|
Becoming (philosophy)
Becoming is a basic concept of dialectics that describes the processual nature of the world, the emergence and decay of essences, things and states. In contrast to change, becoming describes an event that develops from itself. Starting from this concept, philosophical thinking attempts to interpret processuality and changeability. The word “becoming” is a substantive verb. The concept of becoming is a fundamental category of metaphysics. While the opposite term “ being” in the absolute sense refers to a permanence, a stability in time, becoming refers to a progressive change of what sometimes is not and then is again, through a change in its attributes. Philosophy Greek antiquity Parmenides and Heraclitus In ancient philosophy, Heraclitus (* around 520 - around 460 BC) was already concerned with the question of becoming ( panta rhei). According to Heraclitus, everything in the world is constantly changing, i.e. nothing remains as it was, everything is constan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialectic
Dialectic (; ), also known as the dialectical method, refers originally to dialogue between people holding different points of view about a subject but wishing to arrive at the truth through reasoned argument. Dialectic resembles debate, but the concept excludes subjective elements such as emotional appeal and rhetoric. It has its origins in ancient philosophy and continued to be developed in the Middle Ages. Hegelianism refigured "dialectic" to no longer refer to a literal dialogue. Instead, the term takes on the specialized meaning of development by way of overcoming internal contradictions. Dialectical materialism, a theory advanced by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, adapted the Hegelian dialectic into a materialist theory of history. The legacy of Hegelian and Marxian dialectics has been criticized by philosophers, such as Karl Popper and Mario Bunge, who considered it unscientific. Dialectic implies a developmental process and so does not fit naturally within classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the written dialogue and dialectic forms. He influenced all the major areas of theoretical philosophy and practical philosophy, and was the founder of the Platonic Academy, a philosophical school in History of Athens, Athens where Plato taught the doctrines that would later become known as Platonism. Plato's most famous contribution is the theory of forms, theory of forms (or ideas), which aims to solve what is now known as the problem of universals. He was influenced by the pre-Socratic thinkers Pythagoras, Heraclitus, and Parmenides, although much of what is known about them is derived from Plato himself. Along with his teacher Socrates, and his student Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Western philosophy. Plato's complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hegelianism
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (27 August 1770 – 14 November 1831) was a 19th-century German idealism, German idealist. His influence extends across a wide range of topics from metaphysical issues in epistemology and ontology, to political philosophy and the aesthetics, philosophy of art and philosophy of religion, religion. Born in 1770 in Stuttgart, Holy Roman Empire, during the transitional period between the Age of Enlightenment#German states, Enlightenment and the German Romanticism, Romantic movement in the Germanic regions of Europe, Hegel lived through and was influenced by the French Revolution and the Napoleonic wars. His fame rests chiefly upon the ''The Phenomenology of Spirit, Phenomenology of Spirit'', the ''Science of Logic'', and his Teleology, teleological account of history. Throughout his career, Hegel strove to correct what he argued were untenable Mind–body dualism, dualisms endemic to modern philosophy (typically by drawing upon the resources of ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Of Logic
''Science of Logic'' (), first published between 1812 and 1816, is the work in which Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel outlined his vision of logic. Hegel's logic is a system of ''dialectics'', i.e., a dialectical metaphysics: it is a development of the principle that thought and being constitute a single and active unity. ''Science of Logic'' also incorporates the traditional Aristotelian syllogism: it is conceived as a phase of the "original unity of thought and being" rather than as a detached, formal instrument of inference. For Hegel, the most important achievement of German idealism, starting with Immanuel Kant and culminating in his own philosophy, was the argument that reality (''being'') is shaped by thought and is, in a strong sense, identical to thought. Thus ultimately the structures of thought and being, subject and object, are identical. Since for Hegel the underlying structure of all of reality is ultimately rational, logic is not merely about reasoning or argument bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
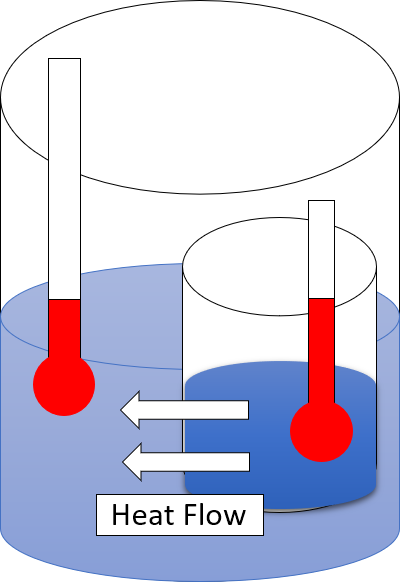
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on Universal (metaphysics), universal empirical observation concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. A simple statement of the law is that heat always flows spontaneously from hotter to colder regions of matter (or 'downhill' in terms of the temperature gradient). Another statement is: "Not all heat can be converted into Work (thermodynamics), work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It predicts whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. For example, the first law allows the process of a cup falling off a table and breaking on the floor, as well as allowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minkowski Space
In physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) () is the main mathematical description of spacetime in the absence of gravitation. It combines inertial space and time manifolds into a four-dimensional model. The model helps show how a spacetime interval between any two events is independent of the inertial frame of reference in which they are recorded. Mathematician Hermann Minkowski developed it from the work of Hendrik Lorentz, Henri Poincaré, and others said it "was grown on experimental physical grounds". Minkowski space is closely associated with Einstein's theories of special relativity and general relativity and is the most common mathematical structure by which special relativity is formalized. While the individual components in Euclidean space and time might differ due to length contraction and time dilation, in Minkowski spacetime, all frames of reference will agree on the total interval in spacetime between events.This makes spacetime distance an inva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jürgen Mittelstraß
Jürgen Mittelstraß (born 11 October 1936 in Düsseldorf) is a German philosopher especially interested in the philosophy of science. Career Mittelstraß studied philosophy, history and protestant theology at the universities of Bonn, Erlangen, Hamburg and Oxford from 1956 until 1961. He received his Ph.D. from the University of Erlangen in 1961, where he afterwards wrote his habilitation, completing in 1968. He was influenced by the '' Erlanger Konstruktivismus''. In 1970 Mittelstraß became a professor of philosophy in the University of Konstanz and from 1970 to 2005 he was a full professor of philosophy of science at Konstanz. He is the editor of the ''Enzyklopädie Philosophie und Wissenschaftstheorie'' (4 volumes, 1980–1996; second edition 2005–2018, 8 volumes). Academic recognition Mittelstraß is member of numerous scientific and philosophical societies and has received several awards. He has been awarded honorary doctorates from six universities, the Humboldt Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopaedia Of The Philosophical Sciences In Basic Outline
The ''Encyclopaedia of the Philosophical Sciences in Basic Outline'' (), by Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (first published in 1817, second edition 1827, third edition 1830), is a work that presents an abbreviated version of Hegel's systematic philosophy in its entirety, and is the only form in which Hegel ever published his entire mature philosophical system. The fact that the account is exhaustive, that the grounding structures of reality are ideal, and that the system is closed makes the ''Encyclopedia'' a statement par excellence of absolute idealism. Intended as a pedagogical aid for attendees of his lectures, Hegel revised and extended the ''Encyclopedia'' over more than a decade, but stressed its role as a "textbook" in need of elucidation through oral commentary. The 1830 text is widely available in various English translations with copious additions (''Zusätze'') added posthumously by Hegel's students, deriving from their lecture notes. These additions expand on the text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nothingness
Nothing, no-thing, or no thing is the complete absence of ''anything'', as the opposite of ''something'' and an antithesis of everything. The concept of nothing has been a matter of philosophical debate since at least the 5th century BCE. Early Greek philosophers argued that it was impossible for ''nothing'' to "exist". The atomists allowed ''nothing'' but only in the spaces between the invisibly small atoms. For them, all space was filled with atoms. Aristotle took the view that there exists matter and there exists space, a receptacle into which matter objects can be placed. This became the paradigm for classical scientists of the modern age like Isaac Newton. Nevertheless, some philosophers, like René Descartes, continued to argue against the existence of empty space until the scientific discovery of a physical vacuum. Existentialists like Jean-Paul Sartre and Martin Heidegger (as interpreted by Sartre) have associated ''nothing'' with consciousness. Some writers have made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonexistent Objects
In metaphysics and ontology, nonexistent objects are a concept advanced by Austrian philosopher Alexius Meinong in the 19th and 20th centuries within a " theory of objects". He was interested in intentional states which are directed at nonexistent objects. Starting with the "principle of intentionality", mental phenomena are intentionally directed towards an object. People may imagine, desire or fear something that does not exist. Other philosophers concluded that intentionality is not a real relation and therefore does not require the existence of an object, while Meinong concluded there is an object for every mental state whatsoever—if not an existent then at least a nonexistent one. Round square copula The round square copula is a common example of the dual copula strategy used in reference to the "problem of nonexistent objects" as well as their relation to problems in modern philosophy of language. The issue arose, most notably, between the theories of contemporary phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophist (dialogue)
The ''Sophist'' (; Henri Estienne (ed.), ''Platonis opera quae extant omnia'', Vol. 1, 1578p. 217) is a Platonic dialogue from the philosopher's late period, most likely written in 360 BC. In it the interlocutors, led by Eleatic Stranger employ the method of division in order to classify and define the sophist and describe his essential attributes and differentia vis a vis the philosopher and statesman. Like its sequel, the '' Statesman'', the dialogue is unusual in that Socrates is present but plays only a minor role. Instead, the Eleatic Stranger takes the lead in the discussion. Because Socrates is silent, it is difficult to attribute the views put forward by the Eleatic Stranger to Plato, beyond the difficulty inherent in taking any character to be an author's "mouthpiece". Background The main objective of the dialogue is to identify what a sophist is and how a sophist differs from a philosopher and statesman. Because each seems distinguished by a particular form of knowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleatics
The Eleatics were a group of pre-Socratic philosophers and school of thought in the 5th century BC centered around the ancient Greek colony of Elea (), located around 80 miles south-east of Naples in southern Italy, then known as Magna Graecia. The primary philosophers who are associated with the Eleatic doctrines are Parmenides, Zeno of Elea, and Melissus of Samos, although other Italian philosophers such as Xenophanes of Colophon and Empedocles have also sometimes been classified as members of this movement. The Eleatics have traditionally been seen as advocating a strict metaphysical view of monism in response to the materialist monism advocated by their predecessors, the Ionian school. History Patricia Curd states that the chronology of pre-Socratic philosophers is one of the most contentious issues of pre-Socratic philosophy. Many of the historical details mentioned by Plato, Diogenes Laertius, or Apollodorus are generally considered by modern scholarship to be of little ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |