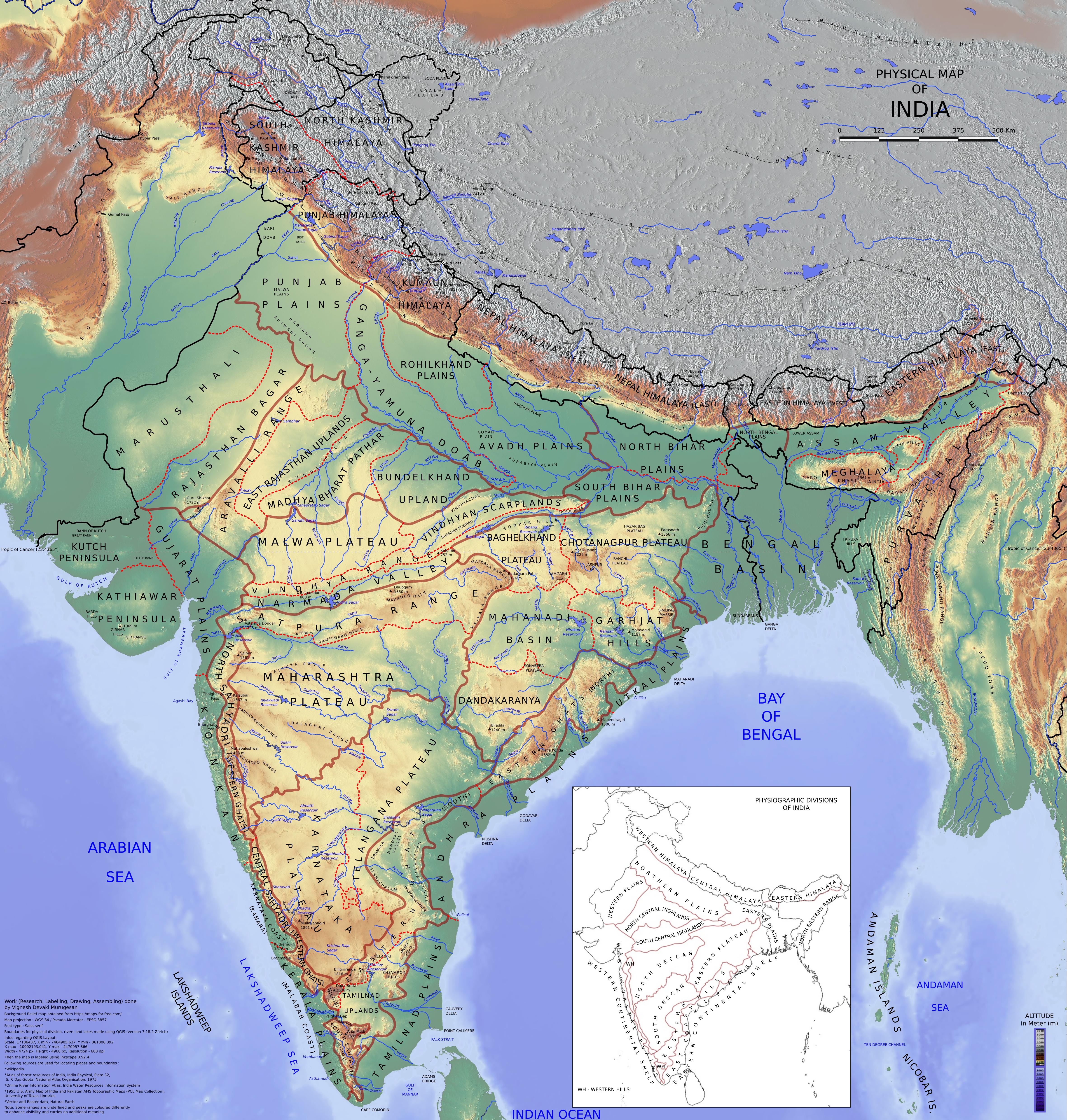
Bhabar
Bhabar or Bhabhar is a region south of the Lower Himalayas and the Sivalik Hills in Garhwal and Kumaon, India. The Bhabhar region contains some of the largest cities of Kumaon and Garhwal: Dehradun, Haridwar, Haldwani, Rishikesh, Ramnagar, Tanakpur and Kotdwar. It is the alluvial apron of sediments washed down from the Sivaliks along the northern edge of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. The Indo-Gangetic Plains are generally thought of as a flat region with no variations, although this isn't true. The plains can be classified into four regions on the basis of relief features. The Bhabar is a belt of 8–16 km lying parallel to the slopes of the Sivaliks, where the river descending from the mountains deposit pebbles. The streams flow through the pebbles the region, hence disappearing from sight. They re-emerge only after some distance south, in the relief feature Terai. Etymology The name ''Bhabar'' refers to a local tall-growing grass, '' Eulaliopsis binata'', used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haldwani
Haldwani (Kumaoni language, Kumaoni: ''Haldvānī'') is the largest city of Kumaon division, Kumaon. It is also the second List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Haldwani is said to be the financial capital of Uttarakhand, having the most commercial, economic and industrial activities of the state. Haldwani is located in the Nainital District, and is one of its List of tehsils of Uttarakhand, thirteen Subdivisions. The Haldwani Urban agglomeration has 656,000 people as of 2021, and is the Second most populous Megacity in Uttarakhand, after Dehradun. Being situated in the immediate foothills of Kumaon Himalayas, the Kathgodam neighbourhood of Haldwani is known as the "Gateway to Kumaon". Located in the Bhabar, Bhabhar region in the Himalayan foothills on the banks of the Gaula River (India), Gaula River, the c:File:Chhota_Kailash_through_morning_mists_from_Haldwani,_Nainital_region._Haldwani.jpg, town of Haldwani was est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumaon Division
Kumaon (; , ; historically romanised as KemāonJames Prinsep (Editor)John McClelland ) is a List of divisions in India, revenue and administrative division in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It spans over the eastern half of the state and is bounded on the north by Tibet, on the east by Nepal, on the south by the state of Uttar Pradesh, and on the west by Garhwal Division, Garhwal. Kumaon comprises six districts of the state: Almora district, Almora, Bageshwar district, Bageshwar, Champawat district, Champawat, Nainital district, Nainital, Pithoragarh district, Pithoragarh and Udham Singh Nagar district, Udham Singh Nagar. Historically known as Manaskhand and then Kurmanchal, the Kumaon region has been ruled by several dynasties over the course of history; most notably the Katyuri kings, Katyuris and the Chand kings, Chands. The Kumaon division was established in 1816, when the British reclaimed this region from the Gorkha Kingdom, Gorkhas, who had annexed the erstwhile Kumaon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sivalik Hills
The Sivalik Hills, also known as Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas. The literal translation of "Sivalik" is 'tresses of Shiva'. The hills are known for their numerous fossils, and are also home to the Soanian Middle Paleolithic archaeological culture. Geography The Sivalik Hills are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas that stretches over about from the Indus River eastwards close to the Brahmaputra River, spanning the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent. It is wide with an average elevation of . Between the Teesta and Raidāk Rivers in Assam is a gap of about . They are well known for their Neogene and Pleistocene aged vertebrate fossils. Geology Geologically, the Sivalik Hills belong to the Tertiary deposits of the outer Himalayas. They are chiefly composed of sandstone and conglomerate rock formations, which are the solidified detritus of the Himalayas to their north; they are poorly consolidated. The sedimentary rocks comprising the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain spanning across the northern and north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses North India, northern and East India, eastern India, eastern Pakistan, southern Nepal, and almost all of Bangladesh. It is named after the two major river systems that drain the region–Indus River, Indus and Ganges. It stretches from the Himalayas in the north to the northern edge of the Deccan plateau in the south, and extends from North East India in the east to the Iranian border in the west. The region is home to many major cities and nearly one-seventh of the world's population. As the region was formed by the deposits of the three major rivers–Indus, Ganges and Brahmaputra, the plains consists of the world's largest expanse of uninterrupted alluvial soil, alluvium. Due to its rich water resources, it is one of the world's most densely populated and intensely farmed areas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramnagar, Nainital
Ramnagar ( Kumaoni: ''Rāmnagar'') is a town and municipal board in the Nainital district of Kumaon in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is located approximately from Nainital, the headquarters of the district. Ramnagar is a gateway to the Corbett National Park, the oldest national park and a famous tourist destination. The Garjiya Devi Temple and Sitabani temple, Sitabani Wildlife Reserve located nearby also attract many visitors. Uttarakhand Board of School Education is headquartered in Ramnagar. The board was set up in 2001, and is responsible for administering courses of instructions, textbooks, and to conduct examinations for secondary school students of the state. Geography Ramnagar is located at 29.40°N 79.12°E. It has an average elevation of roughly 345 metres (1,132 feet). Ramnagar is located at the foothills of the Himalayas on the bank of river Kosi. The town is visited by many tourists due to its geographical location near Corbett National Park. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand has a total geographic area of 53,483 km2, of which 86% is mountainous and 65% is covered by forest. Most of the northern parts of the state are part of Greater Himalaya ranges, covered by the high Himalayan peaks and glaciers, while the lower foothills were densely forested till denuded by the British log merchants and later, after independence, by forest contractors. Recent efforts in reforestation, however, have been successful in restoring the situation to some extent. The unique Himalayan ecosystem plays host to many animals (including bharal, snow leopards, leopards and tigers), plants and rare herbs. Two of India's great rivers, the Ganges and the Yamuna take birth in the glaciers of Uttarakhand, and are fed by myriad lakes, glacial melts and streams. Terrain and vegetation Uttarakhand lies on the southern slope of the Himalaya range, and the climate and vegetation vary greatly with elevation, from glaciers at the highest elevation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand (, ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2007), is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. The state is bordered by Himachal Pradesh to the northwest, Tibet to the north, Nepal to the east, Uttar Pradesh to the south and southeast, with a small part touching Haryana in the west. Uttarakhand has a total area of , equal to 1.6% of the total area of India. Dehradun serves as the state capital, with Nainital being the judicial capital. The state is divided into two divisions, Garhwal division, Garhwal and Kumaon division, Kumaon, with a total of List of districts of Uttarakhand, 13 districts. The forest cover in the state is 45.4% of the state's geographical area. The cultivable area is 16% of the total geographical area. The two major rivers of the state, the Ganges and its tributary Yamuna, originate from the Gangotri and Yamunotri glaciers respectively. Ranked 6th among the Top 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eulaliopsis Binata
''Eulaliopsis binata'', the sabaigrass or Chinese alpine rush, is a perennial plant belonging to the grass family that is grown in many Asian countries like China, Nepal, India, Pakistan, Bhutan, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia and Philippines. It is called '' bhabhar'' in India and lends the name to the region south of Himalayas where it grows. It is called Babiyo in Nepal. It is mainly used for the manufacture of writing and printing paper. Pulping is done using soda and sulfate processes.In Nepal, it is used to make rope for swing for Dashain festival, one of the greatest festivals of Hindu Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ... people. References Flora of Asia Plants described in 1789 Andropogoneae {{Panicoideae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terai
The Terai or Tarai is a lowland region in parts of southern Nepal and northern India that lies to the south of the outer foothills of the Himalayas, the Sivalik Hills and north of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. This lowland belt is characterised by tall grasslands, scrub savannah, sal forests and clay rich swamps. In North India, the Terai spreads from the Yamuna River eastward across Haryana, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal. The Terai is part of the Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands ecoregion. Nepal's Terai stretches over , about 23.1% of Nepal's land area, and lies at an elevation of between . The region comprises more than 50 wetlands. North of the Terai rises the Bhabar, a narrow but continuous belt of forest about wide. Etymology The Urdu word tarāʼī means "lands lying at the foot of a watershed" or "on the banks of a river; low ground flooded with water, valley, basin, marshy ground, marsh, swamp; meadow". In Hindi, the region is called 'tarāī' m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nainital District
Nainital district is a district in Kumaon division which is a part of Uttarakhand state in India. The headquarters is at Nainital. Nainital District is located in Kumaon Division, and is located in the lower Himalayas. Haldwani is the largest city in the district. Geography The district borders Almora and Champawat districts to the north, Udham Singh Nagar district to the south, and Bijnor district of Uttar Pradesh and Pauri Garhwal district to the west. Nainital district is located in the Kumaon Himalaya. The district has part of the Bhabar tract in its south, which is bordered to the north by the Sivalik hills. To the north of this is the Lesser Himalayas, with a maximum altitude of 2600m. The main river in the district is the Kosi, which forms part of the border between Almora and Nainital districts before entering Nainital district proper. It then flows through Nainital district to the Ramganga. History The southern Terai part of the district was ruled by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehradun
Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, district and is governed by the Dehradun Municipal Corporation, with the Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly holding its winter sessions in the city as its winter capital. Part of the Garhwal division, Garhwal region, and housing the headquarters of its Divisional Commissioner, Dehradun is one of the "National Capital Region (India)#Counter magnets, Counter Magnets" of the National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region (NCR) being developed as an alternative centre of growth to help ease the migration and population explosion in the Delhi metropolitan area and to establish a smart city in the Himalayas. Dehradun is located in the Doon Valley on the foothills of the Himalayas nestled between Song River (India), Song River, a tributary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rishikesh
Rishikesh, also spelt as Hrishikesh, is a city near Dehradun in the Indian state Uttarakhand. The northern part of Rishikesh is in the Dehradun district while the southern part is in the Tehri Garhwal district. It is situated on the right bank of the Ganges River and is a pilgrimage town for Hindus, with ancient sages and saints meditating there in search of higher knowledge. There are numerous temples and ashrams built along the banks of the river. It is known as the "''Gateway to the Garhwal Himalayas''" and "''Yoga Capital of the World''". The city has hosted the annual International Yoga Festival on the first week of March since 1999. Rishikesh is a vegetarian-only and alcohol-free city. The Tehri Dam is located away from Rishikesh. Uttarkashi, a popular yoga destination, is uphill on the way to Gangotri Dham, Gangotri. Rishikesh is the starting point for travelling to the four Chota Char Dham pilgrimage places: Badrinath, Kedarnath, Gangotri, and Yamunotri. It is also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |