|
Artiodactyls
Artiodactyls are placental mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla ( , ). Typically, they are ungulates which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes (the third and fourth, often in the form of a hoof). The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, most perissodactyls bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two orders is that many artiodactyls (except for Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine (as perissodactyls do). Molecular biology, along with new fossil discoveries, has found that cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) fall within this taxonomic branch, being most closely related to hippopotamuses. Some modern taxonomists thus apply the name Cetartiodactyla () to this group, while others opt to include cetaceans within the existing name of Artiodactyla. Some researchers use "even-toed ungulates" to excl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined to be a polyphyletic and thereby invalid clade based on molecular data. As a result, true ungulates had since been reclassified to the newer clade Euungulata in 2001 within the clade Laurasiatheria while Paenungulata has been reclassified to a distant clade Afrotheria. Living ungulates are divided into two orders: Perissodactyla including Equidae, equines, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and Artiodactyla including Bos, cattle, antelope, Sus (genus), pigs, giraffes, camels, Ovis, sheep, deer, and Hippopotamidae, hippopotamuses, among others. Cetaceans such as Whale, whales, Dolphin, dolphins, and Porpoise, porpoises are also classified as artiodactyls, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perissodactyl
Perissodactyla (, ), or odd-toed ungulates, is an order of Ungulate, ungulates. The order includes about 17 living species divided into three Family (biology), families: Equidae (wild horse, horses, Asinus, asses, and zebras), Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceroses), and Tapiridae (tapirs). They typically have reduced the weight-bearing toes to three or one of the five original toes, though tapirs retain four toes on their front feet. The nonweight-bearing toes are either present, absent, Vestigiality, vestigial, or positioned posteriorly. By contrast, Artiodactyl, artiodactyls (even-toed ungulates) bear most of their weight equally on four or two (an even number) of the five toes: their third and fourth toes. Another difference between the two is that perissodactyls digest plant cellulose in their intestines, rather than in one or more stomach chambers as artiodactyls, with the exception of Suina, do. The order was considerably more diverse in the past, with notable extinct groups inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully Aquatic animal, aquatic placental mammal, placental marine mammals. As an informal and Colloquialism, colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and porpoises. Dolphins and porpoises may be considered whales from a formal, Cladistics, cladistic perspective. Whales, dolphins and porpoises belong to the order Cetartiodactyla, which consists of even-toed ungulates. Their closest non-cetacean living relatives are the hippopotamuses, from which they and other cetaceans diverged about 54 million years ago. The two parvorders of whales, baleen whales (Mysticeti) and toothed whales (Odontoceti), are thought to have had their Most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor around 34 million years ago. Mysticetes include four Neontology, extant (living) Family (biology), families: Balaenopteridae (the rorquals), Balaenidae (right whales), Cetotheriid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel themselves through the water with powerful up-and-down movements of their tail, which ends in a paddle-like fluke, using their flipper-shaped forelimbs to steer. While the majority of cetaceans live in marine environments, a small number reside solely in brackish water, brackish or fresh water. Having a cosmopolitan distribution, they can be found in some rivers and all of Earth's oceans, and many species migrate throughout vast ranges with the changing of the seasons. Cetaceans are famous for cetacean intelligence, their high intelligence, complex social behaviour, and the enormous size of some of the group's members. For example, the blue whale reaches a maximum confirmed length of and a weight of 173 tonne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whippomorpha
Whippomorpha or Cetancodonta is a suborder of artiodactyls that contains all living cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) and the hippopotamids. This makes it a crown group. Whippomorpha is a suborder within the order Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates). The placement of Whippomorpha within Artiodactyla is a matter of some contention, as hippopotamuses were previously considered to be more closely related to Suidae (pigs) and Tayassuidae (peccaries). Most contemporary scientific phylogenetic and morphological research studies link hippopotamuses with cetaceans, and genetic evidence has overwhelmingly supported an evolutionary relationship between Hippopotamidae and Cetacea. Modern whippomorphs all share a number of behavioural and physiological traits, such as a dense layer of subcutaneous fat and largely hairless bodies. They exhibit amphibious and aquatic behaviors and possess similar auditory structures. Whippomorpha is a subgroup of Cetancodontamorpha, which also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
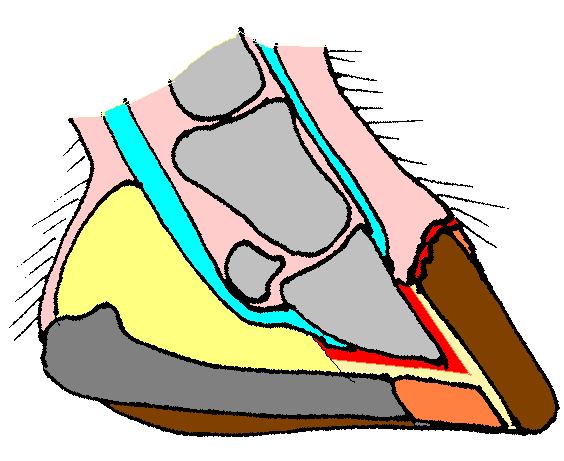
Hoof
The hoof (: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits; the ruminants with two digits are the most numerous, e.g. giraffe, deer, bison, cattle, goats, gazelles, pigs, and sheep. The feet of perissodactyl mammals have an odd number of toes, e.g. the horse, the rhinoceros, and the tapir. Although hooves are limb structures primarily found in placental mammals, hadrosaurs such as '' Edmontosaurus'' possessed hoofed forelimbs. The marsupial '' Chaeropus'' also had hooves. Description The hoof surrounds the distal end of the second phalanx, the distal phalanx, and the navicular bone. The hoof consists of the hoof wall, the bars of the hoof, the sole and frog and soft tissue shock absorption structures. The weight of the animal is normally borne by both the sole and the edge of the hoof wall. Hooves perform man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placental Mammal
Placental mammals ( infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished from monotremes and marsupials in that the fetus is carried in the uterus of its mother to a relatively late stage of development. The name is something of a misnomer, considering that marsupials also nourish their fetuses via a placenta, though for a relatively briefer period, giving birth to less-developed young, which are then nurtured for a period inside the mother's pouch. Placentalia represents the only living group within Eutheria, which contains all mammals that are more closely related to placentals than they are to marsupials. Anatomical features Placental mammals are anatomically distinguished from other mammals by: * a sufficiently wide opening at the bottom of the pelvis to allow the birth of a large baby relative to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancodonta
Ancodonta is an infraorder of artiodactyl ungulates including modern hippopotamus and all mammals closer to hippos than to cetaceans (whales). Ancodonts first appeared in the Middle Eocene, with some of the earliest representatives found in fossil deposits in Southeast Asia. Throughout their evolutionary history they have occupied different browsing and grazing niches in North America, Eurasia and Africa. The last continent is notable as they were among the first laurasiatherian mammals to have migrated to Africa from Europe, where they competed with the native Afrotheria, afrothere herbivores for the same niches. Of the nearly 50 genera that have existed, only two of them are extant – ''Choeropsis'' and ''Hippopotamus (genus), Hippopotamus''. The interrelationships within the ancodonts has been contended. The traditional notion is that there at minimum two families Anthracotheriidae and Hippopotamidae and were merely sister taxa. However many detailed research of the dentition a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruminantia
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again". The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiofabula
Artiofabula is a clade made up of the Suina and the Cetruminantia. The clade was found in molecular phylogenetic analyses and contradicted traditional relationships based on morphological analyses. Etymology The name Artiofabula was derived from Greek "artios" (meaning complete or perfect of its kind or, with respect to numbers, even), and Latin "fabula" (meaning fable). The latter referred to the clade breaking up traditional views on artiodactyl taxonomy based on morphological analyses, where camels grouped with ruminants, hippos with pigs, and whales were unrelated. Phylogeny Phylogenetic analyses of artiodactyls revealed the following relationships:(see e.g. Fig S10) Classification *Order Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates) **Suborder Tylopoda (camelids) **Artiofabula (ruminants, pigs, peccaries, whales, and dolphins) ***Suborder Suina (pigs and peccaries) **** Family Suidae 19 species (pigs) **** Family Tayassuidae 4 species (peccaries) *** Cetruminantia (ruminants, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetruminantia
The Cetruminantia are a clade made up of the Cetancodontamorpha (or Whippomorpha) and their closest living relatives, the Ruminantia. Cetruminantia's placement within Artiodactyla can be represented in the following cladogram: (see fig S10) Classification *Order Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates) ** Tylopoda (camelids) ** Artiofabula ( ruminants, pigs, peccaries, whales, and dolphins) ***Suina (pigs and peccaries) ***Cetruminantia ( ruminants, whales, and dolphins) ****Suborder Ruminantia (antelope, buffalo, cattle, goats, sheep, deer, giraffes, and chevrotains) *****Family Antilocapridae (pronghorn) *****Family Bovidae, 135 species (antelope, bison, buffalo, cattle, goats, and sheep) *****Family Cervidae, 55~94 species ( deer, elk, and moose) *****Family Giraffidae, 2 species ( giraffes, okapis) *****Family Moschidae, 4~7 species (musk deer) *****Family Tragulidae, 6~10 species (chevrotains, or mouse deer) ****Suborder Whippom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore ( osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |