|
Atomic Mirror
In physics, an atomic mirror is a device which reflects neutral atoms in a way similar to the way a conventional mirror reflects visible light. Atomic mirrors can be made of electric fields or magnetic fields, electromagnetic waves or just silicon wafer; in the last case, atoms are reflected by the attracting tails of the van der Waals attraction (see quantum reflection). Such reflection is efficient when the normal component of the wavenumber of the atoms is small or comparable to the effective depth of the attraction potential (roughly, the distance at which the potential becomes comparable to the kinetic energy of the atom). To reduce the normal component, most atomic mirrors are blazed at the grazing incidence. At grazing incidence, the efficiency of the quantum reflection can be enhanced by a surface covered with ridges ( ridged mirror). The set of narrow ridges reduces the van der Waals attraction of atoms to the surfaces and enhances the reflection. Each ridge bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
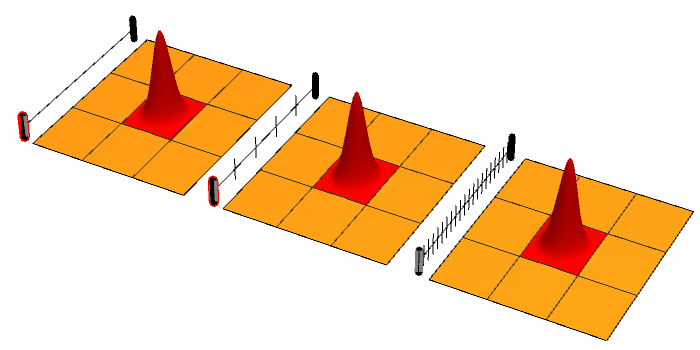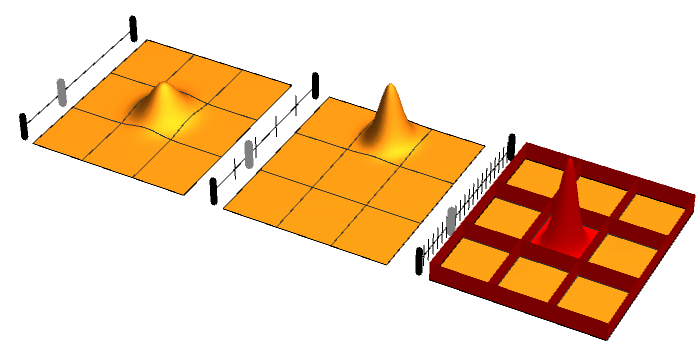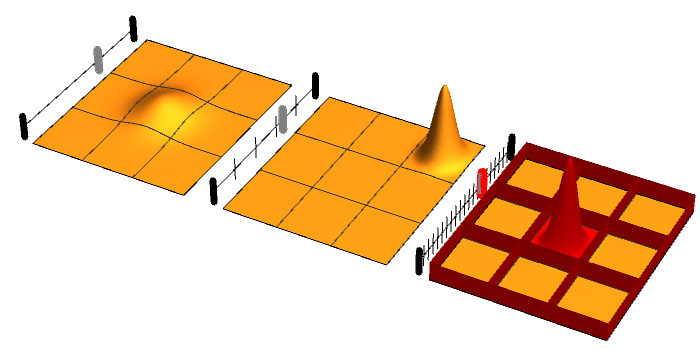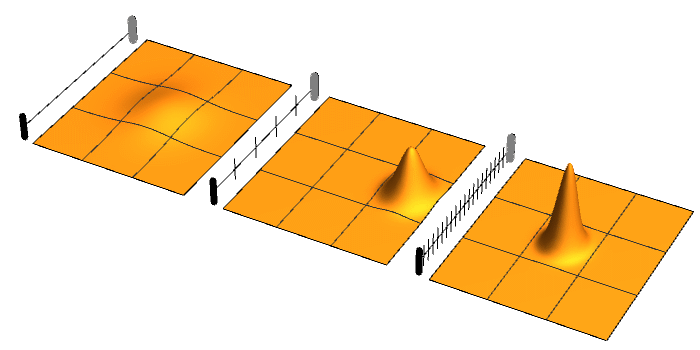
Ridged Mirror
In atomic physics, a ridged mirror (or ridged atomic mirror, or Fresnel diffraction mirror) is a kind of atomic mirror, designed for the specular reflection of neutral particles (atoms) coming at a grazing incidence angle. In order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this surface has narrow ridges. Reflectivity of ridged atomic mirrors Various estimates for the efficiency of quantum reflection of waves from ridged mirror were discussed in the literature. All the estimates explicitly use the de Broglie theory about wave properties of reflected atoms. Scaling of the van der Waals force The ridges enhance the quantum reflection from the surface, reducing the effective constant ~C~ of the van der Waals attraction of atoms to the surface. Such interpretation leads to the estimate of the reflectivity : \displaystyle r \approx r_0\!\left( \frac \ell L C,\!~K\sin(\theta)\right), where ~\ell~ is width of the ridges, ~L~ is distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Nanoscope
The scanning helium microscope (SHeM) is a form of microscopy that uses low-energy (5–100 meV) neutral helium atoms to image the surface of a sample without any damage to the sample caused by the imaging process. Since helium is inert and neutral, it can be used to study delicate and insulating surfaces. Images are formed by rastering a sample underneath an atom beam and monitoring the flux of atoms that are scattered into a detector at each point. The technique is different from a scanning helium ion microscope, which uses charged helium ions that can cause damage to a surface. Motivation Microscopes can be divided into two general classes: those that illuminate the sample with a beam, and those that use a physical scanning probe. Scanning probe microscopy, Scanning probe microscopies raster a small probe across the surface of a sample and monitor the interaction of the probe with the sample. The resolution of scanning probe microscopies is set by the size of the inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ridged Mirror
In atomic physics, a ridged mirror (or ridged atomic mirror, or Fresnel diffraction mirror) is a kind of atomic mirror, designed for the specular reflection of neutral particles (atoms) coming at a grazing incidence angle. In order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this surface has narrow ridges. Reflectivity of ridged atomic mirrors Various estimates for the efficiency of quantum reflection of waves from ridged mirror were discussed in the literature. All the estimates explicitly use the de Broglie theory about wave properties of reflected atoms. Scaling of the van der Waals force The ridges enhance the quantum reflection from the surface, reducing the effective constant ~C~ of the van der Waals attraction of atoms to the surface. Such interpretation leads to the estimate of the reflectivity : \displaystyle r \approx r_0\!\left( \frac \ell L C,\!~K\sin(\theta)\right), where ~\ell~ is width of the ridges, ~L~ is distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Reflection
Quantum reflection is a uniquely quantum phenomenon in which an object, such as a neutron or a small molecule, reflects smoothly and in a wavelike fashion from a much larger surface, such as a pool of mercury. A classically behaving neutron or molecule will strike the same surface much like a thrown ball, hitting only at one atomic-scale location where it is either absorbed or scattered. Quantum reflection provides a powerful experimental demonstration of particle-wave duality, since it is the extended quantum wave packet of the particle, rather than the particle itself, that reflects from the larger surface. It is similar to reflection high-energy electron diffraction, where electrons reflect and diffraction from surfaces, and grazing incidence atom scattering, where the fact that atoms (and ions) can also be waves is used to diffract from surfaces. Definition In a workshop about quantum reflection,Quantum Reflection, workshop; October 22–24, 2007, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference (wave propagation), interference'' of Superposition principle, superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, Optical fiber, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, Nuclear physics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, interactome, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms. Interferometers are devices that extract information from interference. They are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of microscopic displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In the case with most interferometers, light from a single source is split into two beams that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specular Reflection
Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection (physics), reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface. The law of reflection states that a reflected ray (optics), ray of light emerges from the reflecting surface at the same angle to the surface normal as the incident ray, but on the opposing side of the surface normal in the plane formed by the incident and reflected rays. The earliest known description of this behavior was recorded by Hero of Alexandria (Anno Domini, AD c. 10–70). Later, Ibn al-Haytham, Alhazen gave a complete statement of the law of reflection. He was first to state that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in a same plane perpendicular to reflecting plane. Specular reflection may be contrasted with diffuse reflection, in which light is scattered away from the surface in a range of directions. Law of reflection When light encounters a boundary of a material, it is affected by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeno Effect
In quantum mechanics, frequent measurements cause the quantum Zeno effect, a reduction in transitions away from the systems initial state, slowing a systems time evolution. Sometimes this effect is interpreted as "a system cannot change while you are watching it". One can "freeze" the evolution of the system by measuring it frequently enough in its known initial state. The meaning of the term has since expanded, leading to a more technical definition, in which time evolution can be suppressed not only by measurement: the quantum Zeno effect is the suppression of unitary time evolution in quantum systems provided by a variety of sources: measurement, interactions with the environment, stochastic fields, among other factors. As an outgrowth of study of the quantum Zeno effect, it has become clear that applying a series of sufficiently strong and fast pulses with appropriate symmetry can also ''decouple'' a system from its decohering environment. The comparison with Zeno's parado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresnel Diffraction
In optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction is an approximation of the Kirchhoff's diffraction formula, Kirchhoff–Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near and far field, near field. It is used to calculate the diffraction pattern created by waves passing through an aperture or around an object, when viewed from relatively close to the object. In contrast the diffraction pattern in the near and far field, far field region is given by the Fraunhofer diffraction equation. The near field can be specified by the Fresnel number, , of the optical arrangement. When F \ll 1 the diffracted wave is considered to be in the Fraunhofer field. However, the validity of the Fresnel diffraction integral is deduced by the approximations derived below. Specifically, the phase terms of third order and higher must be negligible, a condition that may be written as \frac \ll 1, where \theta is the maximal angle described by \theta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Der Waals Force
In molecular physics and chemistry, the van der Waals force (sometimes van der Waals' force) is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and therefore more susceptible to disturbance. The van der Waals force quickly vanishes at longer distances between interacting molecules. Named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, the van der Waals force plays a fundamental role in fields as diverse as supramolecular chemistry, structural biology, polymer science, nanotechnology, surface science, and condensed matter physics. It also underlies many properties of organic compounds and molecular solids, including their solubility in polar and non-polar media. If no other force is present, the distance between atoms at which the force becomes repulsive rather than attractive as the atoms approach one another is called the van der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Review
''Optical Review'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1994 and is published by Springer Science+Business Media in partnership with the Optical Society of Japan. The editor-in-chief is Masahiro Yamaguchi. The journal publishes research and review papers in all subdisciplines of optical science and optical engineering. Subdisciplines include general and physical optics, spectroscopy, quantum optics, optical computing, photonics, optoelectronics, lasers, nonlinear optics, environmental optics, adaptive optics, and space optics. Optics regarding the visible spectrum, infrared, and short wavelength optics are also included. Coverage encompasses required materials as well as suitable manufacturing tools, technologies, and methodologies. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and/or indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 0.890. See also * ''Applied Physics Express'' * ''Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The Physical Society Of Japan
''Journal of the Physical Society of Japan'' (''JPSJ'') is a monthly, peer-reviewed, scientific journal published by the Physical Society of Japan (JPS). It was first published in July 1946 (volume 1). The editor-in-chief was A. Kawabata until August 2010. The impact factor for ''JPSJ'' in 2017 is 1.485, according to Journal Citation Reports. Volume 1 consists of a single issue designated, on the cover, from July to December 1946. Between 1967 and 1980, this journal published at a rate of two volumes per year. The other (Japanese) title for this journal is ''Nihon Butsuri Gakkai ōji hōkoku''. Volumes for 1967 to the present day are accompanied by an annual supplement. Research paper formats include full papers, letters, short notes, comments, addenda, errata, invited papers and special topics. Organizational structure The organizational structure of the journal is described as follows: The ''Full Papers'', ''Letters'' and ''Short Notes'' sections of the journal comprise the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |