|
Argr
(noun) and (adjective) are two Old Norse terms of insult, denoting effeminacy or other unmanly behaviour. ' (also ') is "unmanly" and ''ergi'' is "unmanliness"; the terms have cognates in other Germanic languages such as ', ', ''arag'', ''arug'', and so on. ''Ergi'' in the Viking Age To accuse another man of being ' was called ''scolding'' (see ') and thus a legal reason to challenge the accuser in holmgang. If holmgang was refused by the accused, he could be outlawed (full outlawry) as this refusal proved that the accuser was right and the accused was '. If the accused fought successfully in ''holmgang'' and had thus proven that he was not ', the ''scolding'' was considered what was in Old English called ', an unjustified, severe defamation, and the accuser had to pay the offended party full compensation. The Gray Goose Laws states: The practice of ' or "sorcery" was considered ' in the Viking Age and in Icelandic accounts and medieval Scandinavian laws, the term ' had conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nīþ
In historical Germanic society, ( non, níð ang, nīþ, nīð; odt, nīth); was a term for a social stigma implying the loss of honour and the status of a villain. A person affected with the stigma is a ( non, níðingr/, ang, nīðing, nīðgæst, or goh, nidding). Middle English retained a cognate , meaning 'envy' (compare modern Dutch and modern German ), 'hate', or 'malice'. A related term is , carrying the connotation of 'unmanliness'. Níð, argr, ragr and ergi ''Ergi'' and ''argr'' or ''ragr'' can be regarded as specifying swearwords. ''Ergi'', ''argr'' and ''ragr'' were the severe insults made by calling someone a ''coward'', and due to its severity old Scandinavian laws demanded retribution for this accusation if it had turned out unjustified. The Icelandic Gray Goose Laws referred to three words that were regarded as equal to ''argr'' by themselves. Those were ''ragr'', ''strodinn'', and ''sordinn'', all three meaning the passive role of a man in sexual activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their Viking expansion, overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 7th to the 15th centuries. The Proto-Norse language developed into Old Norse by the 8th century, and Old Norse began to develop into the modern North Germanic languages in the mid-to-late 14th century, ending the language phase known as Old Norse. These dates, however, are not absolute, since written Old Norse is found well into the 15th century. Old Norse was divided into three dialects: Old West Norse, ''Old West Norse'' or ''Old West Nordic'' (often referred to as ''Old Norse''), Old East Norse, ''Old East Norse'' or ''Old East Nordic'', and ''Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Language
Swedish ( ) is a North Germanic language spoken predominantly in Sweden and in parts of Finland. It has at least 10 million native speakers, the fourth most spoken Germanic language and the first among any other of its type in the Nordic countries overall. Swedish, like the other Nordic languages, is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Era. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish, although the degree of mutual intelligibility is largely dependent on the dialect and accent of the speaker. Written Norwegian and Danish are usually more easily understood by Swedish speakers than the spoken languages, due to the differences in tone, accent, and intonation. Standard Swedish, spoken by most Swedes, is the national language that evolved from the Central Swedish dialects in the 19th century and was well established by the beginning of the 20th century. While distinct regional v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian Language
Estonian ( ) is a Finnic language, written in the Latin script. It is the official language of Estonia and one of the official languages of the European Union, spoken natively by about 1.1 million people; 922,000 people in Estonia and 160,000 outside Estonia. Classification Estonian belongs to the Finnic branch of the Uralic language family. The Finnic languages also include Finnish and a few minority languages spoken around the Baltic Sea and in northwestern Russia. Estonian is subclassified as a Southern Finnic language and it is the second-most-spoken language among all the Finnic languages. Alongside Finnish, Hungarian and Maltese, Estonian is one of the four official languages of the European Union that are not of an Indo-European origin. From the typological point of view, Estonian is a predominantly agglutinative language. The loss of word-final sounds is extensive, and this has made its inflectional morphology markedly more fusional, especially with respec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
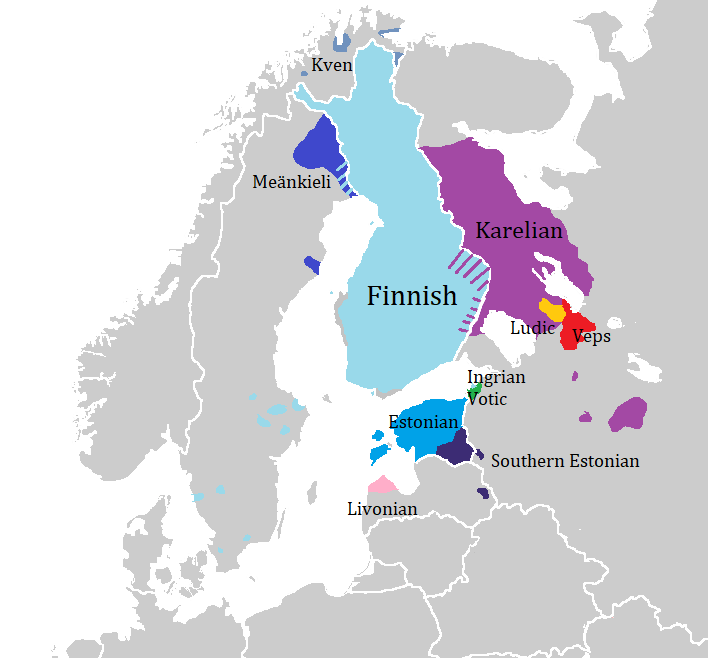
Finnic Languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at Encyclopædia Britannica The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian and |
Austrian German
Austrian German (german: Österreichisches Deutsch), Austrian Standard German (ASG), Standard Austrian German (), or Austrian High German (), is the variety of Standard German written and spoken in Austria. It has the highest sociolinguistic prestige locally, as it is the variation used in the media and for other formal situations. In less formal situations, Austrians use Bavarian and Alemannic dialects, which are traditionally spoken but rarely written in Austria. History Austria German has its beginning in the mid-18th century, when Empress Maria Theresa and her son Joseph II introduced compulsory schooling in 1774, and several reforms of administration in their multilingual Habsburg Empire. At the time, the written standard was ''Oberdeutsche Schreibsprache'' ( Upper German written language), which was highly influenced by the Bavarian and Alemannic dialects of Austria. Another option was to create a new standard based on the Southern German dialects, as proposed by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle ''to'', is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected (modified in form) to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. A verb may also agree with the person, gender or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject, or object. Verbs have tenses: present, to indicate that an action is being carried out; past, to indicate that an action has been done; future, to indicate that an action will be done. For some examples: * I ''washed'' the car yesterday. * The dog ''ate'' my homework. * John ''studies'' English and French. * Lucy ''enjoys'' listening to music. *Barack Obama ''became'' the President of the United States in 2009. ''(occurrence)'' *Mike Trout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjective
In linguistics, an adjective ( abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun. Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the main parts of speech of the English language, although historically they were classed together with nouns. Nowadays, certain words that usually had been classified as adjectives, including ''the'', ''this'', ''my'', etc., typically are classed separately, as determiners. Here are some examples: * That's a funny idea. ( attributive) * That idea is funny. ( predicative) * * The good, the bad, and the funny. (substantive) Etymology ''Adjective'' comes from Latin ', a calque of grc, ἐπίθετον ὄνομα, epítheton ónoma, additional noun (whence also English ''epithet''). In the grammatical tradition of Latin and Greek, because adjectives were inflected for gender, number, and case like nouns (a process called declension), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroese Language
Faroese ( ; ''føroyskt mál'' ) is a North Germanic language spoken as a first language by about 72,000 Faroe Islanders, around 53,000 of whom reside on the Faroe Islands and 23,000 in other areas, mainly Denmark. It is one of five languages descended from Old West Norse spoken in the Middle Ages, the others being Norwegian, Icelandic, and the extinct Norn and Greenlandic Norse. Faroese and Icelandic, its closest extant relative, are not mutually intelligible in speech, but the written languages resemble each other quite closely, largely owing to Faroese's etymological orthography. History Around 900 AD, the language spoken in the Faroes was Old Norse, which Norse settlers had brought with them during the time of the settlement of Faroe Islands () that began in 825. However, many of the settlers were not from Scandinavia, but descendants of Norse settlers in the Irish Sea region. In addition, women from Norse Ireland, Orkney, or Shetland often married native Scandinavian men ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. '' Afrikaans'' is a separate but somewhat mutually intelligible daughter languageAfrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans was historically called Cape Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans is rooted in 17th-century dialects of Dutch; see , , , . Afrikaans is variously described as a creole, a partially creolised language, or a deviant variety of Dutch; see . spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, evolving from the Cape Dutch dialects of Southern Africa. The dialects used in Belgium (including Flemish) and in Suriname, meanwhile, are all guided by the Dutch Language Union. In Europe, most of the population of the Netherlands (where it is the only official language sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German ( ) is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France ( Bas-Rhin), Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Poland ( Upper Silesia), Slovakia (Bratislava Region), and Hungary ( Sopron). German is most similar to other languages within the West Germanic language branch, including Afrikaans, Dutch, English, the Frisian languages, Low German, Luxembourgish, Scots, and Yiddish. It also contains close similarities in vocabulary to some languages in the North Germanic group, such as Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish. German is the second most widely spoken Germanic language after English, which is also a West Germanic language. German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphological Derivation
Morphological derivation, in linguistics, is the process of forming a new word from an existing word, often by adding a prefix or suffix, such as For example, ''unhappy'' and ''happiness'' derive from the root word ''happy.'' It is differentiated from inflection, which is the modification of a word to form different grammatical categories without changing its core meaning: ''determines'', ''determining'', and ''determined'' are from the root ''determine''. Derivational patterns Derivational morphology often involves the addition of a derivational suffix or other affix. Such an affix usually applies to words of one lexical category (part of speech) and changes them into words of another such category. For example, one effect of the English derivational suffix ''-ly'' is to change an adjective into an adverb (''slow'' → ''slowly''). Here are examples of English derivational patterns and their suffixes: * adjective-to-noun: ''-ness'' (''slow'' → ''slowness'') * adjective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |