|
Arc Fault
An arc fault is a high power discharge of electricity between two or more conductors. This discharge generates heat, which can break down the wire's insulation and trigger an electrical fire. Arc faults can range in current from a few amps up to thousands of amps, and are highly variable in strength and duration. Some common causes of arc fault are loose wire connections, over heated wires, or wires pinched by furniture. Location and detection Two types of wiring protection are standard thermal breakers and arc fault circuit breakers. Thermal breakers require an overload condition long enough that a heating element in the breaker trips the breaker off. In contrast, arc fault circuit breakers use magnetic or other means to detect increases in current draw much more quickly. Without such protection, visually detecting arc faults in defective wiring is very difficult, as the arc fault occurs in a very small area. A problem with arc fault circuit breaker is they are more likely t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Ampere
The ampere ( , ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to 1 coulomb (C) moving past a point per second. It is named after French mathematician and physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836), considered the father of electromagnetism along with Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted. As of the 2019 revision of the SI, the ampere is defined by fixing the elementary charge to be exactly , which means an ampere is an electric current equivalent to elementary charges moving every seconds, or approximately elementary charges moving in a second. Prior to the redefinition, the ampere was defined as the current passing through two parallel wires 1 metre apart that produces a magnetic force of newtons per metre. The earlier CGS system has two units of current, one structured similarly to the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Arc-fault Circuit Interrupter
An arc-fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) or arc-fault detection device (AFDD) is a circuit breaker that breaks the circuit when it detects the electric arcs that are a signature of loose connections in home wiring. Loose connections, which can develop over time, can sometimes become hot enough to ignite house fires. An AFCI selectively distinguishes between a harmless arc (incidental to normal operation of switches, plugs, and brushed motors), and a potentially dangerous arc (that can occur, for example, in a lamp cord which has a broken conductor). In Canada and the United States, AFCI breakers have been required by the electrical codes for circuits feeding electrical outlets in residential bedrooms since the beginning of the 21st century; the US ''National Electrical Code'' has required them to protect most residential outlets since 2014, and the ''Canadian Electrical Code'' has since 2015. In regions using 230 V, the combination of higher voltage and lower load currents le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Time-domain Reflectometer
A time-domain reflectometer (TDR) is an electronic instrument used to determine the characteristics of electrical lines by observing reflected pulses. It can be used to characterize and locate faults in metallic cables (for example, twisted pair wire or coaxial cable), and to locate discontinuities in a connector, printed circuit board, or any other electrical path. Description A TDR measures reflections along a conductor. In order to measure those reflections, the TDR will transmit an incident signal onto the conductor and listen for its reflections. If the conductor is of a uniform impedance and is properly terminated, then there will be no reflections and the remaining incident signal will be absorbed at the far-end by the termination. Instead, if there are impedance variations, then some of the incident signal will be reflected back to the source. A TDR is similar in principle to radar. The impedance of the discontinuity can be determined from the amplitude of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cynthia Furse
Cynthia M. Furse (née Mahoney, born 1963) is an American electrical engineer, the director of graduate studies and a distinguished professor in the University of Utah Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Her research involves the use of finite-difference time-domain methods in computational simulations of the absorption and reflection of radio waves by other materials, with applications including the use of spread-spectrum time-domain reflectometry to diagnose aircraft wiring systems, the design of antennae in medical implants, and the effects of cell phone emissions on the human body. Her publications also include works on engineering education. Education and career Furse was born in 1963 in Hartford, Maine. After her father, food scientist Arthur W. Mahoney, took a professorship at Utah State University in 1969, she grew up in Logan, Utah. After beginning her studies in mechanical engineering, she became a student of electrical engineering at the University of Uta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Arc Flash
An arc flash is the light and heat produced as part of an arc fault (sometimes referred to as an electrical flashover), a type of electricity, electrical explosion or discharge that results from a connection through air to ground or another voltage phase in an electrical system. Arc flash is distinctly different from the arc blast, which is the supersonic shockwave produced when the uncontrolled arc vaporizes the metal conductors. Both are part of the same arc fault, and are often referred to as simply an arc flash, but from a safety standpoint they are often treated separately. For example, personal protective equipment (PPE) can be used to effectively shield a worker from the radiation of an arc flash, but that same PPE may likely be ineffective against the flying objects, molten metal, and violent concussion that the arc blast can produce. (For example, category-4 arc-flash protection, similar to a bomb suit, is unlikely to protect a person from the concussion of a very larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
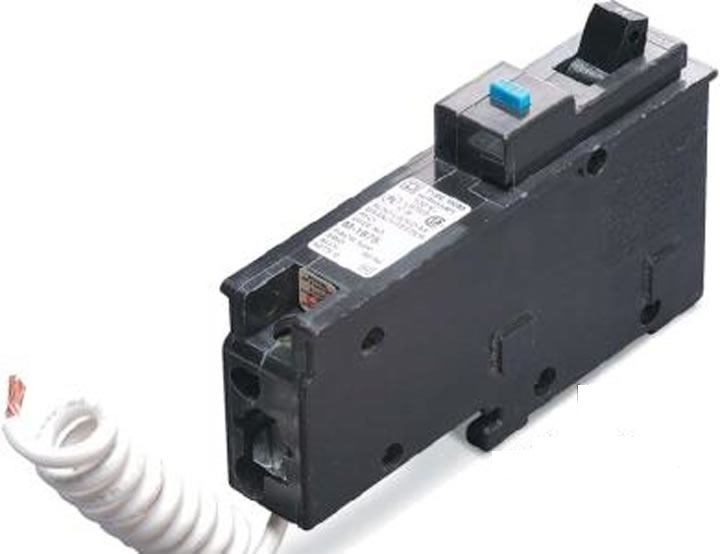 |
Arc-fault Circuit Interrupter
An arc-fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) or arc-fault detection device (AFDD) is a circuit breaker that breaks the circuit when it detects the electric arcs that are a signature of loose connections in home wiring. Loose connections, which can develop over time, can sometimes become hot enough to ignite house fires. An AFCI selectively distinguishes between a harmless arc (incidental to normal operation of switches, plugs, and brushed motors), and a potentially dangerous arc (that can occur, for example, in a lamp cord which has a broken conductor). In Canada and the United States, AFCI breakers have been required by the electrical codes for circuits feeding electrical outlets in residential bedrooms since the beginning of the 21st century; the US ''National Electrical Code'' has required them to protect most residential outlets since 2014, and the '' Canadian Electrical Code'' has since 2015. In regions using 230 V, the combination of higher voltage and lower load currents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
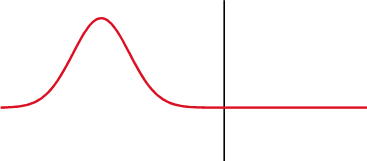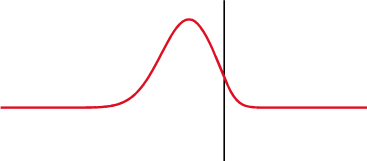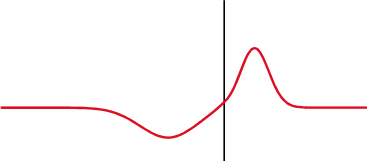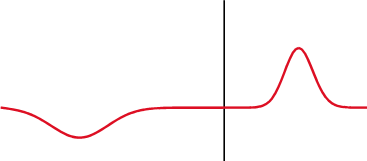 |
Time-domain Reflectometer
A time-domain reflectometer (TDR) is an electronic instrument used to determine the characteristics of electrical lines by observing reflected pulses. It can be used to characterize and locate faults in metallic cables (for example, twisted pair wire or coaxial cable), and to locate discontinuities in a connector, printed circuit board, or any other electrical path. Description A TDR measures reflections along a conductor. In order to measure those reflections, the TDR will transmit an incident signal onto the conductor and listen for its reflections. If the conductor is of a uniform impedance and is properly terminated, then there will be no reflections and the remaining incident signal will be absorbed at the far-end by the termination. Instead, if there are impedance variations, then some of the incident signal will be reflected back to the source. A TDR is similar in principle to radar. The impedance of the discontinuity can be determined from the amplitude of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |