|
Aucubin
Aucubin is an iridoid glycoside. Iridoids are commonly found in plants and function as defensive compounds. Iridoids decrease the growth rates of many generalist herbivores. Natural occurrences Aucubin, as other iridoids, is found in asterids such as '' Aucuba japonica'' (Garryaceae), '' Eucommia ulmoides'' (Eucommiaceae), '' Plantago asiatica'', ''Plantago major'', ''Plantago lanceolata'' (Plantaginaceae), ''Galium aparine'' (Rubiaceae) and others. These plants are used in traditional Chinese and folk medicine. Agnuside is composed of aucubin and ''p''-hydroxybenzoic acid. Health effects Aucubin was found to protect against liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride or alpha-amanitin in mice and rats when 80 mg/kg was dosed intraperitoneally. Chemistry Aucubin is a monoterpenoid based compound. Aucubin, like all iridoids, has a cyclopentan- pyran skeleton. Iridoids can consist of ten, nine, or rarely eight carbons in which C11 is more frequently missing than C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridoid
Iridoids are a type of monoterpenoids in the general form of cyclopentanopyran, found in a wide variety of plants and some animals. They are biosynthetically derived from 8-oxogeranial. Iridoids are typically found in plants as glycosides, most often bound to glucose. The chemical structure is exemplified by iridomyrmecin, a defensive chemical produced by the ant genus '' Iridomyrmex'', for which iridoids are named. Structurally, they are bicyclic ''cis''-fused cyclopentane-pyrans. Cleavage of a bond in the cyclopentane ring gives rise to a subclass known as ''secoiridoids'', such as oleuropein and amarogentin. Occurrence The iridoids produced by plants act primarily as a defense against herbivores or against infection by microorganisms. The variable checkerspot butterfly also contains iridoids obtained through its diet which act as a defense against avian predators. To humans and other mammals, iridoids are often characterized by a deterrent bitter taste. Aucubin a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrophularia Umbrosa
''Scrophularia umbrosa'', the green figwort, is a perennial herbaceous plant found in Europe and Asia. It grows in moist and cultivated waste ground. The species looks very similar to the closely related ''Scrophularia auriculata'' (water figwort). Green figwort has a greener stem than water figwort, and lacks the leaf auricles which give water figwort its Latin name. The plant is probably poisonous to cows. It is pollinated by bees and wasps. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade, but requires moist or wet soil. Conservation The global conservation status of this species, as of 2013, is least concern. In the United Kingdom it is a very locally distributed species though increasingly abundant. Folklore The plant was thought, by the doctrine of signatures The doctrine of signatures, dating from the time of Dioscorides and Galen, states that herbs resembling various parts of the body can be used by herbalists to treat ailments of those body parts. A theolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geniposidic Acid
Geniposidic acid is a natural chemical compound, classified as an iridoid glucoside, found in a variety of plants including ''Eucommia ulmoides'' and ''Gardenia jasminoides ''Gardenia jasminoides'', commonly known as gardenia, is an evergreen flowering plant in the coffee family Rubiaceae. It is native to parts of South-East Asia. Wild plants range from 30 centimetres to 3 metres (about 1 to 10 feet) in height. The ...''. References Iridoid glycosides Glucosides Carboxylic acids Cyclopentenes {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gardenia Jasminoides
''Gardenia jasminoides'', commonly known as gardenia, is an evergreen flowering plant in the coffee family Rubiaceae. It is native to parts of South-East Asia. Wild plants range from 30 centimetres to 3 metres (about 1 to 10 feet) in height. They have a rounded habit with very dense branches with opposite leaves that are lanceolate-oblong, leathery or gathered in groups on the same node and by a dark green, shiny and slightly waxy surface and prominent veins. With its shiny green leaves and heavily fragrant white summer flowers, it is widely used in gardens in warm temperate and subtropical climates. It also is used as a houseplant in temperate climates. It has been in cultivation in China for at least a thousand years, and it was introduced to English gardens in the mid-18th century. Many varieties have been bred for horticulture, with low-growing, and large, and long-flowering forms. Description ''Gardenia jasminoides'' is a shrub that ranges from 30 cm to 3 m (1–10&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terpenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes", terpenoids contain additional functional groups, usually containing oxygen. When combined with the hydrocarbon terpenes, terpenoids comprise about 80,000 compounds. They are the largest class of plant secondary metabolites, representing about 60% of known natural products. Many terpenoids have substantial pharmacological bioactivity and are therefore of interest to medicinal chemists. Plant terpenoids are used for their aromatic qualities and play a role in traditional herbal remedies. Terpenoids contribute to the scent of eucalyptus, the flavors of cinnamon, cloves, and ginger, the yellow color in sunflowers, and the red color in tomatoes. Well-known terpenoids include citral, menthol, camphor, salvinorin A in the plant ''Salvia d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geranyl Pyrophosphate
Geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), also known as geranyl diphosphate (GDP), is the pyrophosphate ester of the terpenoid geraniol. Its salts are colorless. It is a precursor to many natural products. Occurrence GPP is an intermediate in the isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway that produces longer prenyl chains such as farnesyl pyrophosphate and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate as well as many terpenes. It can be prepared in the laboratory from geraniol. Related compounds * Geraniol Geraniol is a monoterpenoid and an alcohol. It is the primary component of citronella oil and is a primary component of rose oil, palmarosa oil. It is a colorless oil, although commercial samples can appear yellow. It has low solubility in w ... * Farnesyl pyrophosphate * Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate See also * Dimethylallyltranstransferase References Further reading *Kulkarni RS, Pandit SS, Chidley HG, Nagel R, Schmidt A, Gershenzon J, Pujari KH, Giri AP and Gupta VS, 2013Characterization of thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP; or alternatively, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP); also isoprenyl pyrophosphate) is an isoprenoid precursor. It is a product of both the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and exists in virtually all life forms. The enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase catalyzes isomerization between DMAPP and IPP. In the mevalonate pathway DMAPP is synthesised from mevalonic acid. In contrast, DMAPP is synthesised from HMBPP in the MEP pathway The non-mevalonate pathway—also appearing as the mevalonate-independent pathway and the 2-''C''-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate/1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (MEP/DOXP) pathway—is an alternative metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of the is .... At present, it is believed that there is crossover between the two pathways in organisms that use both pathways to create terpenes and terpenoids, such as in plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
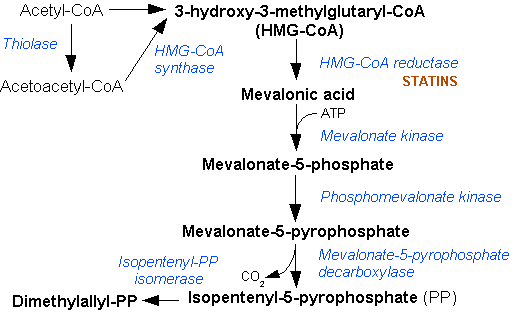
Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate, or IDP) is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway (commonly called the mevalonate pathway) and in the ''non-mevalonate'' MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. Isoprenoid precursors such as IPP, and its isomer DMAPP, are used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. Biosynthesis IPP is formed from acetyl-CoA via the mevalonate pathway (the "upstream" part), and then is isomerized to dimethylallyl pyrophosphate by the enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase. IPP can be synthesised via an alternative non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis, the MEP pathway, where it is formed from (''E'')-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMB-PP) by the enzyme HMB-PP reductase (LytB, IspH). The MEP pathway is present in many bacteria, apicomplexan protozoa such as malaria parasites, and in the plastids of higher plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |