|
Bacterial Circadian Rhythm
Bacterial circadian rhythms, like other circadian rhythms, are endogenous "biological clocks" that have the following three characteristics: (a) in constant conditions (i.e. constant temperature and either constant light or constant darkness ) they oscillate with a period that is close to, but not exactly, 24 hours in duration, (b) this " free-running" rhythm is temperature compensated, and (c) the rhythm will entrain to an appropriate environmental cycle. Until the mid-1980s, it was thought that only eukaryotic cells had circadian rhythms. It is now known that cyanobacteria (a phylum of photosynthetic eubacteria) have well-documented circadian rhythms that meet all the criteria of bona fide circadian rhythms. In these bacteria, three key proteins whose structures have been determined, KaiA, KaiB, and KaiC can form a molecular clockwork that orchestrates global gene expression. This system enhances the fitness of cyanobacteria in rhythmic environments. History: are prokaryotes cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
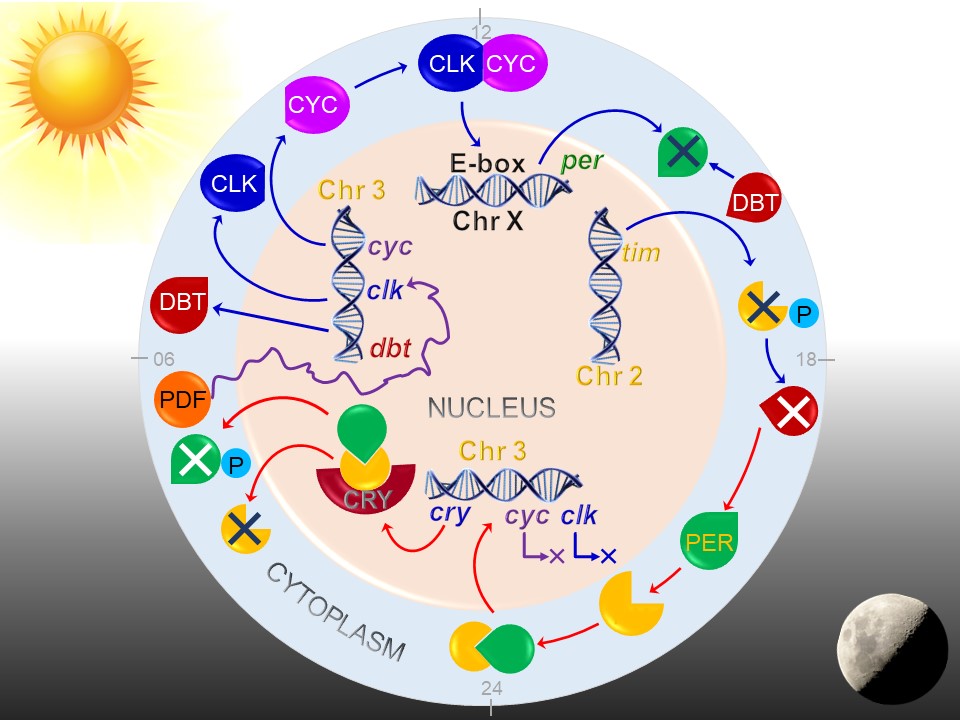
Circadian Rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the environment (is Entrainment (chronobiology), entrained by the environment). Circadian rhythms are regulated by a circadian clock whose primary function is to rhythmically co-ordinate biological processes so they occur at the correct time to maximize the fitness of an individual. Circadian rhythms have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria and there is evidence that they evolved independently in each of these kingdoms of life. The term ''circadian'' comes from the Latin ', meaning "around", and ', meaning "day". Processes with 24-hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitness (biology)
Fitness (often denoted w or ω in population genetics models) is a quantitative representation of individual reproductive success. It is also equal to the average contribution to the gene pool of the next generation, made by the same individuals of the specified genotype or phenotype. Fitness can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment or time. The fitness of a genotype is manifested through its phenotype, which is also affected by the developmental environment. The fitness of a given phenotype can also be different in different selective environments. With asexual reproduction, it is sufficient to assign fitnesses to genotypes. With sexual reproduction, recombination scrambles alleles into different genotypes every generation; in this case, fitness values can be assigned to alleles by averaging over possible genetic backgrounds. Natural selection tends to make alleles with higher fitness more common over time, resulting in Darwini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firmicutes
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have Gram-positive cell wall structure. They have round cells, called cocci (singular coccus), or rod-like forms (bacillus). A few Bacillota, such as '' Megasphaera'', '' Pectinatus'', '' Selenomonas'', and '' Zymophilus'' from the class Negativicutes, have a porous pseudo-outer membrane that causes them to stain Gram-negative. Many Bacillota produce endospores, which are resistant to desiccation and can survive extreme conditions. They are found in various environments, and the group includes some notable pathogens. Those in one family, the Heliobacteria, produce energy through anoxygenic photosynthesis. Bacillota play an important role in beer, wine, and cider spoilage. Taxonomy The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The name "Firmicutes" was derived from the Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut Microbiota
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses, that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut microbiota. The gut is the main location of the human microbiome. The gut microbiota has broad impacts, including effects on colonization, resistance to pathogens, maintaining the intestinal epithelium, metabolizing dietary and pharmaceutical compounds, controlling immune function, and even behavior through the gut–brain axis. The microbial composition of the gut microbiota varies across regions of the digestive tract. The colon contains the highest microbial density of any human-associated microbial community studied so far, representing between 300 and 1000 different species. Bacteria are the largest and to date, best studied component and 99% of gut bacteria come from about 30 or 40 species. About 55% of the dry mass of feces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melatonin
Melatonin, an indoleamine, is a natural compound produced by various organisms, including bacteria and eukaryotes. Its discovery in 1958 by Aaron B. Lerner and colleagues stemmed from the isolation of a substance from the pineal gland of cows that could induce skin lightening in common frogs. This compound was later identified as a hormone secreted in the brain during the night, playing a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle, also known as the circadian rhythm, in vertebrates. In vertebrates, melatonin's functions extend to Entrainment (chronobiology), synchronizing sleep-wake cycles, encompassing sleep-wake timing and blood pressure regulation, as well as controlling seasonal rhythmicity (circannual cycle), which includes reproduction, fattening, molting, and hibernation. Its effects are mediated through the activation of melatonin receptors and its role as an antioxidant. In plants and bacteria, melatonin primarily serves as a defense mechanism against oxidative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luciferase
Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words ''luciferin'' and ''luciferase'', for the substrate and enzyme, respectively. Both words are derived from the Latin word ''lucifer'', meaning "lightbearer", which in turn is derived from the Latin words for "light" (''lux)'' and "to bring or carry" (''ferre)''.Luciferases are widely used in biotechnology, for bioluminescence imaging microscopy and as reporter genes, for many of the same applications as fluorescent proteins. However, unlike fluorescent proteins, luciferases do not require an external light source, but do require addition of luciferin, the consumable substrate. Examples A variety of organisms regulate their light production using different luciferases in a variety of light-emitting reactions. The majority of studied luciferases have been found in anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'' (), known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillus'', ''B. subtilis'' is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. ''B. subtilis'' has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. ''B. subtilis'' is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies. Description ''Bacillus subtilis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, rod-shaped and catalase-positive. It was originally named ''Vibrio subtilis'' by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circadian Advantage
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the environment (is Entrainment (chronobiology), entrained by the environment). Circadian rhythms are regulated by a circadian clock whose primary function is to rhythmically co-ordinate biological processes so they occur at the correct time to maximize the fitness of an individual. Circadian rhythms have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria and there is evidence that they evolved independently in each of these kingdoms of life. The term ''circadian'' comes from the Latin ', meaning "around", and ', meaning "day". Processes with 24-hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Circadian Rhythms
Bacterial circadian rhythms, like other circadian rhythms, are endogenous "biological clocks" that have the following three characteristics: (a) in constant conditions (i.e. constant temperature and either constant light or constant darkness ) they oscillate with a period that is close to, but not exactly, 24 hours in duration, (b) this "free-running sleep, free-running" rhythm is temperature compensated, and (c) the rhythm will entrain to an appropriate environmental cycle. Until the mid-1980s, it was thought that only eukaryotic cells had circadian rhythms. It is now known that cyanobacteria (a phylum of photosynthetic eubacteria) have well-documented circadian rhythms that meet all the criteria of bona fide circadian rhythms. In these bacteria, three key proteins whose structures have been determined, KaiA, KaiB, and KaiC can form a molecular clockwork that orchestrates global gene expression. This system enhances the fitness of cyanobacteria in rhythmic environments. History: a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacterial Clock
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteria's informal common name, blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are probably the most numerous taxon to have ever existed on Earth and the first organisms known to have produced oxygen, having appeared in the middle Archean eon and apparently originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Their photopigments can absorb the red- and blue-spectrum frequencies of sunlight (thus reflecting a greenish color) to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen. The hydrogen ions are used to react with carbon dioxide to produce complex organic compounds such as carbohydrates (a process known as carbon fixation), and the oxygen is released as a byproduct. By continuously producing and releasing oxygen over billions of years, cyanobacteria are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (genetics)
In biology, translation is the process in living cells in which proteins are produced using RNA molecules as templates. The generated protein is a sequence of amino acids. This sequence is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in the RNA. The nucleotides are considered three at a time. Each such triple results in the addition of one specific amino acid to the protein being generated. The matching from nucleotide triple to amino acid is called the genetic code. The translation is performed by a large complex of functional RNA and proteins called ribosomes. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later folds into an active protein and performs its functions in the cell. The polypeptide can also start folding during protein synthesis. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of complementary transfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |