|
Aquatic Science
Aquatic science is the study of the various bodies of water that make up our planet including oceanic and freshwater environments. Aquatic scientists study the movement of water, the chemistry of water, aquatic organisms, aquatic ecosystems, the movement of materials in and out of aquatic ecosystems, and the use of water by humans, among other things. Aquatic scientists examine current processes as well as historic processes, and the water bodies that they study can range from tiny areas measured in millimeters to full oceans. Moreover, aquatic scientists work in Interdisciplinary groups. For example, a physical oceanographer might work with a biological oceanographer to understand how physical processes, such as tropical cyclones or rip currents, affect organisms in the Atlantic Ocean. Chemists and biologists, on the other hand, might work together to see how the chemical makeup of a certain body of water affects the plants and animals that reside there. Aquatic scientists can work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean, Antarctic/Southern, and Arctic Ocean),"Ocean." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/ocean . Accessed March 14, 2021. and are themselves mostly divided into seas, gulfs and Lists of bodies of water#Seawater bodies, subsequent bodies of water. The ocean contains 97% of Water distribution on Earth, Earth's water and is the primary component of Earth's hydrosphere, acting as a huge Ocean heat content, reservoir of heat for Earth's energy budget, as well as for its carbon cycle and water cycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Model
A computational model uses computer programs to simulate and study complex systems using an algorithmic or mechanistic approach and is widely used in a diverse range of fields spanning from physics, engineering, chemistry and biology to economics, psychology, cognitive science and computer science. The system under study is often a complex nonlinear system for which simple, intuitive analytical solutions are not readily available. Rather than deriving a mathematical analytical solution to the problem, experimentation with the model is done by adjusting the parameters of the system in the computer, and studying the differences in the outcome of the experiments. Operation theories of the model can be derived/deduced from these computational experiments. Examples of common computational models are weather forecasting models, earth simulator models, flight simulator models, molecular protein folding models, Computational Engineering Models (CEM), and neural network models. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrothermal Circulation
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water (Ancient Greek ὕδωρ, ''water'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. and θέρμη, ''heat'' ). Hydrothermal circulation occurs most often in the vicinity of sources of heat within the Earth's Crust (geology), crust. In general, this occurs near volcanic activity, but can occur in the shallow to mid crust along deeply penetrating fault irregularities or in the deep crust related to the intrusion of granite, or as the result of orogeny or metamorphism. Hydrothermal circulation often results in Hydrothermal mineral deposit, hydrothermal mineral deposits. Seafloor hydrothermal circulation Hydrothermal circulation in the ocean, oceans is the passage of the water through mid-oceanic ridge systems. The term includes both the circulation of the well- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (geology)
A mantle is a layer inside a planetary body bounded below by a Planetary core, core and above by a Crust (geology), crust. Mantles are made of Rock (geology), rock or Volatile (astrogeology), ices, and are generally the largest and most massive layer of the planetary body. Mantles are characteristic of planetary bodies that have undergone planetary differentiation, differentiation by density. All Terrestrial planet, terrestrial planets (including Earth), half of the giant planets, specifically ice giants, a number of Asteroid, asteroids, and some planetary Natural satellite, moons have mantles. Examples Earth The Earth's mantle is a layer of Silicate minerals, silicate rock between the Crust (geology), crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. Its mass of 4.01 × 1024 kg is 67% the mass of the Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly solid, but in Geologic time scale, geological time it behaves as a Viscosity, visc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Volcano
Submarine volcanoes are underwater vents or fissures in the Earth's surface from which magma can erupt. Many submarine volcanoes are located near areas of tectonic plate formation, known as mid-ocean ridges. The volcanoes at mid-ocean ridges alone are estimated to account for 75% of the magma output on Earth.Martin R. Speight, Peter A. Henderson, "Marine Ecology: Concepts and Applications", John Wiley & Sons, 2013. . Although most submarine volcanoes are located in the depths of seas and oceans, some also exist in shallow water, and these can discharge material into the atmosphere during an eruption. The total number of submarine volcanoes is estimated to be over one million (most are now extinct) of which some 75,000 rise more than above the seabed. Only 119 submarine volcanoes in Earth's oceans and seas are known to have erupted during the last 11,700 years. Hydrothermal vents, sites of abundant biological activity, are commonly found near submarine volcanoes. Effect of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermohaline Circulation
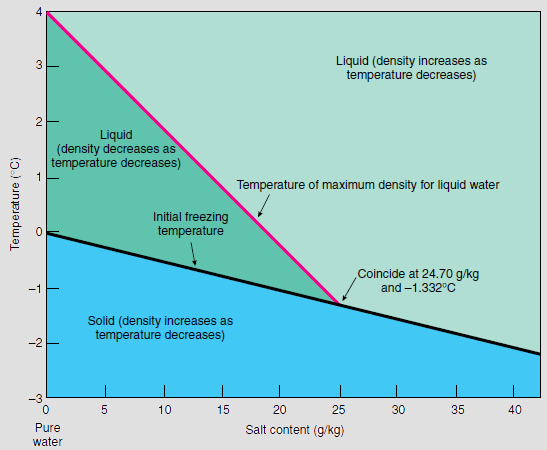
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale Ocean current, ocean circulation driven by global density gradients formed by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The name ''thermohaline'' is derived from ''wikt:thermo-, thermo-'', referring to temperature, and ', referring to salinity, salt content—factors which together determine the Water (molecule)#Density of saltwater and ice, density of sea water. Wind-driven surface currents (such as the Gulf Stream) travel Polar regions of Earth, polewards from the equatorial Atlantic Ocean, cooling and sinking en-route to higher latitudes - eventually becoming part of the North Atlantic Deep Water - before flowing into the ocean basins. While the bulk of thermohaline water upwelling, upwells in the Southern Ocean, the oldest waters (with a transit time of approximately 1000 years) upwell in the North Pacific; extensive mixing takes place between the ocean basins, reducing the difference in their densities, forming the Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
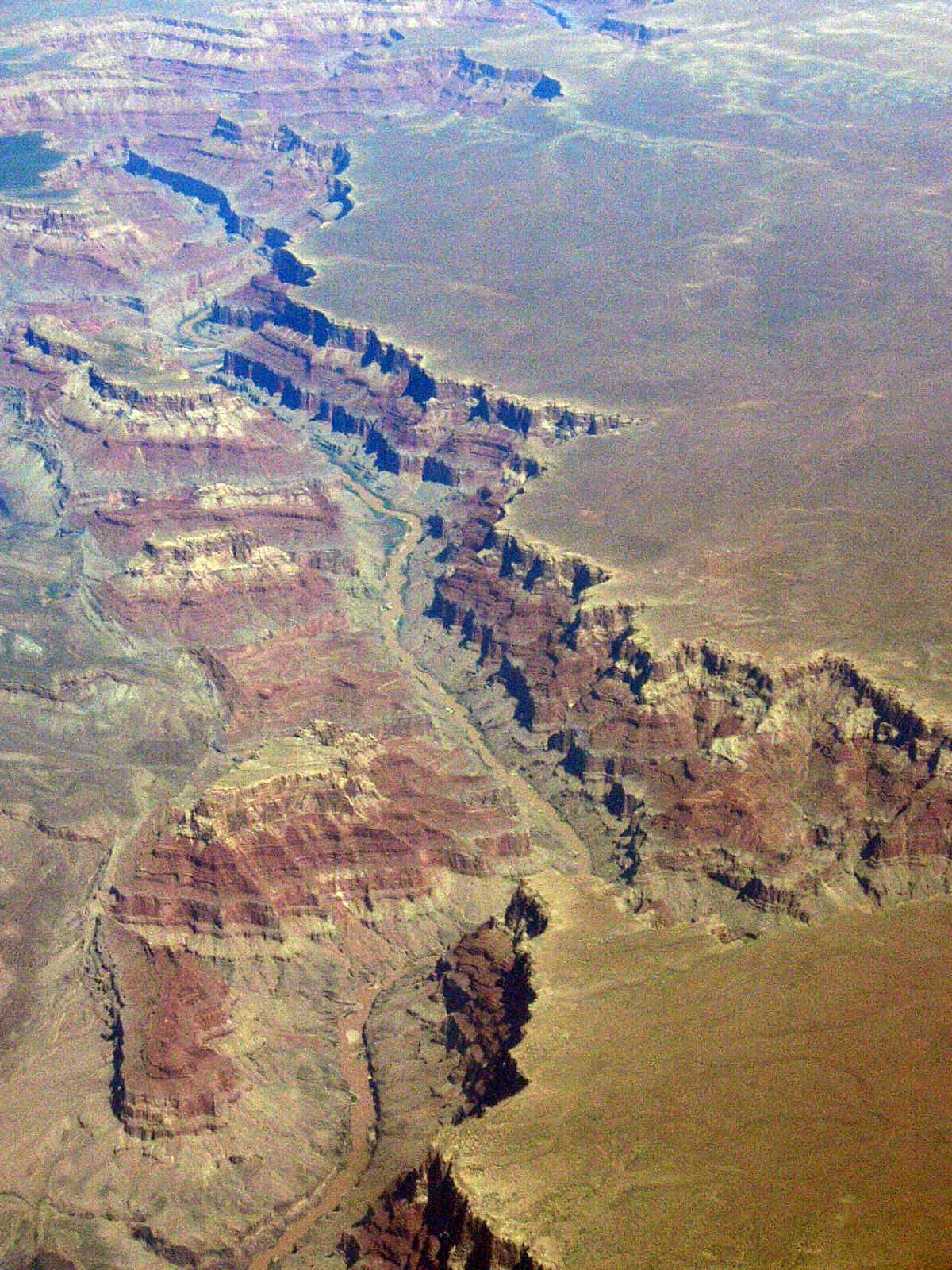
Valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains and typically containing a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a very long period. Some valleys are formed through erosion by glacial ice. These glaciers may remain present in valleys in high mountains or polar areas. At lower latitudes and altitudes, these glacially formed valleys may have been created or enlarged during ice ages but now are ice-free and occupied by streams or rivers. In desert areas, valleys may be entirely dry or carry a watercourse only rarely. In areas of limestone bedrock, dry valleys may also result from drainage now taking place underground rather than at the surface. Rift valleys arise principally from earth movements, rather than erosion. Many different types of valleys are described by geographers, using terms that may be global in use or else applied only locally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canyon
A canyon (; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), gorge or chasm, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tendency to cut through underlying surfaces, eventually wearing away rock layers as sediments are removed downstream. A river bed will gradually reach a baseline elevation, which is the same elevation as the body of water into which the river drains. The processes of weathering and erosion will form canyons when the river's headwaters and estuary are at significantly different elevations, particularly through regions where softer rock layers are intermingled with harder layers more resistant to weathering. A canyon may also refer to a rift between two mountain peaks, such as those in ranges including the Rocky Mountains, the Alps, the Himalayas or the Andes. Usually, a river or stream carves out such splits between mountains. Examples of mountain- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are inselberg, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. mountain formation, Mountains are formed through tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosystems of mountains: different elevations hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, energy change as new products are generated. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollutant
A pollutant or novel entity is a substance or energy introduced into the environment that has undesired effect, or adversely affects the usefulness of a resource. These can be both naturally forming (i.e. minerals or extracted compounds like oil) or anthropogenic in origin (i.e. manufactured materials or byproducts). Pollutants result in environmental pollution or become of public health concern when they reach a concentration high enough to have significant negative impacts. A pollutant may cause long- or short-term damage by changing the growth rate of plant or animal species, or by interfering with resources used by humans, human health or wellbeing, or property values. Some pollutants are biodegradable and therefore will not persist in the environment in a long term. However, the degradation products of some pollutants are themselves pollutants such as DDE and DDD produced from the degradation of DDT. Pollution has widespread negative impact on the environment. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation which produces ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, solar wind, and cosmic rays and thus protects the organisms from genetic damage. The curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |