|
Archaeal Lipid
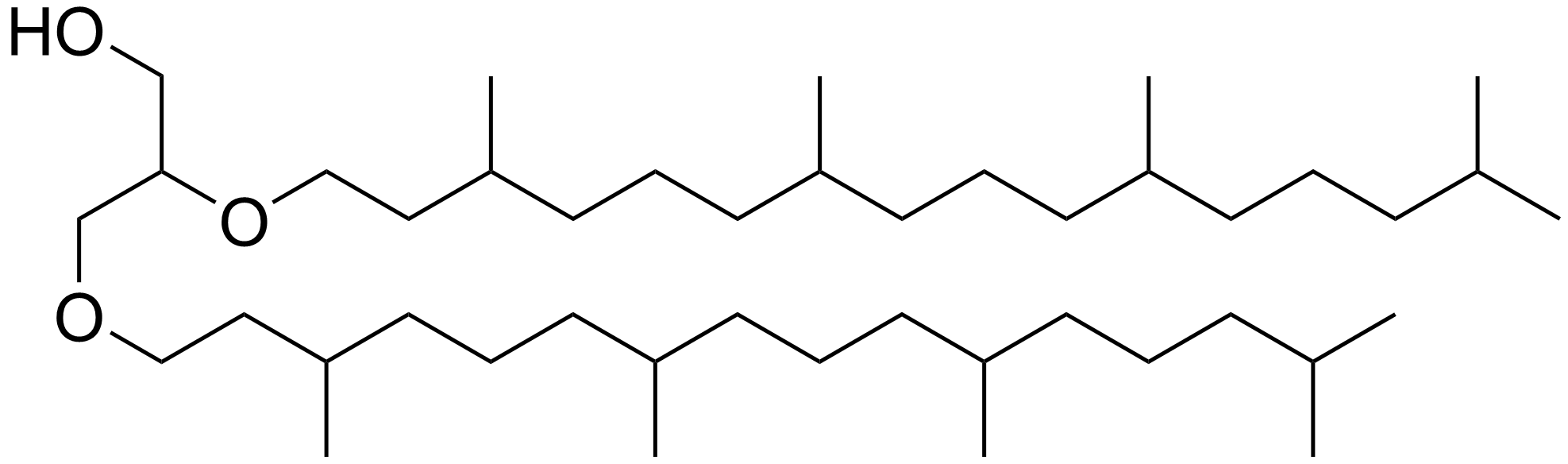
Archaeol is a diether composed of two phytanyl chains linked to the sn-2 and sn-3 positions of glycerol. As its phosphate ester, it is a common component of the membranes of archaea. Structure and contrast with other lipids The 2,3-sn-glycerol structure and ether bond linkage are two key differences between lipids found in archaea vs those of bacteria and eukarya. The latter use 1,2-sn-glycerol, and mostly, ester bonds. Natural archaeol has 3R, 7R, 11R configurations for the three chiral centers in the isoprenoid chains. There are four structural variations, contributing to the complexity of the membrane lipids in function and properties. The two phytanyl chains can form a 36-member ring to yield macrocyclic archaeol. Hydroxylated archaeol has phytanyl chains hydroxylated at the first tertiary carbon atom, while sesterterpanyl archaeol have the phytanyl side chains with C25 sesterterpanyl chains, substituting at C2 of glycerol or at both carbons. Unsaturated archaeol, with the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytane
Phytane is the Diterpenoid, isoprenoid alkane formed when phytol, a chemical substituent of chlorophyll, loses its Hydroxy group, hydroxyl group. When phytol loses one carbon atom, it yields pristane. Other sources of phytane and pristane have also been proposed than phytol. Pristane and phytane are common constituents in petroleum and have been used as Proxy (climate), proxies for Deposition (geology), depositional redox conditions, as well as for correlating oil and its source rock (i.e. elucidating where oil formed). In environmental studies, pristane and phytane are target compounds for investigating oil spills. Chemistry Phytane is a Chemical polarity, non-polar organic compound that is a clear and colorless liquid at room temperature. It is a wikibooks:Structural Biochemistry/Lipids/Isoprenoids#Structural Features and Some Isoprenoid Compounds, head-to-tail linked regular Terpenoid, isoprenoid with chemical formula C20H42. Phytane has List of straight-chain alkanes, many S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
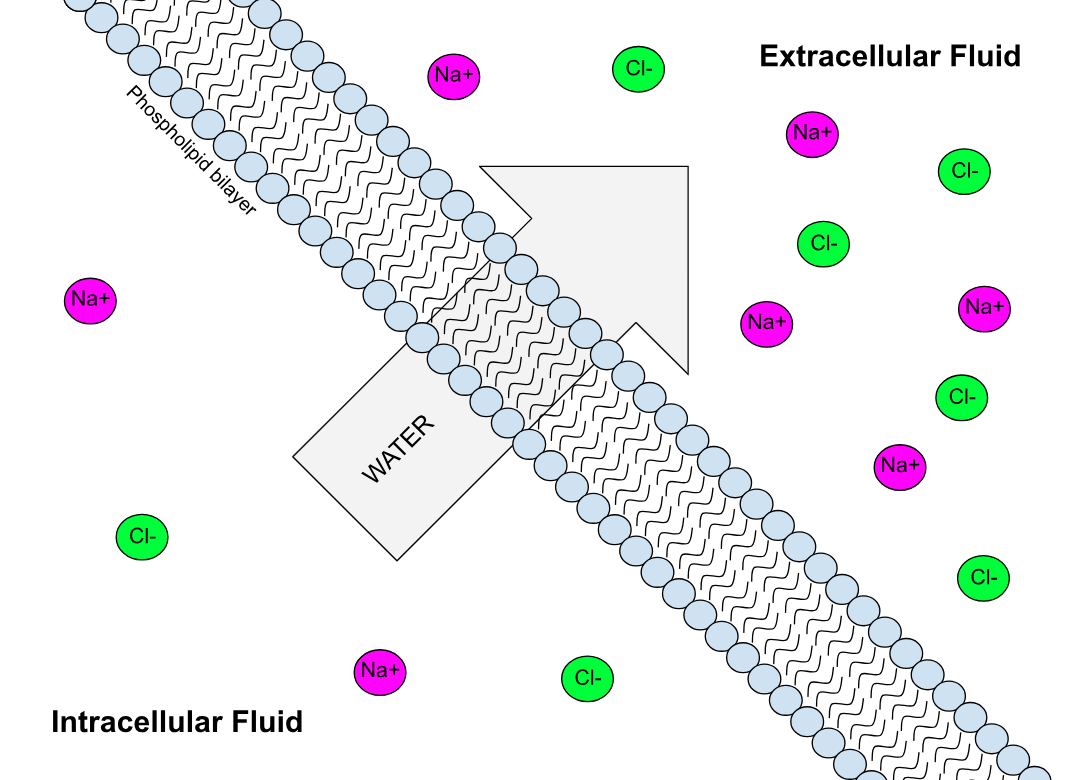
Semipermeable Membrane
Semipermeable membrane is a type of synthetic or biologic, polymeric membrane that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through it by osmosis. The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the molecules or solutes on either side, as well as the permeability of the membrane to each solute. Depending on the membrane and the solute, permeability may depend on solute size, solubility, properties, or chemistry. How the membrane is constructed to be selective in its permeability will determine the rate and the permeability. Many natural and synthetic materials which are rather thick are also semipermeable. One example of this is the thin film on the inside of an egg. Biological membranes are selectively permeable, with the passage of molecules controlled by facilitated diffusion, passive transport or active transport regulated by proteins embedded in the membrane. Biological membranes Phospholipid bilayer A phospholipid bilayer is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesophile
A mesophile is an organism that grows best in moderate temperature, neither too hot nor too cold, with an optimum growth range from . The optimum growth temperature for these organisms is 37 °C (about 99 °F). The term is mainly applied to microorganisms. Organisms that prefer extreme environments are known as extremophiles. Mesophiles have diverse classifications, belonging to two domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and to kingdom Fungi of domain Eucarya. Mesophiles belonging to the domain Bacteria can either be gram-positive or gram-negative. Oxygen requirements for mesophiles can be aerobic or anaerobic. There are three basic shapes of mesophiles: coccus, bacillus, and spiral. Habitat The habitats of mesophiles can include cheese and yogurt. They are often included during fermentation of beer and wine making. Since normal human body temperature is 37 °C, the majority of human pathogens are mesophiles, as are most of the organisms comprising the human microbiome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enol Ether
In organic chemistry an enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent. The general structure is R2C=CR-OR where R = H, alkyl or aryl. A common subfamily of enol ethers are vinyl ethers, with the formula ROCH=CH2. Important enol ethers include the reagent 3,4-dihydropyran and the monomers methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether. Reactions and uses Akin to enamines, enol ethers are electron-rich alkenes by virtue of the electron-donation from the heteroatom via pi-bonding. Enol ethers have oxonium ion character. By virtue of their bonding situation, enol ethers display distinctive reactivity. In comparison with simple alkenes, enol ethers exhibit enhanced susceptibility to attack by electrophiles such as Bronsted acids. Similarly, they undergo inverse demand Diels-Alder reactions. The reactivity of enol ethers is highly dependent on the presence of substituents alpha to oxygen. The vinyl ethers are susceptible to polymerization to give polyvinyl ethers. They also re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require oxygen, molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment. Anaerobes may be unicellular (e.g. protozoans, bacteria) or multicellular. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. However, some species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes; for these species, anaerobic respiration is used because oxygen will disrupt their metabolism or kill them. The sea floor is possibly one of the largest accumulation of anaerobic organisms on Earth, where microbes are primarily concentrated around Hydrothermal_vent, hydrothermal vents. These microbes produce energy in absence of sunlight or oxygen through a process called chemosynthesis, whereby inorganic compounds such as hydrogen gas, hydrogen sulfide or ferrous ions are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobic Organism
An aerobic organism or aerobe is an organism that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment. The ability to exhibit aerobic respiration may yield benefits to the aerobic organism, as aerobic respiration yields more energy than anaerobic respiration. Energy production of the cell involves the synthesis of ATP by an enzyme called ATP synthase. In aerobic respiration, ATP synthase is coupled with an electron transport chain in which oxygen acts as a terminal electron acceptor. In July 2020, marine biologists reported that aerobic microorganisms (mainly), in " quasi-suspended animation", were found in organically poor sediments, up to 101.5 million years old, 250 feet below the seafloor in the South Pacific Gyre (SPG) ("the deadest spot in the ocean"), and could be the longest-living life forms ever found. Types * Obligate aerobes need oxygen to grow. In a process known as cellular respiration, these organisms use oxygen to oxidize substrates (for example sugars and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
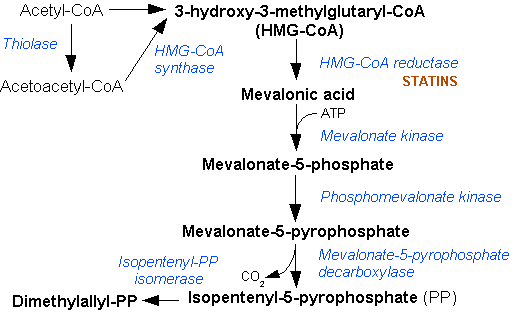
Mevalonic Acid Pathway
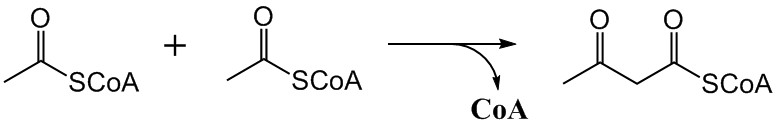
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones. The mevalonate pathway begins with acetyl-CoA and ends with the production of IPP and DMAPP. It is best known as the target of statins, a class of cholesterol lowering drugs. Statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase within the mevalonate pathway. Upper mevalonate pathway The mevalonate pathway of eukaryotes, archaea, and eubacteria all begin the same way. The sole carbon feed stock of the pathway is acetyl-CoA. The first step condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules to yield acetoacetyl-CoA. This is followed by a second condensation to form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP; or alternatively, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP); also isoprenyl pyrophosphate) is an isoprenoid precursor. It is a product of both the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and exists in virtually all life forms. The enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase catalyzes isomerization between DMAPP and IPP. In the mevalonate pathway, DMAPP is synthesised from mevalonic acid. In contrast, DMAPP is synthesised from HMBPP in the MEP pathway. At present, it is believed that there is crossover between the two pathways in organisms that use both pathways to create terpenes and terpenoid The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic compound, organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeabl ...s, such as in plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate, or IDP) is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway (commonly called the mevalonate pathway) and in the ''non-mevalonate'' MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. Isoprenoid precursors such as IPP, and its isomer Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, DMAPP, are used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. Biosynthesis IPP is formed from acetyl-CoA via the mevalonate pathway (the "upstream" part), and then is isomerized to dimethylallyl pyrophosphate by the enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase. IPP can be synthesised via an alternative non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis, the MEP pathway, where it is formed from (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate, (''E'')-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMB-PP) by the enzyme HMB-PP reductase (LytB, IspH). The MEP pathway is present in many bacteria, apicomplex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geranylgeranyl Pyrophosphate
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of diterpenes and diterpenoids. It is also the precursor to carotenoids, gibberellins, tocopherols, and chlorophylls. It is also a precursor to geranylgeranylated proteins, which is its primary use in human cells. It is formed from farnesyl pyrophosphate by the addition of an isoprene unit from isopentenyl pyrophosphate. In ''Drosophila'', geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is synthesised by HMG-CoA encoded by the Columbus gene. Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is utilised as a chemoattractant for migrating germ cells that have traversed the midgut epithelia. The attractant signal is produced at the gonadal precursors, directing the germ cells to these sites, where they will differentiate into eggs and spermatozoa (sperm). Related compounds * Farnesyl pyrophosphate * Geranylgeraniol Geranylgeraniol is a diterpenoid alcohol. It is a colorless waxy solid. It is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
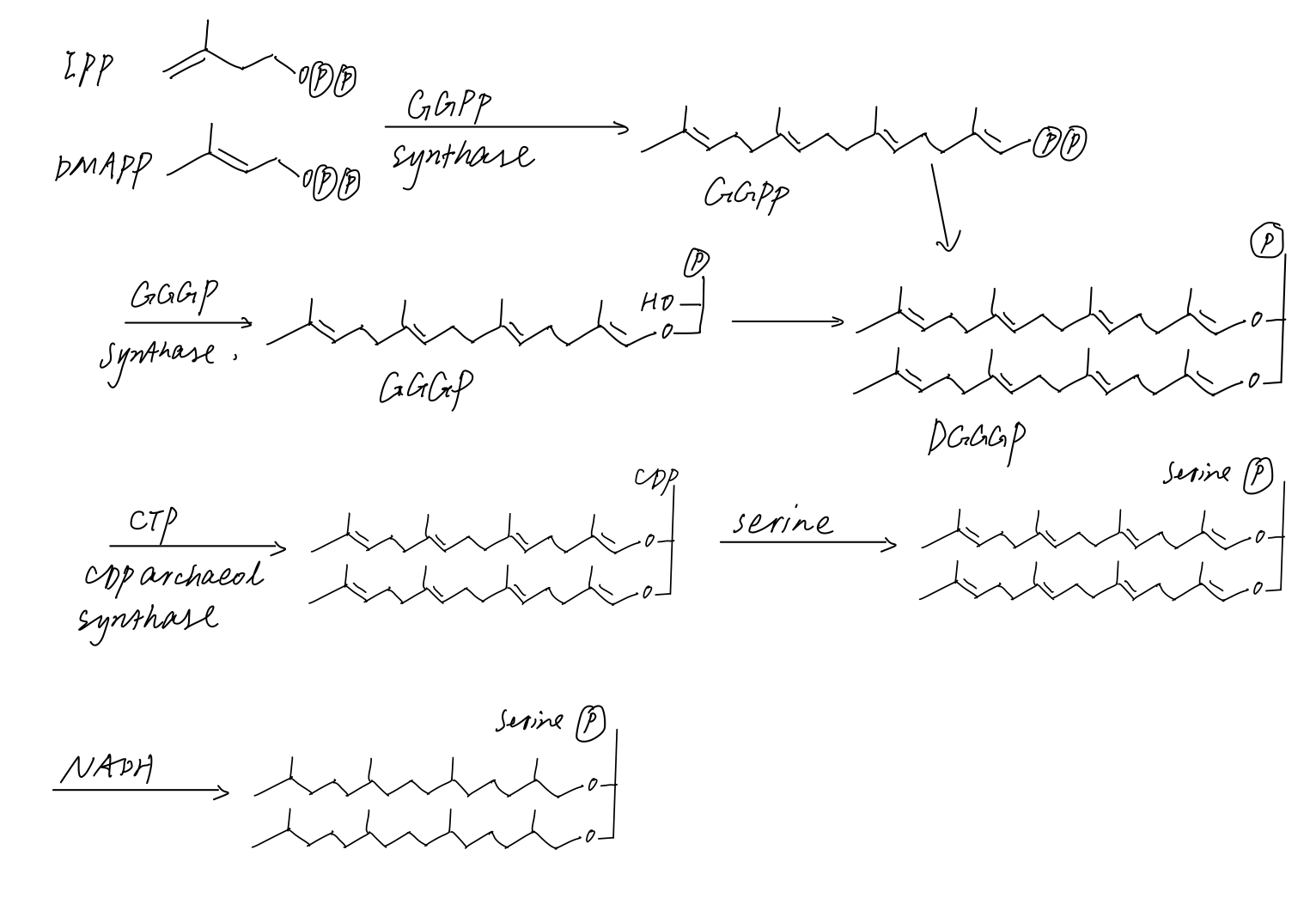
Glycerol 1-phosphate
''sn''-Glycerol 1-phosphate is the conjugate base of a phosphoric ester of glycerol. It is a component of ether lipids, which are common for archaea. Biosynthesis and metabolism Glycerol 1-phosphate is synthesized by reducing dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), a glycolysis intermediate, with sn-glycerol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase, ''sn''-glycerol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase. DHAP and thus glycerol 1-phosphate is also possible to be synthesized from amino acids and citric acid cycle intermediates via glyconeogenesis, gluconeogenesis pathway. : + NAD(P)H + H+ → + NAD(P)+ Glycerol 1-phosphate is a starting material for ''de novo'' synthesis of ether lipids, such as those derived from archaeol and caldarchaeol. It is first geranylgeranylated on its ''sn''-3 position by a cytosolic enzyme, phosphoglycerol geranylgeranyltransferase. A second geranylgeranyl group is then added on the ''sn''-2 position making unsaturated archaetidic acid. Lipid divide Organisms other than archaea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |