|
Automorphisms Of The Symmetric And Alternating Groups
In group theory, a branch of mathematics, the automorphisms and outer automorphisms of the symmetric groups and alternating groups are both standard examples of these automorphisms, and objects of study in their own right, particularly the exceptional outer automorphism of S6, the symmetric group on 6 elements. Summary Generic case * n\neq 2,6: \operatorname(\mathrm_n) = \mathrm_n, and thus \operatorname(\mathrm_n) = \mathrm_1. :Formally, \mathrm_n is complete and the natural map \mathrm_n \to \operatorname(\mathrm_n) is an isomorphism. * n\neq 1,2,6: \operatorname(\mathrm_n)=\mathrm_n/\mathrm_n=\mathrm_2, and the outer automorphism is conjugation by an odd permutation. * n\neq 2,3,6: \operatorname(\mathrm_n)=\operatorname(\mathrm_n)=\mathrm_n :Indeed, the natural maps \mathrm_n \to \operatorname(\mathrm_n) \to \operatorname(\mathrm_n) are isomorphisms. Exceptional cases * n=1,2: trivial: :: \operatorname(\mathrm_1)=\operatorname(\mathrm_1)=\operatorname(\mathrm_1)=\operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Theory
In abstract algebra, group theory studies the algebraic structures known as group (mathematics), groups. The concept of a group is central to abstract algebra: other well-known algebraic structures, such as ring (mathematics), rings, field (mathematics), fields, and vector spaces, can all be seen as groups endowed with additional operation (mathematics), operations and axioms. Groups recur throughout mathematics, and the methods of group theory have influenced many parts of algebra. Linear algebraic groups and Lie groups are two branches of group theory that have experienced advances and have become subject areas in their own right. Various physical systems, such as crystals and the hydrogen atom, and Standard Model, three of the four known fundamental forces in the universe, may be modelled by symmetry groups. Thus group theory and the closely related representation theory have many important applications in physics, chemistry, and materials science. Group theory is also cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exotic Map
Exotic may refer to: Mathematics and physics * Exotic R4, a differentiable 4-manifold, homeomorphic but not diffeomorphic to the Euclidean space R4 *Exotic sphere, a differentiable ''n''-manifold, homeomorphic but not diffeomorphic to the ordinary ''n''-sphere * Exotic atom, an atom with one or more electrons replaced by other negatively charged particles * Exotic hadron **Exotic baryon, bound states of 3 quarks and additional particles **Exotic meson, non-quark model mesons *Exotic matter, a hypothetical concept of particle physics Music * "Exotic" (1963 song), a song by The Sentinals from the 1963 album ''Surf Crazy - Original Surfin' Hits'' * "Exotic" (Lil Baby song), 2018 * "Exotic" (Priyanka Chopra song), a 2012 song by Priyanka Chopra featuring Pitbull Flora and fauna *Exotic pet * Exotic Shorthair, a breed of cat *Exotic species (or introduced species), a species not native to an area Other *Exotic dancer, a type of dancer or stripper * Exotic derivative, a type of fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frobenius Group
In mathematics, a Frobenius group is a transitive permutation group on a finite set, such that no non-trivial element fixes more than one point and some non-trivial element fixes a point. They are named after F. G. Frobenius. Structure Suppose ''G'' is a Frobenius group consisting of permutations of a set ''X''. A subgroup ''H'' of ''G'' fixing a point of ''X'' is called a Frobenius complement. The identity element together with all elements not in any conjugate of ''H'' form a normal subgroup called the Frobenius kernel ''K''. (This is a theorem due to ; there is still no proof of this theorem that does not use character theory, although see .) The Frobenius group ''G'' is the semidirect product of ''K'' and ''H'': :G=K\rtimes H. Both the Frobenius kernel and the Frobenius complement have very restricted structures. proved that the Frobenius kernel ''K'' is a nilpotent group. If ''H'' has even order then ''K'' is abelian. The Frobenius complement ''H'' has the property th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Pierre Serre
Jean-Pierre Serre (; born 15 September 1926) is a French mathematician who has made contributions to algebraic topology, algebraic geometry and algebraic number theory. He was awarded the Fields Medal in 1954, the Wolf Prize in 2000 and the inaugural Abel Prize in 2003. Biography Personal life Born in Bages, Pyrénées-Orientales, to pharmacist parents, Serre was educated at the Lycée de Nîmes. Then he studied at the École Normale Supérieure in Paris from 1945 to 1948. He was awarded his doctorate from the Sorbonne in 1951. From 1948 to 1954 he held positions at the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique in Paris. In 1956 he was elected professor at the Collège de France, a position he held until his retirement in 1994. His wife, Professor Josiane Heulot-Serre, was a chemist; she also was the director of the Ecole Normale Supérieure de Jeunes Filles. Their daughter is the former French diplomat, historian and writer Claudine Monteil. The French mathematician D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitive Group Action
In mathematics, a group action of a group G on a set S is a group homomorphism from G to some group (under function composition) of functions from S to itself. It is said that G acts on S. Many sets of transformations form a group under function composition; for example, the rotations around a point in the plane. It is often useful to consider the group as an abstract group, and to say that one has a group action of the abstract group that consists of performing the transformations of the group of transformations. The reason for distinguishing the group from the transformations is that, generally, a group of transformations of a structure acts also on various related structures; for example, the above rotation group also acts on triangles by transforming triangles into triangles. If a group acts on a structure, it will usually also act on objects built from that structure. For example, the group of Euclidean isometries acts on Euclidean space and also on the figures drawn i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faithful Group Action
In mathematics, a group action of a group G on a set S is a group homomorphism from G to some group (under function composition) of functions from S to itself. It is said that G acts on S. Many sets of transformations form a group under function composition; for example, the rotations around a point in the plane. It is often useful to consider the group as an abstract group, and to say that one has a group action of the abstract group that consists of performing the transformations of the group of transformations. The reason for distinguishing the group from the transformations is that, generally, a group of transformations of a structure acts also on various related structures; for example, the above rotation group also acts on triangles by transforming triangles into triangles. If a group acts on a structure, it will usually also act on objects built from that structure. For example, the group of Euclidean isometries acts on Euclidean space and also on the figures draw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Line
In projective geometry and mathematics more generally, a projective line is, roughly speaking, the extension of a usual line by a point called a '' point at infinity''. The statement and the proof of many theorems of geometry are simplified by the resultant elimination of special cases; for example, two distinct projective lines in a projective plane meet in exactly one point (there is no "parallel" case). There are many equivalent ways to formally define a projective line; one of the most common is to define a projective line over a field ''K'', commonly denoted P1(''K''), as the set of one-dimensional subspaces of a two-dimensional ''K''-vector space. This definition is a special instance of the general definition of a projective space. The projective line over the reals is a manifold; see '' Real projective line'' for details. Homogeneous coordinates An arbitrary point in the projective line P1(''K'') may be represented by an equivalence class of '' homogeneous coordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Field
In mathematics, a finite field or Galois field (so-named in honor of Évariste Galois) is a field (mathematics), field that contains a finite number of Element (mathematics), elements. As with any field, a finite field is a Set (mathematics), set on which the operations of multiplication, addition, subtraction and division are defined and satisfy certain basic rules. The most common examples of finite fields are the integers mod n, integers mod p when p is a prime number. The ''order'' of a finite field is its number of elements, which is either a prime number or a prime power. For every prime number p and every positive integer k there are fields of order p^k. All finite fields of a given order are isomorphism, isomorphic. Finite fields are fundamental in a number of areas of mathematics and computer science, including number theory, algebraic geometry, Galois theory, finite geometry, cryptography and coding theory. Properties A finite field is a finite set that is a fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Linear Group
In mathematics, especially in the group theoretic area of algebra, the projective linear group (also known as the projective general linear group or PGL) is the induced action of the general linear group of a vector space ''V'' on the associated projective space P(''V''). Explicitly, the projective linear group is the quotient group : PGL(''V'') = GL(''V'')/Z(''V'') where GL(''V'') is the general linear group of ''V'' and Z(''V'') is the subgroup of all nonzero scalar transformations of ''V''; these are quotiented out because they act trivially on the projective space and they form the kernel of the action, and the notation "Z" reflects that the scalar transformations form the center of the general linear group. The projective special linear group, PSL, is defined analogously, as the induced action of the special linear group on the associated projective space. Explicitly: : PSL(''V'') = SL(''V'')/SZ(''V'') where SL(''V'') is the special linear group over ''V'' and SZ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylow Subgroup
In mathematics, specifically in the field of finite group theory, the Sylow theorems are a collection of theorems named after the Norwegian mathematician Peter Ludwig Sylow that give detailed information about the number of subgroups of fixed order that a given finite group contains. The Sylow theorems form a fundamental part of finite group theory and have very important applications in the classification of finite simple groups. For a prime number p, a ''p''-group is a group whose cardinality is a power of p; or equivalently, the order of each group element is some power of p. A Sylow ''p''-subgroup (sometimes ''p''-Sylow subgroup) of a finite group G is a maximal p-subgroup of G, i.e., a subgroup of G that is a ''p''-group and is not a proper subgroup of any other p-subgroup of G. The set of all Sylow p-subgroups for a given prime p is sometimes written \text_p(G). The Sylow theorems assert a partial converse to Lagrange's theorem. Lagrange's theorem states that for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
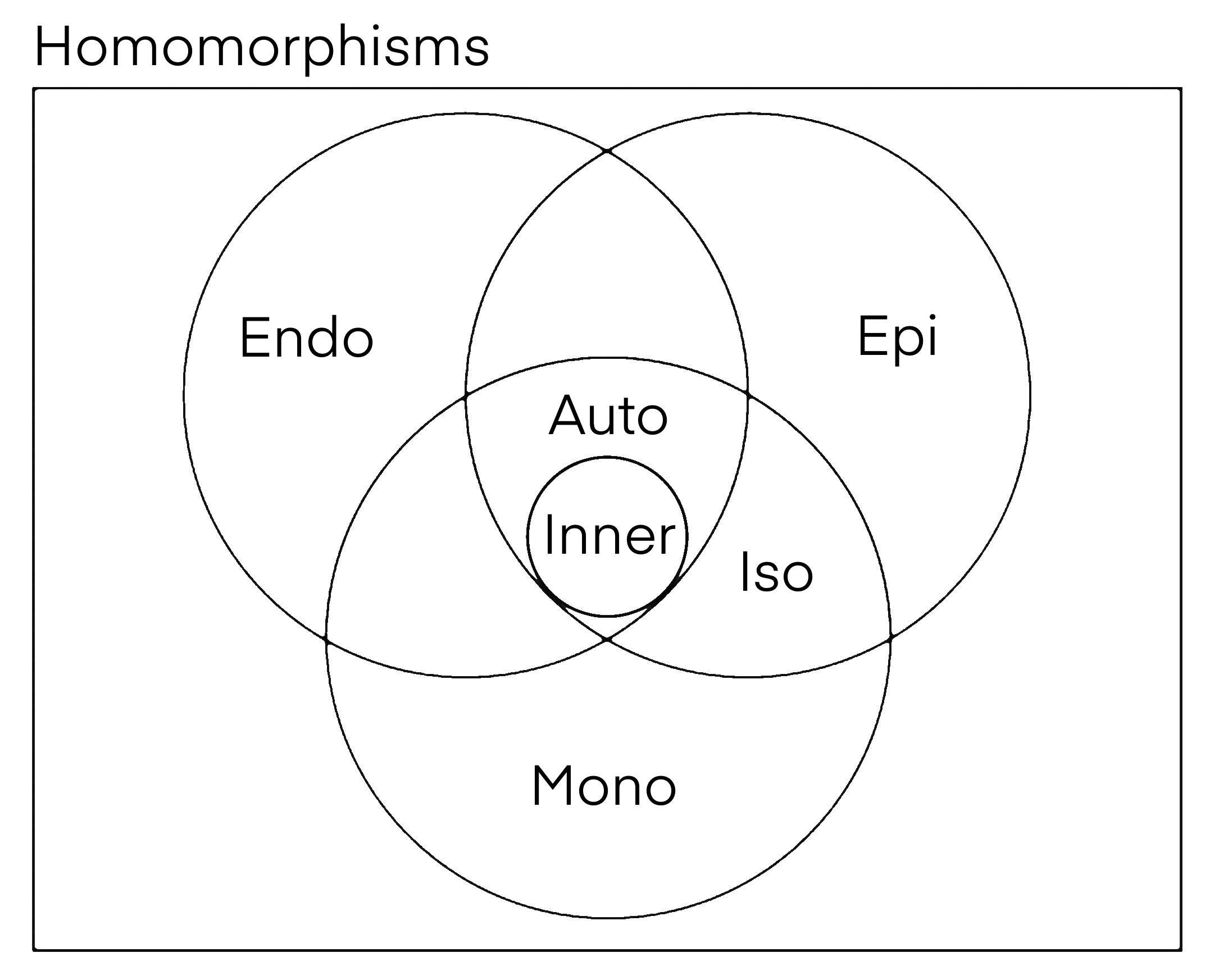
Inner Automorphism
In abstract algebra, an inner automorphism is an automorphism of a group, ring, or algebra Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic ope ... given by the conjugation action of a fixed element, called the ''conjugating element''. They can be realized via operations from within the group itself, hence the adjective "inner". These inner automorphisms form a subgroup of the automorphism group, and the Quotient_group, quotient of the automorphism group by this subgroup is defined as the outer automorphism group. Definition If is a group and is an element of (alternatively, if is a ring, and is a Unit (ring theory), unit), then the function :\begin \varphi_g\colon G&\to G \\ \varphi_g(x)&:= g^xg \end is called (right) conjugation by (see also conjugacy class). This func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Factorization
In graph theory, a factor of a graph ''G'' is a spanning subgraph, i.e., a subgraph that has the same vertex set as ''G''. A ''k''-factor of a graph is a spanning ''k''- regular subgraph, and a ''k''-factorization partitions the edges of the graph into disjoint ''k''-factors. A graph ''G'' is said to be ''k''-factorable if it admits a ''k''-factorization. In particular, a 1-factor is a perfect matching, and a 1-factorization of a ''k''-regular graph is a proper edge coloring with ''k'' colors. A 2-factor is a collection of disjoint cycles that spans all vertices of the graph. 1-factorization If a graph is 1-factorable then it has to be a regular graph. However, not all regular graphs are 1-factorable. A ''k''-regular graph is 1-factorable if it has chromatic index ''k''; examples of such graphs include: * Any regular bipartite graph. Hall's marriage theorem can be used to show that a ''k''-regular bipartite graph contains a perfect matching. One can then remove the perfec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |