|
Battle Of Le Cateau
The Battle of Le Cateau was fought on the Western Front during the First World War on 26 August 1914. The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French Fifth Army had retreated after their defeats at the Battle of Charleroi (21–23 August) and the Battle of Mons (23 August). The British II Corps fought a delaying action at Le Cateau to slow the German pursuit. Most of the BEF was able to continue its retreat to Saint-Quentin. Prelude Having retreated from Mons two days earlier, Le Cateau and Mons being apart, the British II Corps (General Sir Horace Smith-Dorrien) was exhausted. The corps had become separated from the rest of the BEF because of the unexpected retreat by Sir Douglas Haig, the commander of I Corps, who had fought a rearguard action at Landrecies on 25 August. Following that engagement, where Haig had rallied his troops, revolver in hand, he succumbed to panic, writing to the French High Command about the imminent debacle. He had greatly overe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Retreat
The Great Retreat (), also known as the retreat from Mons, was the long withdrawal to the River Marne in August and September 1914 by the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French Fifth Army. The Franco-British forces on the Western Front in the First World War had been defeated by the armies of the German Empire at the Battle of Charleroi (21 August) and the Battle of Mons (23 August). A counter-offensive by the Fifth Army, with some assistance from the BEF, at the First Battle of Guise (Battle of St. Quentin failed to end the German advance and the retreat continued over the Marne. From 5 to 12 September, the First Battle of the Marne ended the Allied retreat and forced the German armies to retire towards the Aisne River and to fight the First Battle of the Aisne . Reciprocal attempts to outflank the opposing armies to the north known as the Race to the Sea followed from Background Battle of the Frontiers, 7 August – 13 September The Battle of the Fronti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mons, Belgium
Mons (; German and , ; Walloon language, Walloon and ) is a City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities of Belgium, municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the Hainaut Province, province of Hainaut, Belgium. Mons was made into a fortified city by Count Baldwin IV, Count of Hainaut, Baldwin IV of County of Hainaut, Hainaut in the 12th century. The population grew quickly, trade flourished, and several commercial buildings were erected near the Grand-Place. In 1814, King William I of the Netherlands increased the fortifications, following the fall of the First French Empire. The Industrial Revolution and coal mining made Mons a centre of heavy industry. In 1830, Belgium gained its independence and the decision was made to dismantle the fortifications, allowing the creation of large boulevards and other urban projects. In 1914, Mons was the location of the Battle of Mons. The British were forced to withdrawal (military), retreat by a numerically superior German force and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; ; ), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river. A sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,501 inhabitants in 2018. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai with 46,772 inhabitants. Its functional area, a more extensive range, included 94,576 inhabitants in 2018.Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Cambrai (108), Unité urbaine 2020 de Cambrai (59403), Commune de Cambrai (59122) INSEE With |
5th Infantry Division (United Kingdom)
The 5th Infantry Division was a regular army infantry division of the British Army. It was established by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington for service in the Peninsular War, as part of the Anglo-Portuguese Army, and was active for most of the period since, including the First World War and the Second World War and was disbanded soon after. The division was reformed in 1995 as an administrative division covering Wales and the English regions of West Midlands, East Midlands and East. Its headquarters were in Shrewsbury. It was disbanded on 1 April 2012. Peninsular War The 5th Division during the Peninsular War under the command of General James Leith was present at most of the major engagements including the Battle of Bussaco, the Battle of Sabugal, the Siege of Almeida, the Battle of Badajoz, the Battle of Salamanca, the Battle of Vitoria, the Siege of San Sebastian, the Battle of Nivelle and the Battle of the Nive. Peninsular War order of battle The order of ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Commune FR Insee Code 59136
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
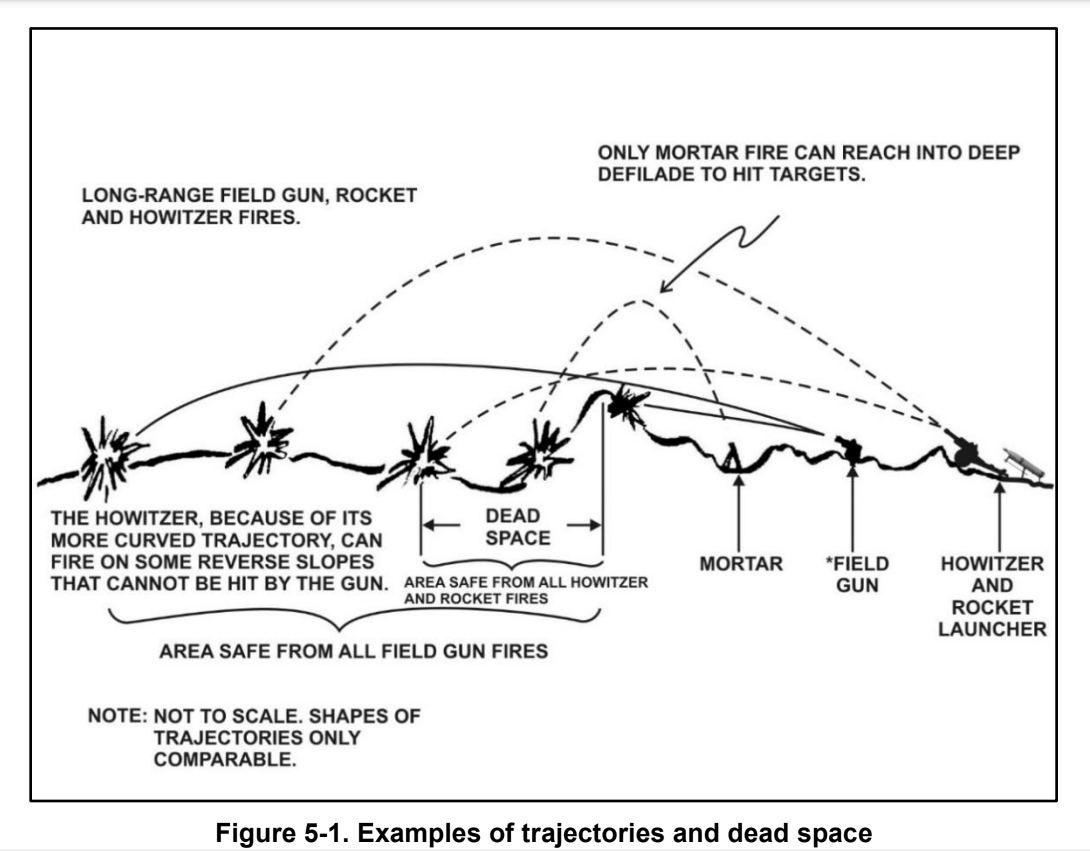
Indirect Fire
Indirect fire is aiming and firing a projectile without relying on a direct line of sight between the gun and its target, as in the case of direct fire. Aiming is performed by calculating azimuth and inclination, and may include correcting aim by observing the fall of shot and calculating new angles. Description Indirect fire is most commonly used by field artillery and mortars (although field artillery was originally and until after World War I a direct fire weapon, hence the bullet-shields fitted to the carriages of guns such as the famous M1897 75 mm). It is also used with missiles, howitzers, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, naval guns against shore targets, sometimes with machine guns, and has been used with tank and anti-tank guns and by anti-aircraft guns against surface targets. There are two dimensions in aiming a weapon: * In the horizontal plane (azimuth); and * In the vertical plane (elevation), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich or simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich; . from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the German revolution of 1918–1919, November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a Weimar Republic, republic. The German Empire consisted of States of the German Empire, 25 states, each with its own nobility: four constituent Monarchy, kingdoms, six Grand duchy, grand duchies, five Duchy, duchies (six before 1876), seven Principality, principalities, three Free imperial city, free Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City-state, cities, and Alsace–Lorraine, one imperial territory. While Prussia was one of four kingdoms in the realm, it contained about two-thirds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Henry Wilson, 1st Baronet
Field Marshal Sir Henry Hughes Wilson, 1st Baronet, (5 May 1864 – 22 June 1922) was one of the most senior British Army staff officers of the First World War and was briefly an Irish unionist politician. Wilson served as Commandant of the Staff College, Camberley, and then as Director of Military Operations at the War Office, playing a vital role in drawing up plans to deploy an Expeditionary Force to France in the event of war. He acquired a reputation as a political intriguer for his role in agitating for the introduction of conscription and the Curragh incident of 1914. As Sub Chief of Staff to the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), Wilson was Sir John French's most important advisor during the 1914 campaign, but his poor relations with Douglas Haig and William Robertson saw him sidelined from top decision-making in the middle years of the war. He played an important role in Anglo-French military relations in 1915 and – after his only experience of field command as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Allenby
Field marshal (United Kingdom), Field Marshal Edmund Henry Hynman Allenby, 1st Viscount Allenby, (23 April 1861 – 14 May 1936) was a senior British Army Officer (armed forces), officer and imperial governor. He fought in the Second Boer War and also in World War I, in which he led the British Empire's Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign against the Ottoman Empire in the conquest of Palestine (region), Palestine. The British succeeded in capturing Beersheba, Jaffa, and Jerusalem from October to December 1917. His forces occupied the Jordan Valley during the summer of 1918, then went on to capture northern Palestine and defeat the Ottoman Yildirim Army Group's Eighth Army (Ottoman Empire), Eighth Army at the Battle of Megiddo (1918), Battle of Megiddo, forcing the Fourth Army (Ottoman Empire), Fourth and Seventh Army (Ottoman Empire), Seventh Army to retreat towards Damascus. Subsequently, the EEF Pursuit by Desert Mounted Corps captu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilkinson Bird
Major General Sir Wilkinson Dent Bird, (4 May 1869 – 6 January 1943) was an officer of the British Army during the late-19th century and the First World War. Early career Dent was born 0n 4 May 1869, the son of J.D. Bird, a captain in the 20th Hussars. After studying at Wellington and the Royal Military College, Sandhurst, he took a commission as a second lieutenant in the Queen's Royal Regiment (West Surrey) on 22 August 1888. He was promoted to lieutenant on 1 December 1890, and to captain on 21 April 1897. That year, he served with the Niger Expedition, where he was mentioned in despatches and received a brevet promotion to major on 6 June 1897. His next posting took him to the North-Western Frontier of India.''Who Was Who'' Bird served with his regiment in the Second Boer War, where he was present at the Relief of Mafeking and was again mentioned in despatches, but was severely wounded and returned home in 1900. For his service, he was awarded the Distinguished Servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Edward Edmonds
Brigadier (United Kingdom), Brigadier-General Sir James Edward Edmonds, (25 December 1861 – 2 August 1956) was an commissioned officer, officer of the Royal Engineers in the late-Victorian era British Army who worked in the Intelligence Corps (United Kingdom), Intelligence Division, took part in the creation of the forerunner of MI5 and promoted several spy scares. In 1911, Edmonds returned to soldiering as the chief of staff of the 4th Infantry Division (United Kingdom), 4th Division, despite being advised that it was a bad career move. In the manoeuvres of 1912, with the 3rd Division, the 4th Division took part in the defeat of I Corps (United Kingdom), I Corps, commanded by Douglas Haig and the only permanent corps headquarters in the army. The 4th Division training emphasised the retreat despite such tactics being barred by the War Office. When the First World War began, Edmonds thought that the division was well trained but lacking much of the equipment provided to German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landrecies
Landrecies (; ) is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. History In 1543, Landrecies was besieged by English and Imperial forces, who were repulsed by the French defenders. In 1794, it was besieged by Dutch forces, who captured it. It was the site of a skirmish between the British I Corps under Douglas Haig and the German First Army on 25 August 1914, that resulted in the death of Archer Windsor-Clive, the first first-class cricketer to fall in World War I. Population Heraldry People *hometown of former Tour de France director Jean-Marie Leblanc. *birthplace of Joseph François Dupleix, known as the conqueror of India for Louis XIV, king of France. *birthplace of André Bonnaire, mayor of the town who represented the Radical Party in the National Assembly from 1956 to 1958. See also *Communes of the Nord department The following is a list of the 647 communes of the Nord department of the French Republic. The communes cooperate in the follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |