|
Aptamers
Aptamers are short sequences of artificial DNA, RNA, XNA, or peptide that bind a specific target molecule, or family of target molecules. They exhibit a range of affinities ( KD in the pM to μM range), with little or no off-target binding and are sometimes classified as chemical antibodies. Aptamers and antibodies can be used in many of the same applications, but the nucleic acid-based structure of aptamers, which are mostly oligonucleotides, is very different from the amino acid-based structure of antibodies, which are proteins. This difference can make aptamers a better choice than antibodies for some purposes (see antibody replacement). Aptamers are used in biological lab research and medical tests. If multiple aptamers are combined into a single assay, they can measure large numbers of different proteins in a sample. They can be used to identify molecular markers of disease, or can function as drugs, drug delivery systems and controlled drug release systems. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Therapeutics
RNA therapeutics are a new class of medications based on ribonucleic acid (RNA). Research has been working on clinical use since the 1990s, with significant success in cancer therapy in the early 2010s. In 2020 and 2021, mRNA vaccines have been developed globally for use in combating the coronavirus disease (COVID-19 pandemic). The Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine was the first mRNA vaccine approved by a medicines regulator, followed by the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine, and others. The main types of RNA therapeutics are those based on messenger RNA (mRNA), antisense RNA (asRNA), RNA interference (RNAi), and RNA aptamers. Of the four types, mRNA-based therapy is the only type which is based on triggering synthesis of proteins within cells, making it particularly useful in vaccine development. Antisense RNA is complementary to coding mRNA and is used to trigger mRNA inactivation to prevent the mRNA from being used in protein translation. RNAi-based systems use a similar mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
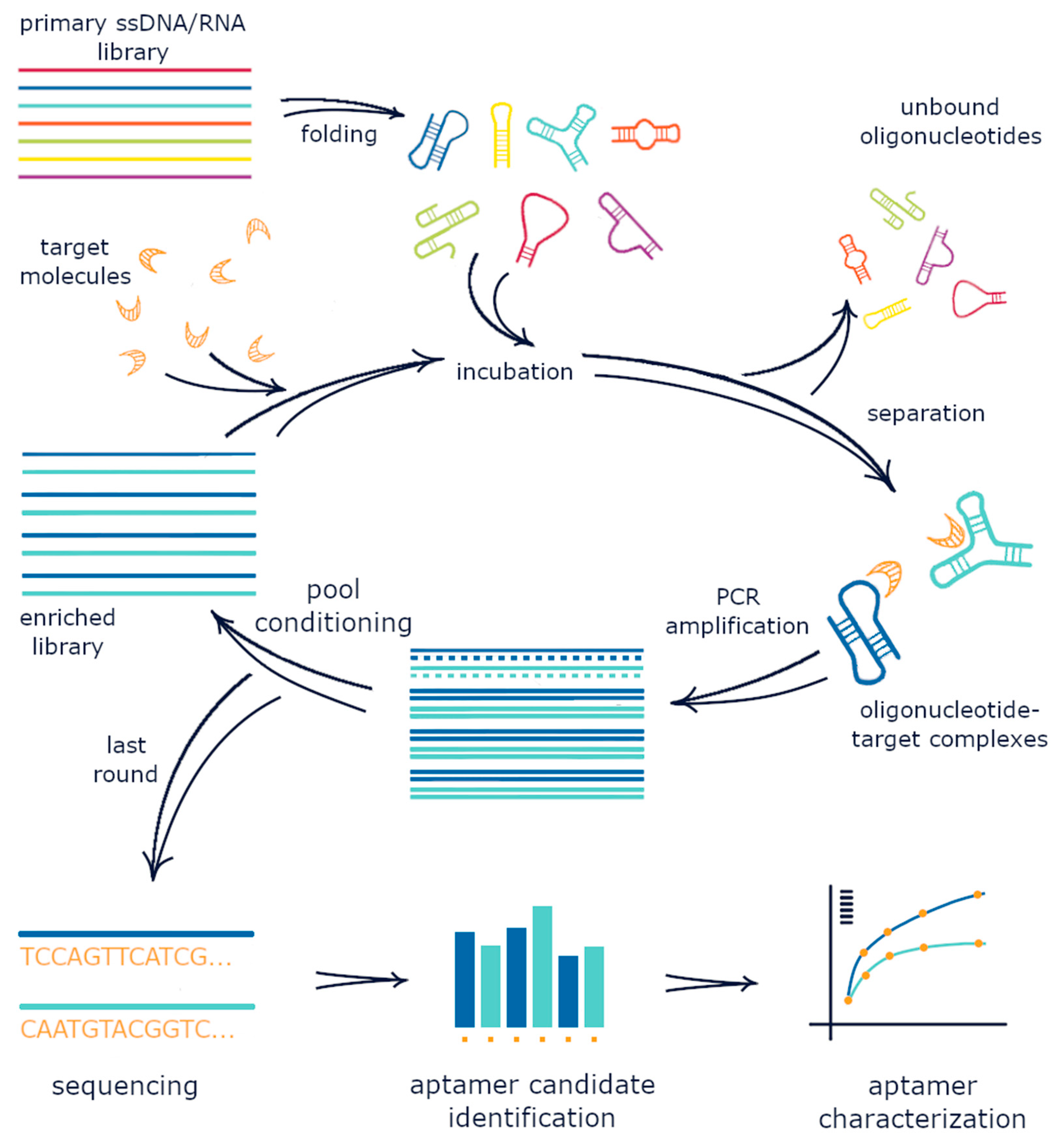
Systematic Evolution Of Ligands By Exponential Enrichment
Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX), also referred to as '' in vitro selection'' or '' in vitro evolution'', is a combinatorial chemistry technique in molecular biology for producing oligonucleotides of either single-stranded DNA or RNA that specifically bind to a target ligand or ligands. These single-stranded DNA or RNA are commonly referred to as aptamers. Although SELEX has emerged as the most commonly used name for the procedure, some researchers have referred to it as SAAB (selected and amplified binding site) and CASTing (cyclic amplification and selection of targets) SELEX was first introduced in 1990. In 2015, a special issue was published in the Journal of Molecular Evolution in the honor of quarter century of the discovery of SELEX. The process begins with the synthesis of a very large oligonucleotide library, consisting of randomly generated sequences of fixed length flanked by constant 5' and 3' ends. The constant ends serve as pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. In addition, other kinds of proteins include antibodies that protect an organism from infection, and hormones that send important signals throughout the body. The proteome is the entire set of proteins produced or modified by an organism or system. Proteomics enables the identification of ever-increasing numbers of proteins. This varies with time and distinct requirements, or stresses, that a cell or organism undergoes. Proteomics is an interdisciplinary domain that has benefited greatly from the genetic information of various genome projects, including the Human Genome Project. It covers the exploration of proteomes from the overall level of protein composition, structure, and activity, and is an important component of functional genomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomarker Discovery
Biomarker discovery is a medical term describing the process by which biomarkers are discovered. Many commonly used blood tests in medicine are biomarkers. There is interest in biomarker discovery on the part of the pharmaceutical industry; blood-test or other biomarkers could serve as intermediate markers of disease in clinical trials, and as possible drug targets. Mechanism of action The way that these tests have been found can be viewed as biomarker discovery; however, their identification has primarily been made one at a time. Many well-known tests have been identified based on biological insight from the fields of physiology or biochemistry; therefore, only a few markers at a time have been considered. An example of biomarker discovery is the use of inulin to assess kidney function. From this process a naturally occurring molecule (creatinine) was discovered, enabling the same measurements to be made without insulin injections. The recent interest in biomarker discovery is spu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rational Design
In chemical biology and biomolecular engineering, rational design (RD) is an umbrella term which invites the strategy of creating new molecules with a certain functionality, based upon the ability to predict how the molecule's structure (specifically derived from motifs) will affect its behavior through physical models. This can be done either from scratch or by making calculated variations on a known structure, and usually complements directed evolution. Applications As an example, rational design is used to decipher collagen stability, mapping ligand-receptor interactions, unveiling protein folding and dynamics, and creating extra-biological structures by using fluorinated amino acids. To treat cancer, rational design is used for targeted therapies where proteins are engineered to modify the communication of cells with their environment. There is also the rational design of alfa-alkyl auxin molecules, which are auxin analogs capable of binding and blocking the formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioconjugation
Bioconjugation is a chemical strategy to form a stable covalent link between two molecules, at least one of which is a biomolecule. Function Recent advances in the understanding of biomolecules enabled their application to numerous fields like medicine and materials. Synthetically modified biomolecules can have diverse functionalities, such as tracking cellular events, revealing enzyme function, determining protein biodistribution, imaging specific biomarkers, and delivering drugs to targeted cells. Bioconjugation is a crucial strategy that links these modified biomolecules with different substrates. Synthesis Synthesis of bioconjugates involves a variety of challenges, ranging from the simple and nonspecific use of a fluorescent dye marker to the complex design of antibody drug conjugates. As a result, various bioconjugation reactions – chemical reactions connecting two biomolecules together – have been developed to chemically modify proteins. Common types of bioconjug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutate
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligonucleotide Synthesis
Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure ( sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpensive access to custom-made oligonucleotides of the desired sequence. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5' to 3' direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not have this limitation, although it is most often carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Currently, the process is implemented as solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite method and phosphoramidite building blocks derived from protected 2'-deoxynucleosides ( dA, dC, dG, and T), ribonucleosides ( A, C, G, and U), or chemically modified nucleosides, e.g. LNA or BNA. To obtain the desired oligonucleotide, the building blocks are sequentially coupled to the growing oligonucleotide chain in the order required by the sequence of the product ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrillion
Two naming scales for large numbers have been used in English and other European languages since the early modern era: the long and short scales. Most English variants use the short scale today, but the long scale remains dominant in many non-English-speaking areas, including continental Europe and Spanish-speaking countries in Latin America. These naming procedures are based on taking the number ''n'' occurring in 103''n''+3 (short scale) or 106''n'' (long scale) and concatenating Latin roots for its units, tens, and hundreds place, together with the suffix ''-illion''. Names of numbers above a trillion are rarely used in practice; such large numbers have practical usage primarily in the scientific domain, where powers of ten are expressed as ''10'' with a numeric superscript. Indian English does not use millions, but has its own system of large numbers including lakhs and crores. English also has many words, such as "zillion", used informally to mean large but unspecified a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
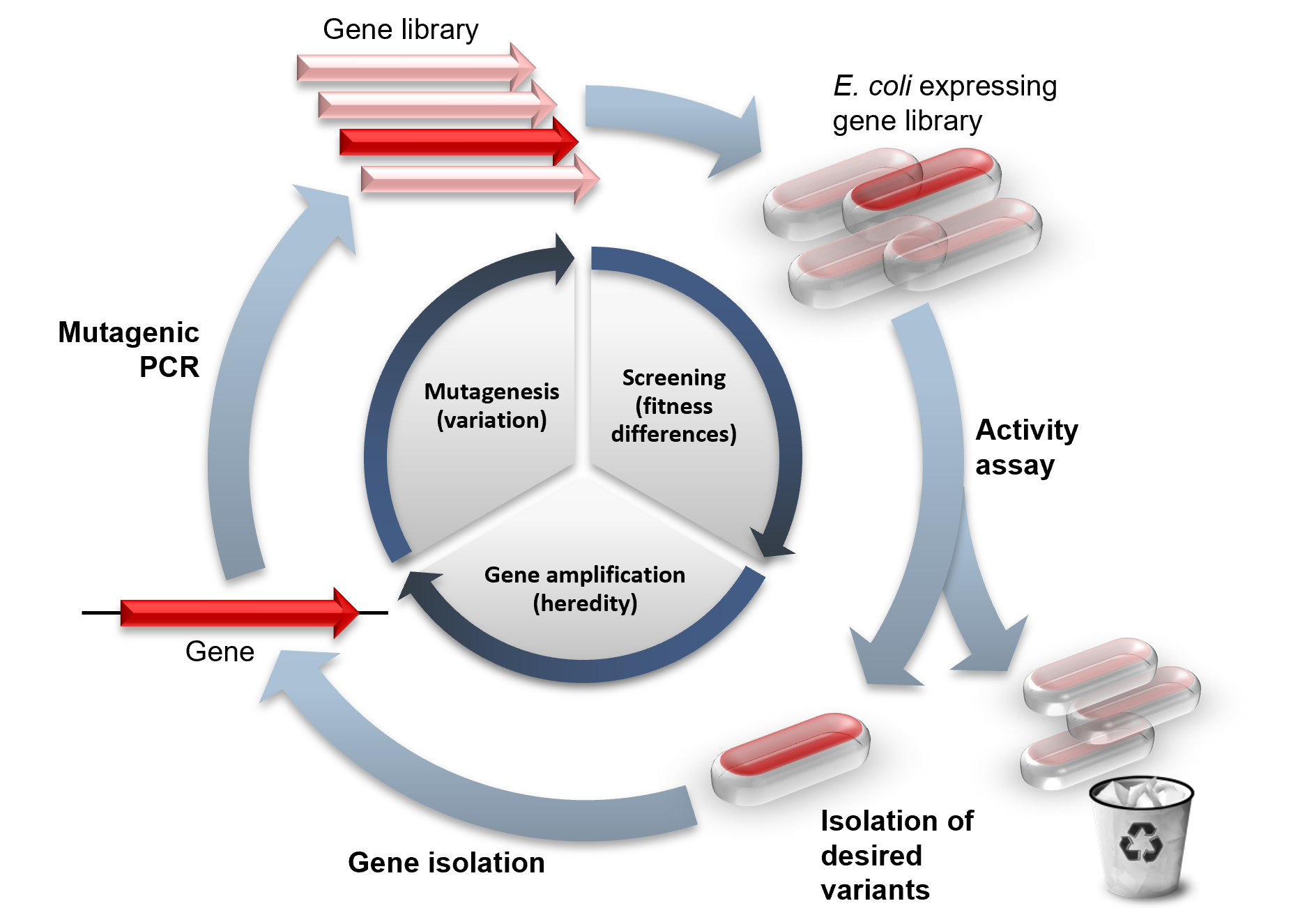
Directed Evolution
Directed evolution (DE) is a method used in protein engineering that mimics the process of natural selection to steer proteins or nucleic acids toward a user-defined goal. It consists of subjecting a gene to iterative rounds of mutagenesis (creating a library of variants), selection (expressing those variants and isolating members with the desired function) and amplification (generating a template for the next round). It can be performed ''in vivo'' (in living organisms), or ''in vitro'' (in cells or free in solution). Directed evolution is used both for protein engineering as an alternative to rationally designing modified proteins, as well as for experimental evolution studies of fundamental evolutionary principles in a controlled, laboratory environment. History Directed evolution has its origins in the 1960s with the evolution of RNA molecules in the " Spiegelman's Monster" experiment. The concept was extended to protein evolution via evolution of bacteria under select ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with artificial selection, which in his view is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and their offspring can inherit such mutations. Throughout the lives of the individuals, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment. Because individuals with certain variants of the trait tend to survive and reproduce more than individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, '' in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)