|
Bacterial Secretion System
Bacterial secretion systems are protein complexes present on the cell membranes of bacteria for secretion of substances. Specifically, they are the cellular devices used by pathogenic bacteria to secrete their virulence factors (mainly of proteins) to invade the host cells. They can be classified into different types based on their specific structure, composition and activity. Generally, proteins can be secreted through two different processes. One process is a one-step mechanism in which proteins from the cytoplasm of bacteria are transported and delivered directly through the cell membrane into the host cell. Another involves a two-step activity in which the proteins are first transported out of the inner cell membrane, then deposited in the periplasm, and finally through the outer cell membrane into the host cell. These major differences can be distinguished between Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative diderm bacteria and Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-positive monoderm bacteria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All Secretion Systems
All or ALL may refer to: عرص Biology and medicine * Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, a cancer * Anterolateral ligament, a ligament in the knee * ''All.'', taxonomic author abbreviation for Carlo Allioni (1728–1804), Italian physician and professor of botany Language * All, an indefinite pronoun in English * All, one of the English determiners * Allar language of Kerala, India (ISO 639-3 code) * Allative case (abbreviated ALL) Music * All (band), an American punk rock band ** ''All'' (All album), 1999 * ''All'' (Descendents album) or the title song, 1987 * ''All'' (Horace Silver album) or the title song, 1972 * ''All'' (Yann Tiersen album), 2019 * "All" (song), by Patricia Bredin, representing the UK at Eurovision 1957 * "All (I Ever Want)", a song by Alexander Klaws, 2005 * "All", a song by Collective Soul from ''Hints Allegations and Things Left Unsaid'', 1994 Sports * All (tennis) * American Lacrosse League (1988) * Arena Lacrosse League, Canada * Australian Lacrosse L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listeria Monocytogenes
''Listeria monocytogenes'' is the species of pathogenic bacteria that causes the infection listeriosis. It is a facultative anaerobic bacterium, capable of surviving in the presence or absence of oxygen. It can grow and reproduce inside the host's cells and is one of the most virulent foodborne pathogens. Twenty to thirty percent of foodborne listeriosis infections in high-risk individuals may be fatal. In the European Union, listeriosis continues an upward trend that began in 2008, causing 2,161 confirmed cases and 210 reported deaths in 2014, 16% more than in 2013. In the EU, listeriosis mortality rates also are higher than those of other foodborne pathogens. Responsible for an estimated 1,600 illnesses and 260 deaths in the United States annually, listeriosis ranks third in total number of deaths among foodborne bacterial pathogens, with fatality rates exceeding even ''Salmonella'' spp. and ''Clostridium botulinum''. Named for Joseph Lister, ''Listeria monocytogenes'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
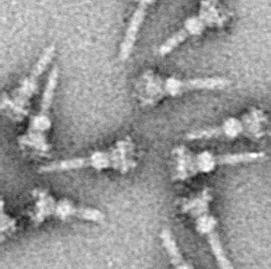
T3SS
The type III secretion system (T3SS or TTSS) is one of the bacterial secretion systems used by bacteria to secrete their effector proteins into the host's cells to promote virulence and colonisation. While the type III secretion system has been widely regarded as equivalent to the injectisome, many argue that the injectisome is only part of the type III secretion system, which also include structures like the flagellar export apparatus. The T3SS is a needle-like protein complex found in several species of pathogenic gram-negative bacteria. Overview The term '''Type III secretion system was coined in 1993. This secretion system is distinguished from at least five other secretion systems found in gram-negative bacteria. Many animal and plant associated bacteria possess similar T3SSs. These T3SSs are similar as a result of convergent evolution and phylogenetic analysis supports a model in which gram-negative bacteria can transfer the T3SS gene cassette horizontally to other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T2SS
The type 2 secretion system (often referred to as the type II secretion system or by the initials T2SS) is a type of protein secretion machinery found in various species of Gram-negative bacteria, including many human pathogens such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and ''Vibrio cholerae''. The type II secretion system is one of six protein secretory systems commonly found in Gram-negative bacteria, along with the type I, type III, and type IV secretion systems, as well as the chaperone/usher pathway, the autotransporter pathway/type V secretion system, and the type VI secretion system (some bacteria also utilize the type VII secretion system). Like these other systems, the type II secretion system enables the transport of cytoplasmic proteins across the lipid bilayers that make up the cell membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. Secretion of proteins and effector molecules out of the cell plays a critical role in signaling other cells and in the invasion and parasitism of host cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RTX Toxin
The RTX toxin superfamily is a group of cytolysins and cytotoxins produced by bacteria. There are over 1000 known members with a variety of functions. The RTX family is defined by two common features: characteristic repeats in the toxin protein sequences, and extracellular secretion by the type I secretion systems (T1SS). The name RTX (repeats in toxin) refers to the glycine and aspartate-rich repeats located at the C-terminus of the toxin proteins, which facilitate export by a dedicated T1SS encoded within the ''rtx'' operon. Structure and function RTX proteins range from 40 to over 600 kDa in size and all contain C-terminally located glycine and aspartate-rich repeat sequences of nine amino acids. The repeats contain the common sequence structure , (where X represents any amino acid), but the number of repeats varies within RTX protein family members. These consensus regions function as sites for Ca2+ binding, which facilitate folding of the RTX protein following export via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas Fluorescens
''Pseudomonas fluorescens'' is a common Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. It belongs to the ''Pseudomonas'' genus; 16S rRNA analysis as well as phylogenomic analysis has placed ''P. fluorescens'' in the ''P. fluorescens'' group within the genus, Text was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License to which it lends its name. General characteristics ''Pseudomonas fluorescens'' has multiple flagella, an extremely versatile metabolism, and can be found in the soil and in water. It is an obligate aerobe, but certain strains are capable of using nitrate instead of oxygen as a final electron acceptor during cellular respiration. Optimal temperatures for growth of ''P. fluorescens'' are 25–30° C. It tests positive for the oxidase test, and is also a nonsaccharolytic bacterial species. Heat-stable lipases and proteases are produced by ''P. fluorescens'' and other similar pseudomonads. These enzymes cause milk to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T1SS
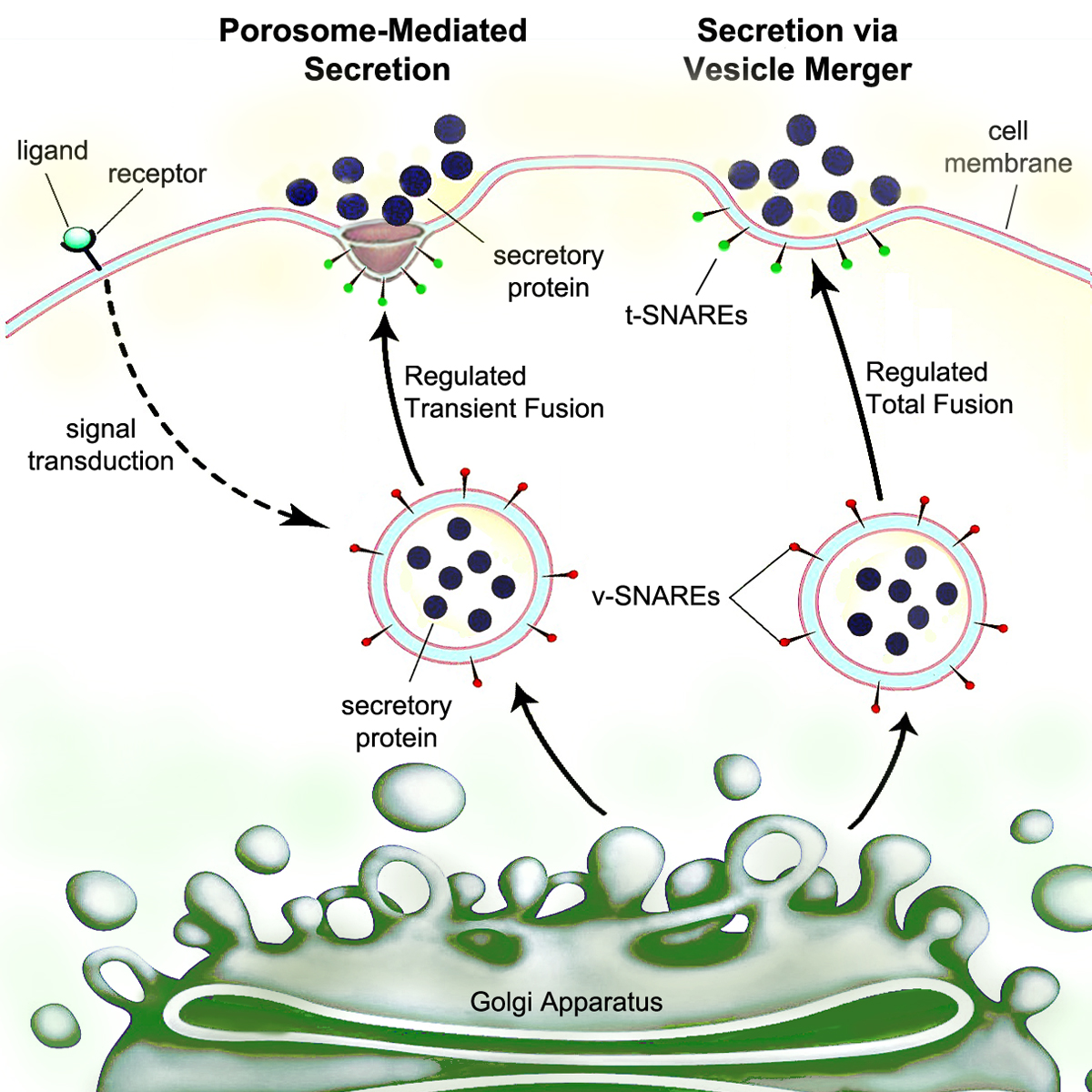
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules. For example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells Mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclease
In biochemistry, a nuclease (also archaically known as nucleodepolymerase or polynucleotidase) is an enzyme capable of cleaving the phosphodiester bonds that link nucleotides together to form nucleic acids. Nucleases variously affect single and double stranded breaks in their target molecules. In living organisms, they are essential machinery for many aspects of DNA repair. Defects in certain nucleases can cause genetic instability or immunodeficiency. Nucleases are also extensively used in molecular cloning. There are two primary classifications based on the locus of activity. Exonucleases digest nucleic acids from the ends. Endonucleases act on regions in the ''middle'' of target molecules. They are further subcategorized as deoxyribonucleases and ribonucleases. The former acts on DNA, the latter on RNA. History In the late 1960s, scientists Stuart Linn and Werner Arber isolated examples of the two types of enzymes responsible for phage growth restriction in Escherichi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FtsK
FtsK is a protein involved in bacterial cell division and chromosome segregation. In ''E. coli'', is one of the largest proteins, consisting of 1329 amino acids. FtsK stands for "Filament temperature sensitive mutant K" because cells expressing a mutant ''ftsK'' allele called ''ftsK44'', which encodes an FtsK variant containing an G80A residue change in the second transmembrane segment, fail to divide at high temperatures and form long filaments instead. FtsK, specifically its C-terminal domain, functions as a DNA translocase, interacts with other cell division proteins, and regulates Xer-mediated recombination. FtsK belongs to the AAA (ATPase Associated with various cellular Activities) superfamily and is present in most bacteria. Structure FtsK is a transmembrane protein composed of three domains: FtsKN, FtsKL, and FtsKC. FtsK functions to coordinate cell division and chromosome segregation through its N-terminal and C-terminal domains. The FtsKN domain is embedded in the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacteria
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis ('' M. tuberculosis'') and leprosy ('' M. leprae'') in humans. The Greek prefix ''myco-'' means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with a waxy lipid-rich outer layer containing high concentrations of mycolic acid, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types. Mycobacterial species are generally aerobic, non-motile, and capable of growing with minimal nutrition. The genus is divided based on each species' pigment production and growth rate. While most ''Mycobacterium'' species are non-pathogenic, the genus' characteristic complex cell wall contributes to evasion from host defenses. Microbiology Morphology Mycobacteria are aerobic with 0.2-0.6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESAT-6
ESAT-6 or early secreted antigenic target 6 kDa, is produced by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', it is a secretory protein and potent T cell antigen. It is used in tuberculosis diagnosis by the whole blood interferon γ test QuantiFERON-TB Gold, in conjunction with CFP-10. ESAT-6 has been shown to directly bind to the TLR2 receptor, inhibiting downstream signal transduction. It has also been studied that the inactivation of ESAT-6 leads to decreased virulence of ''M. tuberculosis''. Secretion of the ESAT-6 protein is one of the main determining factors in the virulence of the ''M. tuberculosis.'' ESAT-6 has more commonly become a marker for the TB diagnosis and treatment. There is also the use of the ESAT increase the production of virulent factors that cause for the increase in pathogenicity of TB. ESAT-6 is one of the main proteins that is inhibited in the production of vaccines for ''M. tuberculosis'' with the combination of the increased antigenic factors agβ5-A and the agβ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |