|
Backswamp
In geology, a backswamp is a type of depositional environment commonly found in a floodplain. It is where deposits of fine silts and clays settle after a flood A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con .... These deposits create a marsh-like landscape that is often poorly drained and usually lower than the rest of the floodplain. Levees form as a result of the flooding process. Large amounts of rainfall cause the river to become too full during the flooding, where it overflows, carrying sediments into the floodplain. As the flooding slows and stops, the sediments are deposited, with the largest deposited closer to the river channel and the smaller ones deposited further away. These deposits result from the larger sediments losing energy faster than their smaller counterparts, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depositional Environment
In geology, depositional environment or sedimentary environment describes the combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will be formed after lithification, if the sediment is preserved in the rock record. In most cases, the environments associated with particular rock types or associations of rock types can be matched to existing analogues. However, the further back in geological time sediments were deposited, the more likely that direct modern analogues are not available (e.g. banded iron formations). Types of depositional environments Continental * – type of Fluvial deposit. Caused by moving water in a fan shape (Alluvial Fan) and containing mostly impermeable and nonporous sediments well sorted. * . Often in deserts and coastal regions and well sorted, large scale cross-beds * – processes due to moving water, mainly streams. Common sediments are g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high Discharge (hydrology), discharge.Goudie, A. S., 2004, ''Encyclopedia of Geomorphology'', vol. 1. Routledge, New York. The soils usually consist of clays, silts, sands, and gravels deposited during floods. Because of regular flooding, floodplains frequently have high soil fertility since nutrients are deposited with the flood waters. This can encourage farming; some important agricultural regions, such as the Nile and Mississippi Basin, Mississippi Drainage basin, river basins, heavily exploit floodplains. Agricultural and urban regions have developed near or on floodplains to take advantage of the rich soil and freshwater. However, the Flood risk, risk of inundation has led to increasing efforts to Flood control, control flooding. Formation Most floodplai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension (chemistry), suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel when dry, and lacks Plasticity (physics), plasticity when wet. Silt can also be felt by the tongue as granular when placed on the front teeth (even when mixed with clay particles). Silt is a common material, making up 45% of average modern mud. It is found in many river deltas and as wind-deposited accumulations, particularly in central Asia, north China, and North America. It is produced in both very hot climates (through such processes as collisions of quartz grains in dust storms) and very cold climates (through such processes as glacial grinding of quartz grains.) Loess is soil rich in silt which makes up some of the most fertile agricultural land on Earth. However, silt is very vulnerable to erosion, and it has poo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clays develop plasticity (physics), plasticity when wet but can be hardened through Pottery#Firing, firing. Clay is the longest-known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been radiocarbon dating, dated to around 14,000 BCE, and Clay tablet, clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtration, filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, often baked into brick, as an essenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant concern in agriculture, civil engineering and public health. Environmental issues, Human changes to the environment often increase the intensity and frequency of flooding. Examples for human changes are land use changes such as deforestation and Wetland conservation, removal of wetlands, changes in waterway course or flood controls such as with levees. Global environmental issues also influence causes of floods, namely climate change which causes an Effects of climate change on the water cycle, intensification of the water cycle and sea level rise. For example, climate change makes Extreme weather, extreme weather events more frequent and stronger. This leads to more intense floods and increased flood risk. Natural types of floods include riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meandering River
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank ( cut bank or river cliff) and deposits sediments on an inner, convex bank which is typically a point bar. The result of this coupled erosion and sedimentation is the formation of a sinuous course as the channel migrates back and forth across the axis of a floodplain. The zone within which a meandering stream periodically shifts its channel is known as a meander belt. It typically ranges from 15 to 18 times the width of the channel. Over time, meanders migrate downstream, sometimes in such a short time as to create civil engineering challenges for local municipalities attempting to maintain stable roads and bridges.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl Jr., and J.A. Jackson, J.A., eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. Charlton, R., 2007 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluvial Landforms
Landforms related to rivers and other watercourses include: * * * * * (watershed) * * *Fluvial landforms of streams A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a strea ... * * (Gorge) * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *{{annotated link, Yazoo stream See also * Glossary_of_landforms ** Glossary_of_landforms#Fluvial_landforms F F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
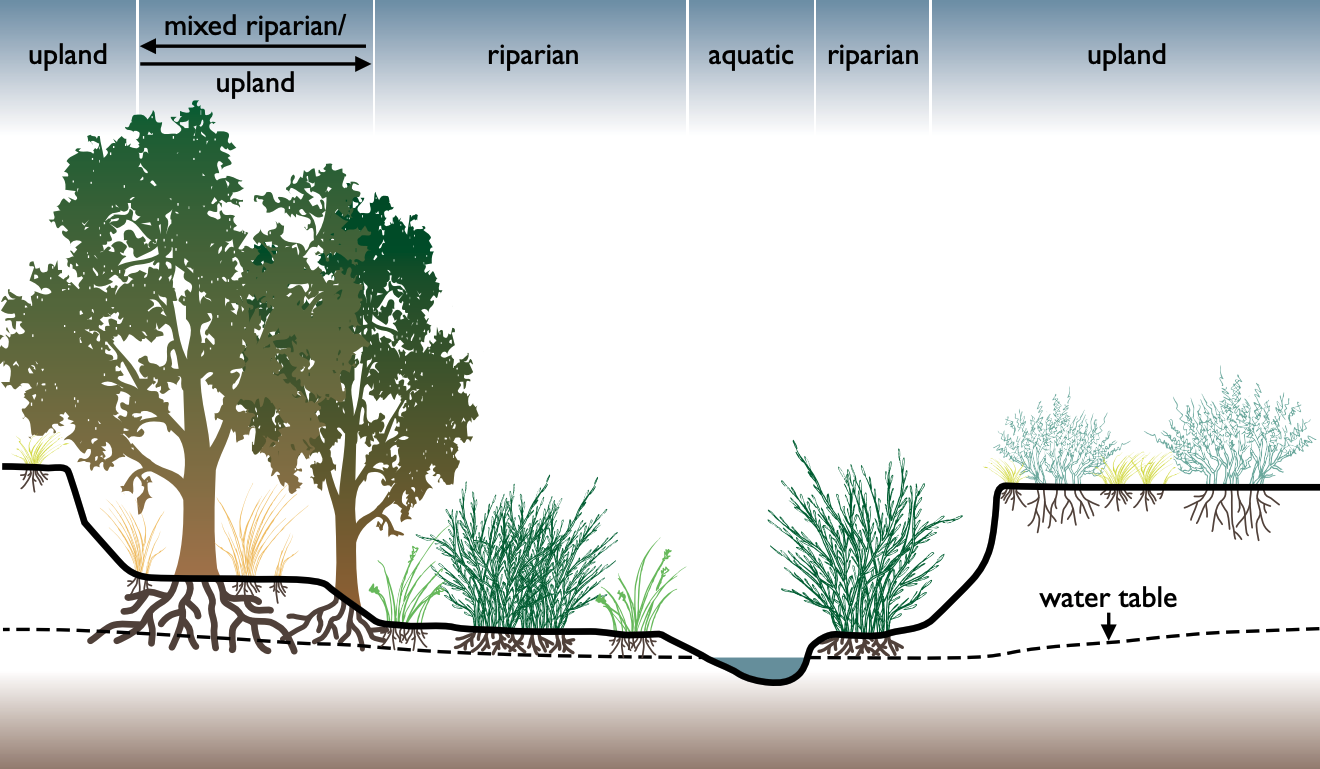
Riparian Zone
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin ''wiktionary:ripa, ripa'', meaning "bank (geography), river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by aquatic plant, hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentology
Sedimentology encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand, silt, and clay, and the processes that result in their formation (erosion and weathering), transport, deposition and diagenesis. Sedimentologists apply their understanding of modern processes to interpret geologic history through observations of sedimentary rocks and sedimentary structures. Sedimentary rocks cover up to 75% of the Earth's surface, record much of the Earth's history, and harbor the fossil record. Sedimentology is closely linked to stratigraphy, the study of the physical and temporal relationships between rock layers or strata. The premise that the processes affecting the earth today are the same as in the past is the basis for determining how sedimentary features in the rock record were formed. By comparing similar features today to features in the rock record—for example, by comparing modern sand dunes to dunes preserved in ancient aeolian sandstones—geologists reconstruct past environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |