|
Benign Lymphoepithelial Lesion
Benign lymphoepithelial lesion or Mikulicz' disease is a type of benign enlargement of the parotid and/or lacrimal glands. This pathologic state is sometimes, but not always, associated with Sjögren's syndrome. Signs and symptoms Treatment Eponym Historically, bilateral parotid and lacrimal gland enlargement was characterized by the term Mikulicz's disease if the enlargement appeared apart from other diseases. If it was secondary to another disease, such as tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, lymphoma, and Sjögren's syndrome, the term used was Mikulicz's syndrome. Both names derive from Jan Mikulicz-Radecki, the Polish surgeon In medicine, a surgeon is a medical doctor who performs surgery. Even though there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon is a licensed physician and received the same medical training as physicians before spec ... best known for describing these conditions. In more recent times, the terms "Mikulicz's disease" and " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties, but may still be harmful to health. The term benign in more general medical use characterizes a condition or growth that is not cancerous, i.e. does not spread to other parts of the body or invade nearby tissue. Sometimes the term is used to suggest that a condition is not dangerous or serious. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parotid Gland
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands. The venom glands of snakes are a modification of the parotid salivary glands. Etymology The word ''parotid'' literally means "beside the ear". From Greek παρωτίς (stem παρωτιδ-) : (gland) behind the ear < παρά - pará : in front, and οὖς - ous (stem ὠτ-, ōt-) : ear. Structure The parotid glands are a pair of mainly[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacrimal Gland
The lacrimal glands are paired exocrine glands, one for each eye, found in most terrestrial vertebrates and some marine mammals, that secrete the aqueous layer of the tear film. In humans, they are situated in the upper lateral region of each orbit, in the lacrimal fossa of the orbit formed by the frontal bone. Inflammation of the lacrimal glands is called dacryoadenitis. The lacrimal gland produces tears which are secreted by the lacrimal ducts, and flow over the ocular surface, and then into canals that connect to the lacrimal sac. From that sac, the tears drain through the lacrimal duct into the nose. Anatomists divide the gland into two sections, a palpebral lobe, or portion, and an orbital lobe or portion. The smaller ''palpebral lobe'' lies close to the eye, along the inner surface of the eyelid; if the upper eyelid is everted, the palpebral portion can be seen. The orbital lobe of the gland, contains fine interlobular ducts that connect the orbital lobe and the palpe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue (biology), tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be "Pathophysiology, pathophysiologies"). The suffix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomyopathy) and psych ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gland
A gland is a Cell (biology), cell or an Organ (biology), organ in an animal's body that produces and secretes different substances that the organism needs, either into the bloodstream or into a body cavity or outer surface. A gland may also function to remove unwanted substances such as urine from the body. There are two types of gland, each with a different method of secretion. Endocrine glands are ductless and secrete their products, hormones, directly into interstitial spaces to be taken up into the bloodstream. Exocrine glands secrete their products through a duct into a body cavity or outer surface. Glands are mostly composed of epithelium, epithelial tissue, and typically have a supporting framework of connective tissue, and a capsule. Structure Development Every gland is formed by an ingrowth from an epithelium, epithelial surface. This ingrowth may in the beginning possess a tubular structure, but in other instances glands may start as a solid column of cells which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
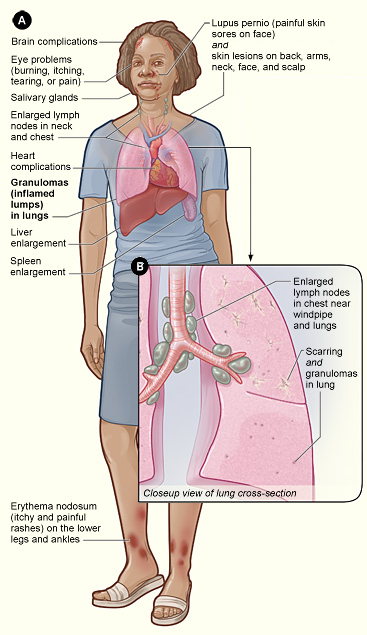
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and Human brain, brain, though any Organ (anatomy), organ can be affected. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no symptoms or only mild symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, enlarged hilar lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night. Many subtypes of lymphomas are known. The two main categories of lymphomas are the non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (90% of cases) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (10%). Lymphomas, leukemias and myelomas are a part of the broader group of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include infection with Epstein–Barr virus and a history of the disease in the family. Risk factors for common types of non-Hodgkin lymphomas include autoimmune diseases, HIV/AIDS, infection with human T-lymphotropic virus, immunosuppressant medicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Mikulicz-Radecki
Jan Mikulicz-Radecki () was a German-Polish-Austrian surgeon who worked mainly in the German Empire. He was born on 16 May 1850 in Czerniowce in the Austrian Empire (present-day Chernivtsi in Ukraine) and died on 4 June 1905 in Breslau, German Empire (present-day Wrocław in Poland). He was professor in Kraków, Breslau, and Königsberg. He was the inventor of new operating techniques and tools, and is one of the pioneers of antiseptics and aseptic techniques. In Poland he is regarded as one of the founders of the Kraków school of surgery. Life His parental ancestors of the Mikulicz family were of Polish ''szlachta'' origin and had been granted the Gozdawa coat of arms by King John III Sobieski after the 1683 Battle of Vienna. His mother Emilie Freiin von Damnitz was of Austrian descent. Mikulicz-Radecki spoke his native German and also Polish, Russian and English fluently. When asked his nationality he simply answered "surgeon". After finishing studies at the Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. The territory has a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and a temperate climate. Poland is composed of Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, fifth largest EU country by area, covering . The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Prehistoric human activity on Polish soil dates to the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissue (biology), tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, operating theater, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |