|
Ashigaru
were peasant infantry employed by the warlords of Japan to supplement the samurai in their armies. The first known reference to ''ashigaru'' was in the 14th century, but it was during the Ashikaga shogunate (Muromachi period) that the use of ''ashigaru'' became prevalent by various warring factions.''War in the early modern world'' Jeremy Black, Taylor & Francis, 1999 p.59 Origins Attempts were made in Japan by (673–686) to have a conscripted national army, but this did not come about, and by the 10th century Japan instead relied on individual landowners to provide men for conflicts and wars. These horse-owning landowners were the beginnings of the ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samurai
The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court downsized the national army and delegated the security of the countryside to these privately trained warriors. Eventually the samurai clans grew so powerful that they became the ''de facto'' rulers of the country. In the aftermath of the Gempei War (1180-1185), Japan formally passed into military rule with the founding of the first shogunate. The status of samurai became heredity by the mid-eleventh century. By the start of the Edo period, the shogun had disbanded the warrior-monk orders and peasant conscript system, leaving the samurai as the only men in the country permitted to carry weapons at all times. Because the Edo period was a time of peace, many samurai neglected their warrior training and focused on peacetime activities such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yari
is the term for a traditionally-made Japanese blade (日本刀; nihontō) in the form of a spear, or more specifically, the straight-headed spear. The martial art of wielding the is called . History The forerunner of the is thought to be a derived from a Chinese spear. These are thought to be from the Nara period (710–794). The term appeared for the first time in written sources in 1334, but this type of spear did not become popular until the late 15th century. The original warfare of the was not a thing for commoners; it was a ritualized combat usually between two warriors who would challenge each other via horseback archery. In the late Heian period, battles on foot began to increase and , a bladed polearm, became a main weapon along with a ''yumi'' (longbow).Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
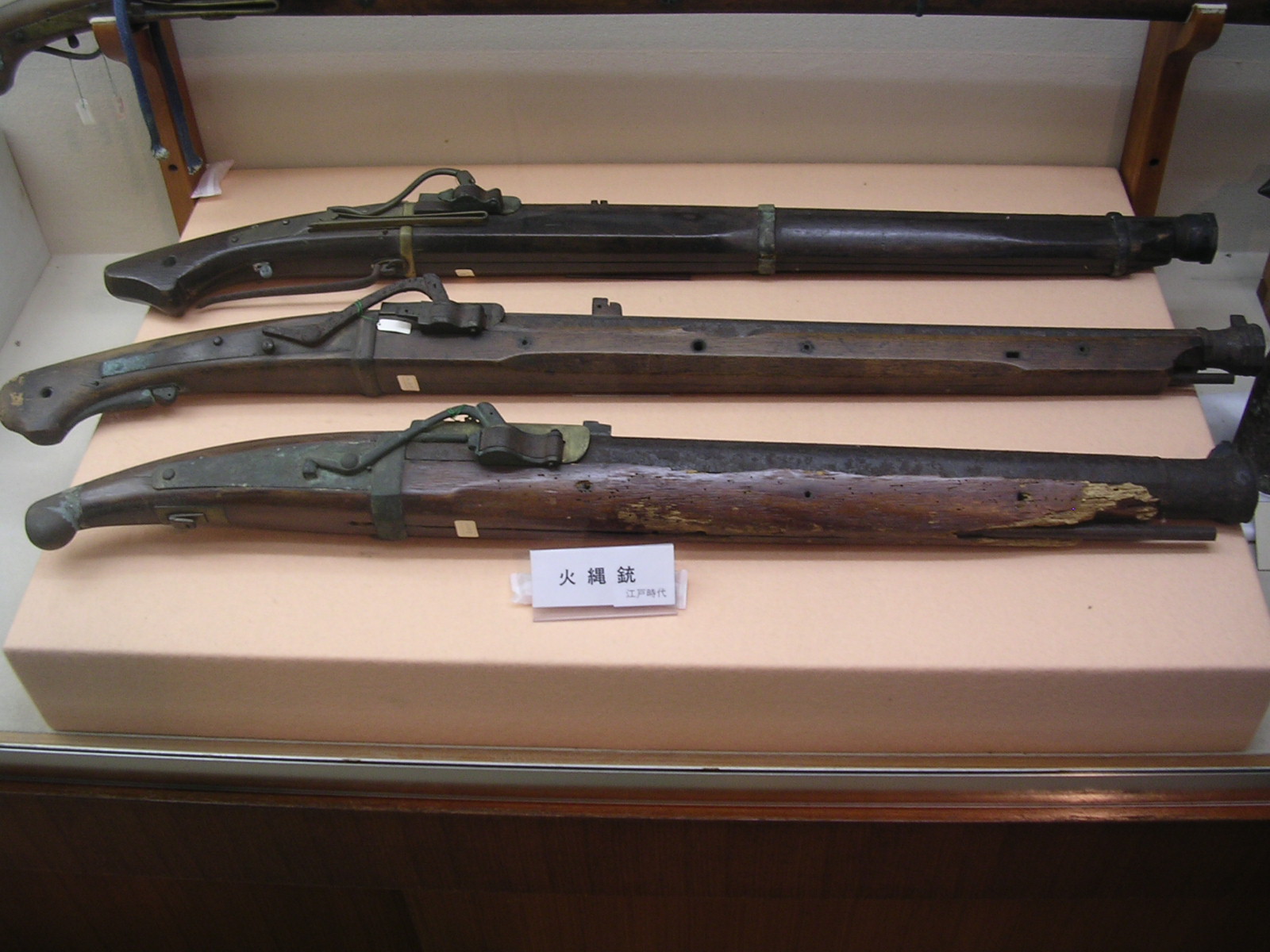
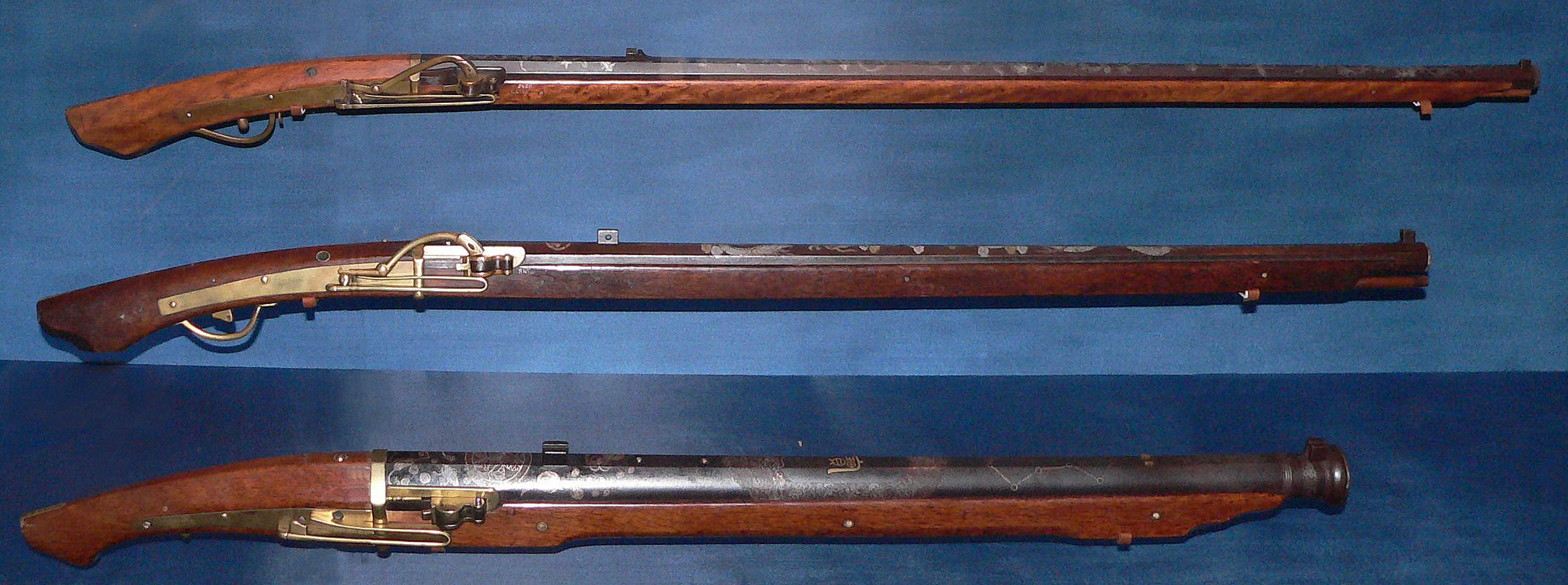
Tanegashima (gun)
, most often called in Japanese and sometimes in English , was a type of matchlock-configured arquebus firearm introduced to Japan through the Portuguese Empire in 1543. It was used by the samurai class and their "foot soldiers", and within a few years its introduction in battle changed the way war was fought in Japan forever. It, however, could not completely replace the (longbow). Although the Japanese developed various techniques to improve the gun's shortcomings, specifically its slow rate of fire and inability to fire in the rain, it remained inferior to the in these respects, and the latter continued to be an important weapon on the battlefield. After Tokugawa Ieyasu destroyed the Toyotomi clan in the siege of Osaka and established the Tokugawa shogunate, the relatively peaceful Edo period arrived, and the use of declined. History Origins The seems to have been based on snap matchlocks that were produced in the armory of Goa in Portuguese India, which was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katana
A is a Japanese sword characterized by a curved, single-edged blade with a circular or squared guard and long grip to accommodate two hands. Developed later than the ''tachi'', it was used by samurai in feudal Japan and worn with the edge facing upward. Since the Muromachi period, many old ''tachi'' were cut from the root and shortened, and the blade at the root was crushed and converted into a ''katana''. The specific term for ''katana'' in Japan is and the term ''katana'' (刀) often refers to single-edged swords from around the world. Etymology and loanwords The word ''katana'' first appears in Japanese in the ''Nihon Shoki'' of 720. The term is a compound of ''kata'' ("one side, one-sided") + ''na'' ("blade"),1995, (''w:Daijisen, Daijisen'') (in Japanese), w:Tōkyō, Tōkyō: w:Shogakukan, Shogakukan, , entry available onlinhere/span> in contrast to the double-sided ''Tsurugi (sword), tsurugi''. The ''katana'' belongs to the ''nihontō'' family of swords, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dō (armour)
is one of the major components of Japanese armour worn by the samurai and ashigaru or foot soldiers of feudal Japan. History The predecessor of the dō was manufactured in Japan as early as the fourth century. ''Tankō'', worn by foot soldiers, and ''keikō'', worn by horsemen, were both pre-samurai types of early Japanese ''cuirass'' constructed from iron plates connected by leather thongs. During the Heian period (794 to 1185), the cuirass evolved into the more familiar style of armour worn by the samurai known as the ''dō''. Japanese armourers started to use hardened leather along with iron in their construction methods, and lacquer was used to weather-proof the parts. By the end of the Heian period the Japanese cuirass had arrived at the shape recognized as being distinctly samurai. Leather and or iron scales were used to construct samurai armours, with leather and eventually silk lace used to connect the individual scales (''kozane'') which these cuirasses were now bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabuto
' (兜, 冑) is a type of helmet first used by ancient Japanese warriors that, in later periods, became an important part of the traditional Japanese armour worn by the samurai class and their retainers in History of Japan#Medieval Japan (1185–1573/1600), feudal Japan. Note that in the Japanese language, the word is an appellative, not a type description, and can refer to any combat helmet. Every year on Children's Day (Japan), Children's Day, May 5, Japanese households display miniature kabuto and samurai armor in keeping with the tradition of ''Tango no Sekku''. In feudal times, real samurai armor, ''kabuto'', and ''tachi'' were displayed. History Japanese helmets dating from the fifth century have been found in excavated tombs. Called (attached-visor helmet), the style of these kabuto came from China and Korea. They had a pronounced central ridge. , now known as samurai helmets, first appeared in the 10th century Heian period with the appearance of ''ō-yoroi''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Course of History, Viking Press 1988. p. 68. Although he came from a peasant background, his immense power earned him the rank and title of and , the highest official position and title in the nobility class. He was the first person in history to become a ''Kampaku'' who was not born a noble. He then passed the position and title of ''Kampaku'' to his nephew, Toyotomi Hidetsugu. He remained in power as , the title of retired ''Kampaku'', until his death. It is believed, but not certain, that the reason he refused or could not obtain the title of , the leader of the warrior class, was because he was of peasant origin. Hideyoshi rose from a peasant background as a Affinity (medieval), retainer of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sengoku Period
The was the period in History of Japan, Japanese history in which civil wars and social upheavals took place almost continuously in the 15th and 16th centuries. The Kyōtoku incident (1454), Ōnin War (1467), or (1493) are generally chosen as the period's start date, but there are many competing historiographies for its end date, ranging from 1568, the date of Oda Nobunaga#Ise campaign, Omi campaign, and march to Kyoto, Oda Nobunaga's march on Kyoto, to the suppression of the Shimabara Rebellion in 1638, deep into what was traditionally considered the Edo period. Regardless of the dates chosen, the Sengoku period overlaps substantially with the Muromachi period (1336–1573). This period was characterized by the overthrow of a superior power by a subordinate one. The Ashikaga shogunate, the ''de facto'' central government, declined and the , a local power, seized wider political influence. The people rebelled against the feudal lords in revolts known as . The period saw a break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatami (Japanese Armour)
''Tatami'' (畳具足), or ''tatami gusoku'' (from 畳む ''tatamu'', "to fold", and ''gusoku'', "full suit of armour"), was a type of lightweight portable folding Japanese armour worn during the feudal era of Japan by the samurai class and their foot soldiers ( ashigaru). The ''Tatami dō'' (a foldable cuirass) or the ''tatami katabira'' (an armoured jacket) were the main components of a full suit of tatami armour. Structure A '' tatami gusoku'' (complete suit of folding armor) includes a ''tatami dō'' or '' tatami katabira'' (jacket) and a ''tatami kabuto'' (helmet) '' chochin kabuto'', or '' tatami zukin'' (hood) or similar type of head protection along with the other related parts of a full suit of Japanese armour. Collapsible head protection such as '' hachi gane'' and other collapsible armor are also ''tatami'' armor; a traditional kabuto could also be part of a tatami gusoku. Tatami armour was lightweight, portable, convenient for transportation, and they were ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sashimono
''Sashimono'' (, , ) were small banners historically worn by soldiers in feudal Japan, for identification during battles. Description Sashimono poles were attached to the backs of the dō "cuirass" by special fittings. Sashimono were worn both by foot soldiers, including the common soldiers known as '' ashigaru'', as well as by the elite samurai and members of the shogunate, and in special holders on the horses of some cavalry. The banners, resembling small flags and bearing clan symbols, were most prominent during the Sengoku period, a long period of civil war in Japan from the middle 15th to early 17th century. Variety Given the great variety in Japanese armour, sashimono were used to provide a kind of "uniform" to armies. Sashimono typically came in either square or short rectangular forms, although many variations existed. A variation that is often bigger and coloured is the '' uma-jirushi'', which were large, personalized, sashimono-like flags worn by commanders. Simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yumi
is the Japanese term for a bow. As used in English, refers more specifically to traditional Japanese asymmetrical bows, and includes the longer and the shorter used in the practice of and , or Japanese archery. The was an important weapon of the samurai warrior during the feudal period of Japan. It is typically shot with Japanese arrows known as . The most famous style of is an asymmetrically shaped long bow with a length of more than , characterized by the archer holding the part of the bow below the center to shoot the arrow. History Most of the excavated Jōmon period () bows are in length, while most of the Yayoi period () bows are in length. The bows in these periods were made from a single processed wood, and the bows with this structure were called and were used until the Nara period (710–794 CE). It is unknown when the asymmetrical came into use, but the first written record is found in the ''Book of Wei'', a Chinese historical manuscript dating to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matchlock
A matchlock or firelock is a historical type of firearm wherein the gunpowder is ignited by a burning piece of flammable cord or twine that is in contact with the gunpowder through a mechanism that the musketeer activates by pulling a lever or Trigger (firearms), trigger with their finger. This firing mechanism was an improvement over the hand cannon, which lacked a trigger and required the musketeer or an assistant to apply a match directly to the gunpowder by hand. The matchlock mechanism allowed the musketeer to apply the match himself without losing his concentration. Description The classic matchlock gun held a burning slow match in a clamp at the end of a small curved lever known as the ''serpentine''. Upon the pull of a lever (or in later models a trigger) protruding from the bottom of the gun and connected to the serpentine, the clamp dropped down, lowering the smoldering match into the flash pan and igniting the priming powder. The flash from the primer traveled throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |