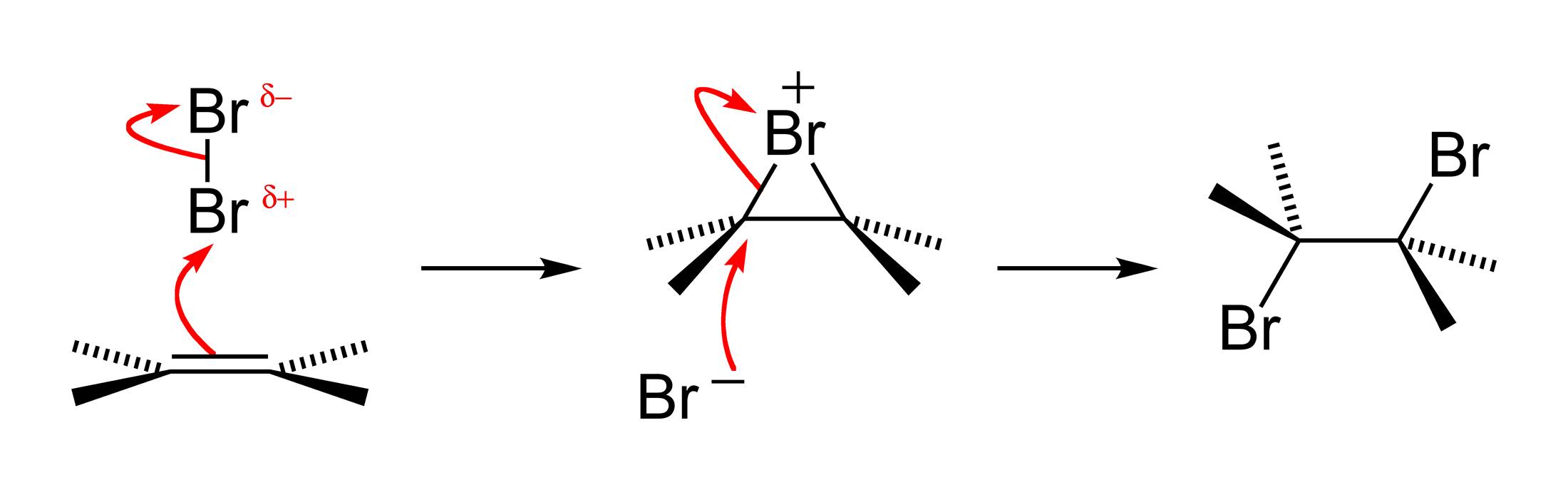|
Astatonium
A halonium ion is any onium ion containing a halogen atom carrying a positive charge. This cation has the general structure where X is any halogen and no restrictions on R, this structure can be cyclic or an open chain molecular structure. Halonium ions formed from fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine are called fluoronium, chloronium, bromonium, and iodonium, respectively. The 3-membered cyclic variety commonly proposed as intermediates in electrophilic halogenation may be called haliranium ions, using the Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature, Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature system. Structure The simplest halonium ions are of the structure (X = F, Cl, Br, I). Many halonium ions have a three-atom cyclic structure, similar to that of an epoxide, resulting from the formal addition of a halogenium ion to a C=C double bond, as when a halogen is added to an alkene. The formation of 5-membered halonium ions (e.g., chlorolanium, bromolanium ions) via Neighbouring group participation, neighb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onium Ion
In chemistry, an onium ion is a cation formally obtained by the protonation of mononuclear parent hydride of a pnictogen (group 15 of the periodic table), chalcogen (group 16), or halogen (group 17). The oldest-known onium ion, and the namesake for the class, is ammonium, , the protonated derivative of ammonia, . The name onium is also used for cations that would result from the substitution of hydrogen atoms in those ions by other groups, such as organic groups, or halogens; such as tetraphenylphosphonium, . The substituent groups may be divalent or trivalent, yielding ions such as iminium and nitrilium. A simple onium ion has a charge of +1. A larger ion that has two onium ion subgroups is called a double onium ion, and has a charge of +2. A triple onium ion has a charge of +3, and so on. Compounds of an onium cation and some other anion are known as onium compounds or onium salts. Onium ions and onium compounds are inversely analogous to ions and ate complexe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Halide
The monohalomethanes are organic compounds in which a hydrogen atom in methane is replaced by a halogen. They belong to the haloalkanes or to the subgroup of halomethanes. The four common members are fluoromethane, chloromethane, bromomethane and iodomethane. Historical name for this group is methyl halides; it's still widely used. The compounds of this class are often described as or MeX (X - any halogen, Me - methyl group). Related compounds There are analogs with more than one hydrogen atom in methane is replaced by a halogen: * Dihalomethane, , two hydrogen atoms replaced * Trihalomethane, , three hydrogen atoms replaced * Tetrahalomethane, , all four hydrogen atoms replaced Analogs with carbon atom replaced with a heavier group 14 element are also known: * Monohalosilane, (with silicon, related to silane) * Monohalogermane, (with germanium, related to germane) * Monohalostannane, (with tin, related to stannane) See also * Methyl halide transferase, an enzyme produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions ( cations) and negatively charged ions ( anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). The constituent ions are held together by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The component ions in a salt can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic, such as ammonium () and carbonate () ions in ammonium carbonate. Salts containing basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−) are classified as bases, such as sodium hydroxide and potassium oxide. Individual ions within a salt usually have multiple near neighbours, so they are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network. Salts usually form crystalline structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George A
George may refer to: Names * George (given name) * George (surname) People * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Papagheorghe, also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George, son of Andrew I of Hungary Places South Africa * George, South Africa, a city ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa, a city * George, Missouri, a ghost town * George, Washington, a city * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Computing * George (algebraic compiler) also known as 'Laning and Zierler system', an algebraic compiler by Laning and Zierler in 1952 * GEORGE (computer), early computer built by Argonne National Laboratory in 1957 * GEORGE (operating system), a range of operating systems (George 1–4) for the ICT 1900 range of computers in the 1960s * GEORGE (programming language), an autocode system invented by Charles Leonard Hamblin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionization Potential
In physics and chemistry, ionization energy (IE) is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated gaseous atom, positive ion, or molecule. The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as :X(g) + energy ⟶ X+(g) + e− where X is any atom or molecule, X+ is the resultant ion when the original atom was stripped of a single electron, and e− is the removed electron. Ionization energy is positive for neutral atoms, meaning that the ionization is an endothermic process. Roughly speaking, the closer the outermost electrons are to the nucleus of the atom, the higher the atom's ionization energy. In physics, ionization energy (IE) is usually expressed in electronvolts (eV) or joules (J). In chemistry, it is expressed as the energy to ionize a mole of atoms or molecules, usually as kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). Comparison of ionization energies of atoms in the periodic table reveals two period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelectronic
Isoelectronicity is a phenomenon observed when two or more molecules have the same structure (positions and connectivities among atoms) and the same electronic configurations, but differ by what specific elements are at certain locations in the structure. For example, , , and are isoelectronic, while and = are not. This definition is sometimes termed valence isoelectronicity. Definitions can sometimes be not as strict, sometimes requiring identity of the total electron count and with it the entire electronic configuration. More usually, definitions are broader, and may extend to allowing different numbers of atoms in the species being compared.A. A. Aradi & T. P. Fehlner, "Isoelectronic Organometallic Molecules", in F. G. A. Stone & Robert West (eds.) ''Advances in Organometallic Chemistry Vol. 30'' (1990), Chapter 5 (at p. 190google books link/ref> The importance of the concept lies in identifying significantly related species, as pairs or series. Isoelectronic specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syn And Anti Addition
In organic chemistry, syn- and anti-addition are different ways in which substituent molecules can be added to an alkene () or alkyne (). The concepts of syn and anti addition are used to characterize the different reactions of organic chemistry by reflecting the stereochemistry of the products in a reaction. The type of addition that occurs depends on multiple different factors of a reaction, and is defined by the final orientation of the substituents on the parent molecule. Syn and anti addition are related to Markovnikov's rule for the orientation of a reaction, which refers to the bonding preference of different substituents for different carbons on an alkene or alkyne. In order for a reaction to follow Markovnikov's rule, the intermediate carbocation of the mechanism of a reaction must be on the more-substituted carbon, allowing the substituent to bond to the more-stable carbocation and the more-substituted carbon. Syn addition is the addition of two substituents to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Bond
In chemistry, a single bond is a chemical bond between two atoms involving two valence electrons. That is, the atoms share one pair of electrons where the bond forms. Therefore, a single bond is a type of covalent bond. When shared, each of the two electrons involved is no longer in the sole possession of the Atomic orbital, orbital in which it originated. Rather, both of the two electrons spend time in either of the orbitals which overlap in the bonding process. As a Lewis structure, a single bond is denoted as AːA or A-A, for which A represents an element. In the first rendition, each dot represents a shared electron, and in the second rendition, the bar represents both of the electrons shared in the single bond. A covalent bond can also be a double bond or a triple bond. A single bond is weaker than either a double bond or a triple bond. This difference in strength can be explained by examining the component bonds of which each of these types of covalent bonds consists (Moo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halogen Addition Reaction
A halogen addition reaction is a simple organic reaction where a halogen molecule is added to the carbon–carbon double bond of an alkene functional group. The general chemical formula of the halogen addition reaction is: :C=C + X2 → X−C−C−X (X represents the halogens bromine or chlorine, and in this case, a solvent could be CH2Cl2 or CCl4). The product is a vicinal dihalide. This type of reaction is a halogenation and an electrophilic addition. Reaction mechanism The reaction mechanism for an alkene bromination can be described as follows. In the first step of the reaction, a bromine molecule approaches the electron-rich alkene carbon–carbon double bond. The bromine atom closer to the bond takes on a partial positive charge as its electrons are repelled by the electrons of the double bond. The atom is electrophilic at this time and is attacked by the pi electrons of the alkene arbon–carbon double bond It forms for an instant a single sigma bond to ''both' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diastereoselectivity
In stereochemistry, diastereomers (sometimes called diastereoisomers) are a type of stereoisomer. Diastereomers are defined as non-mirror image, non-identical stereoisomers. Hence, they occur when two or more stereoisomers of a compound have different configurations at one or more (but not all) of the equivalent (related) stereocenters and are not mirror images of each other. When two diastereoisomers differ from each other at only one stereocenter, they are epimers. Each stereocenter gives rise to two different configurations and thus typically increases the number of stereoisomers by a factor of two. Diastereomers differ from enantiomers in that the latter are pairs of stereoisomers that differ in all stereocenters and are therefore mirror images of one another. Enantiomers of a compound with more than one stereocenter are also diastereomers of the other stereoisomers of that compound that are not their mirror image (that is, excluding the opposing enantiomer). Diastereome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbocation
Carbocation is a general term for ions with a positively charged carbon atom. In the present-day definition given by the IUPAC, a carbocation is any even-electron cation with significant partial positive charge on a carbon atom. They are further classified in two main categories according to the coordination number of the charged carbon: three in the carbenium ions and five in the carbonium ions. Among the simplest carbocations are the methenium (a carbenium ion), methanium (a carbonium ion), acylium ions , and Vinyl cation, vinyl cations. Until the early 1970s, carbocations were called ''carbonium ions''. This nomenclature was proposed by George Andrew Olah, G. A. Olah. Carbonium ions, as originally defined by Olah, are characterized by a Three-center two-electron bond, three-center two-electron delocalized bonding scheme and are essentially synonymous with so-called 'non-classical carbocations', which are carbocations that contain bridging C–C or C–H σ-bonds. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |