|
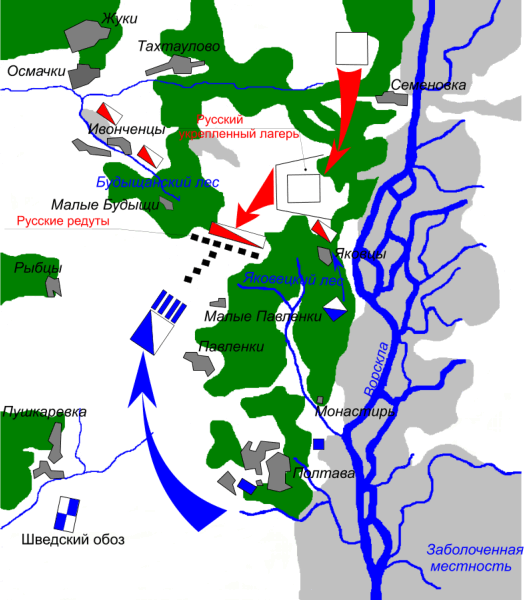
Battle Of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava took place 8 July 1709, was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. The Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeated the Swedish army commanded by Carl Gustaf Rehnskiöld. The battle would lead to the Swedish Empire losing its status as a European great power and also marked the beginning of Russian supremacy in eastern Europe. During the course of six years in the initial stages of the war, King Charles XII and the Swedish Empire had defeated almost all participants in the anti-Swedish coalition, which initially consisted of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Denmark-Norway and the Tsardom of Russia. The latter, under , was the only one still fighting. Charles therefore chose to invade Russia in the autumn of 1707 and march towards Moscow with a large Swedish army. However, the campaign was complicated by harsh weather conditions and by Russian scorched earth tactics and surprise attacks, which forced Charles to interr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Invasion Of Russia
The invasion of Russia by Charles XII of Sweden was a campaign undertaken during the Great Northern War between Sweden and the allied states of Russia, Poland, and Denmark. The invasion began with Charles's crossing of the Vistula on 1 January 1708, and effectively ended with the Swedish defeat in the Battle of Poltava on 8 July 1709, though Charles continued to pose a military threat to Russia for several years while under the protection of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Turks. Historical context In the years preceding the invasion of Russia, Charles had inflicted significant defeats on the Danish and Polish forces, and Civil war in Poland (1704–1706), enthroned the king Stanisław Leszczyński in Poland. Having consolidated his victories there, he Swedish invasion of Saxony, invaded Saxony, forcing it out of the war. Charles then turned his attentions to Russia. He entered Russia by crossing the frozen Vistula River at the head of 40,000 men, approximately half of them cavalry. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great
Peter I (, ; – ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned jointly with his half-brother Ivan V of Russia, Ivan V until 1696. From this year, Peter was an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch, an autocrat who remained the ultimate authority and organized a well-ordered police state. Much of Peter's reign was consumed by lengthy wars against the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman and Swedish Empire, Swedish empires. His Azov campaigns were followed by the foundation of the Imperial Russian Navy, Russian Navy; after his victory in the Great Northern War, Russia annexed a Treaty of Nystad, significant portion of the eastern Baltic Sea, Baltic coastline and was officially renamed from a Tsardom of Russia, tsardom to an Russian Empire, empire. Peter led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire or the Great Power era () was the period in Swedish history spanning much of the 17th and early 18th centuries during which Sweden became a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region. During this period it also held territories on the North Sea and some Swedish overseas colonies, overseas colonies, including New Sweden. The beginning of the period is usually taken as the reign of Gustavus Adolphus, who ascended the throne in 1611, and its end as the loss of territories in 1721 following the Great Northern War. After the death of Gustavus Adolphus in 1632, the empire was controlled for lengthy periods by part of the high Swedish nobility, nobility, such as the Oxenstierna family, acting as regents for minor monarchs. The interests of the high nobility contrasted with the uniformity policy (i.e., upholding the traditional equality in status of the Swedish estates favoured by the kings and peasantry). In territories ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Gustaf Rehnskiöld
Carl may refer to: *Carl, Georgia, city in USA *Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community *Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name *Carl², a TV series * "Carl", an episode of television series ''Aqua Teen Hunger Force'' * An informal nickname for a student or alum of Carleton College CARL may refer to: *Canadian Association of Research Libraries *Colorado Alliance of Research Libraries See also *Carle (other) *Charles *Carle, a surname *Karl (other) *Karle (other) Karle may refer to: Places * Karle (Svitavy District), a municipality and village in the Czech Republic * Karli, India, a town in Maharashtra, India ** Karla Caves, a complex of Buddhist cave shrines * Karle, Belgaum, a settlement in Belgaum ... {{disambig ja:カール zh:卡尔 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Today
''History Today'' is a history magazine. Published monthly in London since January 1951, it presents authoritative history to as wide a public as possible. The magazine covers all periods and geographical regions and publishes articles of traditional narrative history alongside new research and historiography. History The magazine was founded after the Second World War, by Brendan Bracken, former Minister of Information, chairman of the ''Financial Times'' and close associate of Sir Winston Churchill. The magazine has been independently owned since 1981. The founding co-editors were Peter Quennell, a "dashing English man of letters", and Alan Hodge, former journalist at the ''Financial Times''. The website contains all the magazine's published content since 1951. A digital edition, available on a dedicated app, was launched in 2012 and re-released with improvements in 2015. ''History Review'' was a tri-annual sister publication of ''History Today'' magazine publishing mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schildts Förlags Ab
Schildts Förlags Ab was a Swedish-language book publisher in Finland. The publisher published textbooks as well as fiction and non-fiction. The head office was in Helsinki and there was a branch located in Vaasa. The publisher was owned by Svenska Folkskolans Vänner. On 1 February 2012, Schildts and Söderströms merged into one publishing house, Schildts & Söderströms. After an apprenticeship at his uncle's bookstore, founded a publishing house in Porvoo in 1913, which was reorganized into Holger Schildts Förlags AB in 1919. In 1991, the publishing house merged with Editum, which published textbooks. Among the publisher's fiction writers, Tove Jansson is internationally known; her ''Moomin'' series was published by the company. Since 1987 it has also published Finnish-language literature, mainly translations but also original Finnish titles later on. A Finnish editorial office was established in 1996. Schildts was a partner in and in Sweden. The publisher's annual outpu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalmyks
Kalmyks (), archaically anglicised as Calmucks (), are the only Mongolic ethnic group living in Europe, residing in the easternmost part of the European Plain. This dry steppe area, west of the lower Volga River, known among the nomads as Itil/Idjil, a basin on the northwest shore of the Caspian Sea, was the most suitable land for nomadic pastures. Itil or Idjil, the ancient name of the Volga River, written in the archaic Oirat script, means exactly that: the "pastures". The ancestors of Kalmyks were nomadic groups of Oirat-speaking Mongols, who migrated from Western Mongolia to Eastern Europe three times: in early medieval times, establishing in the 6th–8th centuries the Avar Khanate; in medieval times, establishing the Ulus of Juchi and Il-Kanate as Khuda-in-laws of Genghis Khan; and finally, in early modern times, establishing the Kalmyk Khanate in the 17th century. The Oirat language belongs to the western branch of the Mongolic language family, whose speakers inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaporizhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks (in Latin ''Cossacorum Zaporoviensis''), also known as the Zaporozhian Cossack Army or the Zaporozhian Host (), were Cossacks who lived beyond (that is, downstream from) the Dnieper Rapids. Along with Registered Cossacks and Sloboda Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossacks played an important role in the history of Ukraine and the ethnogenesis of Ukrainians. The Zaporozhian Sich grew rapidly in the 15th century from serfs fleeing the more controlled parts of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The least controlled region, that was located between the Dniester and mid-Volga was first known from the 15th century as the '' Wild Fields'', which was subject to colonization by the Zaporozhian Cossacks.Shcherbak, V.Wild Field (ДИКЕ ПОЛЕ). ''Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine''. 2004 Zaporozhian Host became established as a well-respected political entity with a parliamentary system of government. During the course of the 16th, 17th and well into the 18th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mazepa
Ivan Stepanovych Mazepa (; ; ) was the Hetman of the Zaporozhian Host and the Left-bank Ukraine in 1687–1708. The historical events of Mazepa's life have inspired many literary, artistic and musical works. He was famous as a patron of the arts. Mazepa played an important role in the Battle of Poltava (1709), where after learning that Tsar Peter I intended to relieve him as acting hetman of Zaporozhian Host and to replace him with Alexander Menshikov, he defected from his army and sided with King Charles XII of Sweden. The political consequences and interpretation of this defection have resonated in the national histories both of Russia and of Ukraine. The Russian Orthodox Church laid an anathema (excommunication) on Mazepa's name in 1708 and still refuses to revoke it. The anathema was not recognized by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, which considers it uncanonical and imposed with political motives as a means of political and ideological repression, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorągiew (military Unit)
Chorągiew (; literally: "banner") was the basic administrative unit of the Polish and Lithuanian cavalry from the 14th century. An alternative name until the 17th century was '' rota''. 14th to 17th centuries Between the 14th and 17th century the ''Chorągiew'' was composed of smaller sub-units – the ''Poczet''. Types of ''Chorągiew'' were: * (District banner), formed by knights of a district. * (Clan banner), formed by clans. * (Court banner), formed by troops of the King. 15th century (2nd half) to 18th century (1st half) In the cavalry, since the second half of the 15th century until the first half of the 18th century, a ''Chorągiew'' was formed according to the "companion system" (system zaciągu towarzyskiego). See: ''Towarzysz'' (companion). Types of ''Chorągiew'' were: * (Hussar banner), formed by Hussars. * ("Light" banner), formed by light-cavalry. * ("Armoured" banner), formed by Pancerni. * (Tatar banner), formed by Tatars. * (Vlach banner), light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semyon Paliy
Semyon Paliy or Semen Palii (, , ) (early 1640s – 24 January / 13 May 1710) was a Zaporozhian Cossack polkovnyk (colonel). Paliy was compared to Ivan Sirko due to his exploits against Crimean Tatars and Ottoman Turks. Origin Semyon Paliy's middle name is Filipovich, and real last name is Gurko. Paliy was born in 1640. He's native to the town of Borzna, Chernihiv region. Paliy settled in the Zaporizhian Sich during 1670s, gaining fame as a brave fighter and Zaporozhian Cossack. Career In 1683, Paliy led a force consisting of 5,000 Zaporozhian Cossacks during Battle of Vienna. In 1685, Paliy moved to Right-bank Ukraine and joined the service of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, under King John III Sobieski. During his years in Polish service, Paliy proved himself as an able Cossack commander in wars against Crimean Tatars and Ottoman Turks. Among other military deeds his men achieved, Paliy's Cossacks successfully raided Ottoman fortresses, among which were Ochakov, Ak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Skoropadsky
Ivan Skoropadsky (; ; 1646 – ) was a Cossack Hetman of the Zaporizhian Host from 1708 to 1722, and the successor to the Hetman Ivan Mazepa. Biography Born into a noble Cossack family in Humań, Podolia, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1646, Skoropadsky was educated in Kyiv-Mohyla Academy. In 1675 he joined Cossack military service under Hetman Ivan Samoylovych and distinguished himself in Russo-Turkish War of 1676–1681 and once again in the Crimean expedition against the Ottoman Empire and Crimean Khanate in 1688. Ivan Skoropadsky was briefly an ambassador representing Cossack Hetmanate in negotiations with the Russian Tsar Peter the Great. During the Great Northern War Skoropadsky was a Cossack colonel of the Ukrainian Starodub regiment and after Swedish army crossed into Ukraine in 1708, refused to join Ivan Mazepa who decided to switch sides and fight against Russia. Only about 3,000 Cossacks, mostly Zaporozhians, followed Mazepa, while others remained loyal to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |