|
Beta-barrel
In protein structures, a beta barrel (β barrel) is a beta sheet (β sheet) composed of tandem repeats that twists and coils to form a closed toroidal structure in which the first strand is bonded to the last strand (hydrogen bond). Beta-strands in many beta-barrels are arranged in an antiparallel fashion. Beta barrel structures are named for resemblance to the barrels used to contain liquids. Most of them are water-soluble outer membrane proteins and frequently bind hydrophobic ligands in the barrel center, as in lipocalins. Others span cell membranes and are commonly found in porins. Porin-like barrel structures are encoded by as many as 2–3% of the genes in Gram-negative bacteria. It has been shown that more than 600 proteins with various function such as oxidase, dismutase, and amylase contain the beta barrel structure. In many cases, the strands contain alternating polar and non-polar (hydrophilic and hydrophobic) amino acids, so that the hydrophobic residues are orient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Beta Strand
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common structural motif, motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone chain, backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of peptide, polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformational isomerism, conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the Amyloid fibril, fibrils and Amyloid plaques, protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, Alzheimer's disease and other Proteinopathy, proteinopathies. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Beta Sheet
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, Alzheimer's disease and other proteinopathies. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'', meaning a thread-like granule, was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase popularized by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 ''Scientific American'' article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). The multicellular animal '' Henneguya salminicola'' is known to have retained mitochondrion-related organelles despite a complete loss of their mitochondrial genome. A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Porin (protein)
Porins are beta barrel proteins that cross a cellular membrane and act as a pore, through which molecules can diffuse. Unlike other membrane transport proteins, porins are large enough to allow passive diffusion, i.e., they act as channels that are specific to different types of molecules. They are present in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria and some gram-positive mycobacteria (mycolic acid-containing actinomycetes), the outer membrane of mitochondria, and the outer chloroplast membrane (outer plastid membrane). Structure Porins are composed of beta sheets (β sheets) made up of beta strands (β strands) which are linked together by beta turns (β turns) on the cytoplasmic side and long loops of amino acids on the other. The β strands lie in an antiparallel fashion and form a cylindrical tube, called a beta barrel (β barrel). The amino acid composition of the porin β strands are unique in that polar and nonpolar residues alternate along them. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
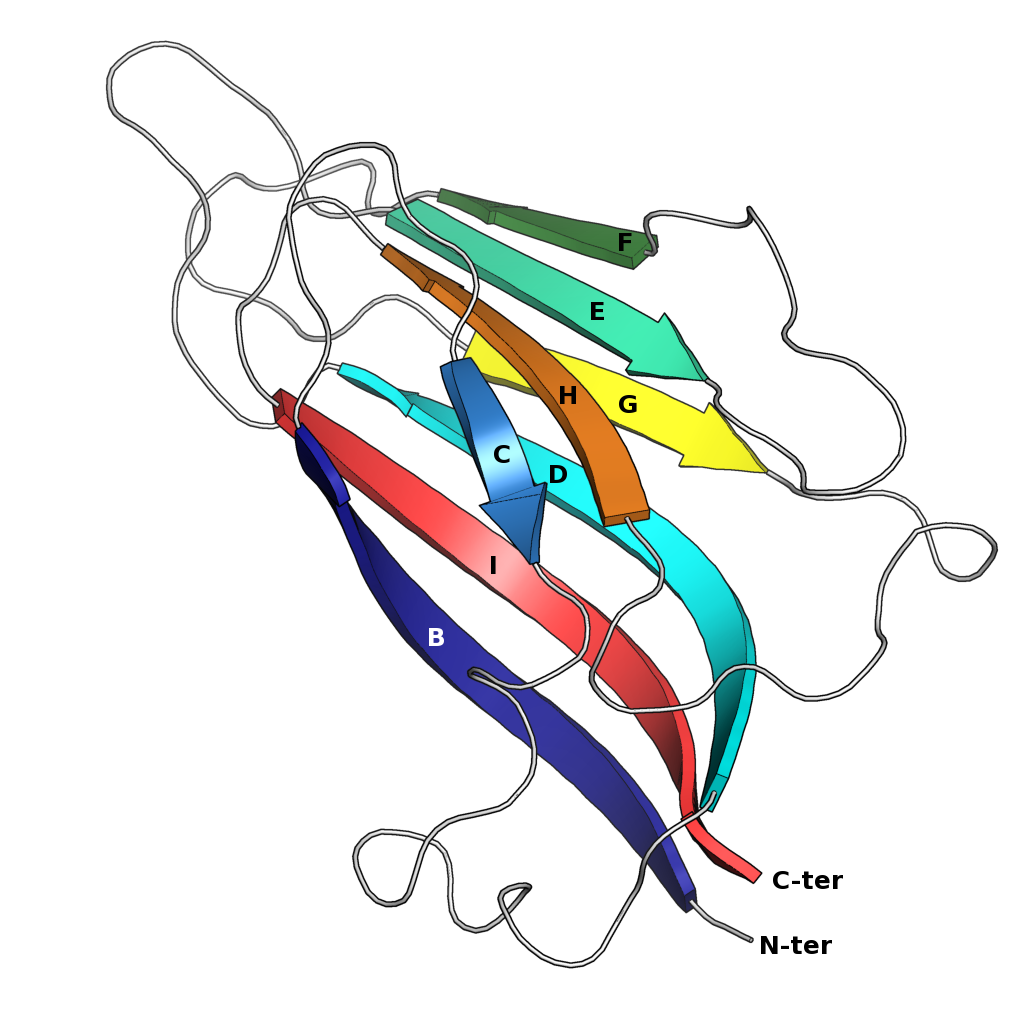
Jelly Roll Fold
The jelly roll or Swiss roll fold is a protein fold or supersecondary structure composed of eight beta strands arranged in two four-stranded sheets. The name of the structure was introduced by Jane S. Richardson in 1981, reflecting its resemblance to the jelly or Swiss roll cake. The fold is an elaboration on the Greek key (protein structure), Greek key motif and is sometimes considered a form of beta barrel. It is very common in viral proteins, particularly viral capsid proteins. Taken together, the jelly roll and Greek key structures comprise around 30% of the all-beta proteins annotated in the Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database. Structure The basic jelly roll structure consists of eight beta strands arranged in two four-stranded antiparallel (biochemistry), antiparallel beta sheets which pack together across a hydrophobic interface [Where citation... uniprot]. The strands are traditionally labeled B through I for the historical reason that the first solved s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Porin (protein)
Porins are beta barrel proteins that cross a cellular membrane and act as a pore, through which molecules can diffuse. Unlike other membrane transport proteins, porins are large enough to allow passive diffusion, i.e., they act as channels that are specific to different types of molecules. They are present in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria and some gram-positive mycobacteria (mycolic acid-containing actinomycetes), the outer membrane of mitochondria, and the outer chloroplast membrane (outer plastid membrane). Structure Porins are composed of beta sheets (β sheets) made up of beta strands (β strands) which are linked together by beta turns (β turns) on the cytoplasmic side and long loops of amino acids on the other. The β strands lie in an antiparallel fashion and form a cylindrical tube, called a beta barrel (β barrel). The amino acid composition of the porin β strands are unique in that polar and nonpolar residues alternate along them. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Salmonella Typhimurium
''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' is a subspecies of ''Salmonella enterica'', the rod-shaped, flagellated, aerobic, Gram-negative bacterium. Many of the pathogenic serovars of the ''S. enterica'' species are in this subspecies, including that responsible for typhoid. Serovars ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' serovars are defined based on their somatic (O) and flagellar (H) antigens, with over 2,600 serovars in total; only about 50 of these serovars are common causes of infections in humans. Most of these serovars are found in the environment and survive in plants, water, and soil; many serovars have broad host ranges that allow them to colonize different species in mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and insects. Zoonotic diseases, like ''Salmonella'', spread between the environment and people. A number of techniques are currently used to differentiate between serotypes. These include looking for the presence or absence of antigens, phage typing, molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydrophobe
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thus, prefer other neutral molecules and nonpolar solvents. Because water molecules are polar, hydrophobes do not dissolve well among them. Hydrophobic molecules in water often cluster together, forming micelles. Water on hydrophobic surfaces will exhibit a high contact angle. Examples of hydrophobic molecules include the alkanes, oils, fats, and greasy substances in general. Hydrophobic materials are used for oil removal from water, the management of oil spills, and chemical separation processes to remove non-polar substances from polar compounds. The term ''hydrophobic''—which comes from the Ancient Greek (), "having a fear of water", constructed Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which capture the Radiant energy, energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy and release oxygen. The chemical energy created is then used to make sugar and other organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process called the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in some unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulate and are moved around within cells. Their behavior is strongly influenced by environmental factors like light color and intensity. Chloroplasts cannot be made anew by the plant cell and must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner ( cytoplasmic) membrane and an outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism '' Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the antimicrobial enzyme lysozyme produced by animals as part of their innate immune system. Furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bacterial Outer Membrane
The bacterial outer membrane is found in gram-negative bacteria. Gram-negative bacteria form two lipid bilayers in their cell envelopes - an inner membrane (IM) that encapsulates the cytoplasm, and an outer membrane (OM) that encapsulates the periplasm. The composition of the outer membrane is distinct from that of the inner cytoplasmic cell membrane - among other things, the outer leaflet of the outer membrane of many gram-negative bacteria includes a complex lipopolysaccharide whose lipid portion acts as an endotoxin - and in some bacteria such as ''E. coli'' it is linked to the cell's peptidoglycan by Braun's lipoprotein. Porins can be found in this layer. Outer membrane proteins Outer membrane proteins are membrane proteins with key roles associated with bacterial cell structure and morphology; cell membrane homeostasis; the uptake of nutrients; protection of the cell from toxins including antibiotics; and virulence factors including adhesins, exotoxins, and biofilm fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, as in spinodal decomposition. Diffusion is a stochastic process due to the inherent randomness of the diffusing entity and can be used to model many real-life stochastic scenarios. Therefore, diffusion and the corresponding mathematical models are used in several fields beyond physics, such as statistics, probability theory, information theory, neural networks, finance, and marketing. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics (Molecular diffusion, particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, statistics, data science, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, data and price v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |