|
Aphakic
Aphakia is the absence of the lens of the eye, due to surgical removal, such as in cataract surgery, a perforating wound or ulcer, or congenital anomaly. It causes a loss of accommodation, high degree of farsightedness (hyperopia), and a deep anterior chamber. Complications include detachment of the vitreous or retina, and glaucoma. Babies are rarely born with aphakia. Occurrence most often results from surgery to remove congenital cataract. Congenital cataracts usually develop as a result of infection of the fetus or genetic reasons. It is often difficult to identify the exact cause of these cataracts, especially if only one eye is affected. People with aphakia have relatively small pupils and their pupils dilate to a lesser degree. Causes Surgical removal of a lens, mainly in cataract surgery, is the most common cause of aphakia. Spontaneous traumatic absorption or congenital absence of lens matter is rare. Traumatic subluxation or dislocation of a lens may cause it. Signs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudophakia
Intraocular lens (IOL) is a lens implanted in the eye as part of a treatment for cataracts or myopia. If the natural lens is left in the eye, the IOL is known as phakic, otherwise it is a pseudophakic, or false lens. Such a lens is typically implanted during cataract surgery, after the eye's cloudy natural lens (cataract) has been removed. The pseudophakic IOL provides the same light-focusing function as the natural crystalline lens. The phakic type of IOL is placed over the existing natural lens and is used in refractive surgery to change the eye's optical power as a treatment for myopia (nearsightedness). This is an alternative to LASIK. IOLs usually consist of a small plastic lens with plastic side struts, called haptics, to hold the lens in place in the capsular bag inside the eye. IOLs were conventionally made of an inflexible material (PMMA), although this has largely been superseded by the use of flexible materials, such as silicone. Most IOLs fitted today are fixed mono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraocular Lens
Intraocular lens (IOL) is a lens (optics), lens implanted in the human eye, eye as part of a treatment for cataracts or myopia. If the natural lens is left in the eye, the IOL is known as Phakic intraocular lens, phakic, otherwise it is a pseudophakic, or false lens. Such a lens is typically implanted during cataract surgery, after the eye's cloudy lens (anatomy), natural lens (cataract) has been removed. The pseudophakic IOL provides the same light-focusing function as the natural crystalline lens. The phakic type of IOL is placed over the existing natural lens and is used in refractive surgery to change the eye's optical power as a treatment for myopia (nearsightedness). This is an alternative to LASIK. IOLs usually consist of a small plastic lens with plastic side struts, called haptics, to hold the lens in place in the capsular bag inside the eye. IOLs were conventionally made of an inflexible material (Polymethyl methacrylate, PMMA), although this has largely been superseded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
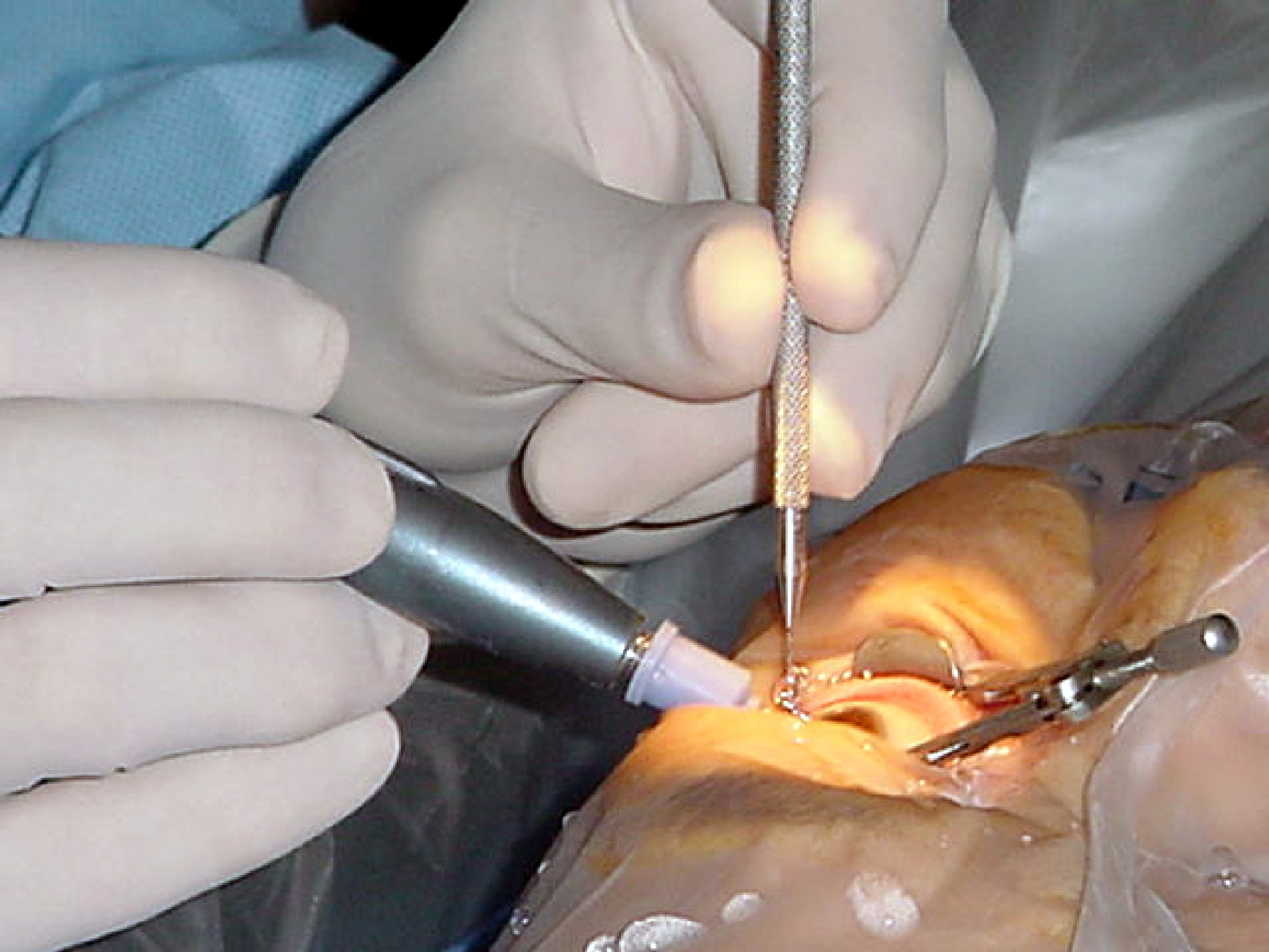
Cataract Surgery
Cataract surgery, also called lens replacement surgery, is the removal of the natural lens of the eye (also called "crystalline lens") that has developed an opacification, which is referred to as a cataract, and its replacement with an intraocular lens. Metabolic changes of the crystalline lens fibers over time lead to the development of the cataract, causing impairment or loss of vision. Some infants are born with congenital cataracts, and certain environmental factors may also lead to cataract formation. Early symptoms may include strong glare from lights and small light sources at night, and reduced acuity at low light levels. During cataract surgery, a patient's cloudy natural cataract lens is removed, either by emulsification in place or by cutting it out. An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is implanted in its place. Cataract surgery is generally performed by an ophthalmologist in an ambulatory setting at a surgical center or hospital rather than an inpatient setting. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanopsia
''Cyanopsia'' is a medical term for seeing everything tinted with blue. It is also referred to as ''blue vision''. Cyanopsia often occurs for a few days, weeks, or months after removal of a cataract from the eye. Cyanopsia also sometimes occurs as a side effect of taking sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil. Cyanopsia is a medical symptom and not a sign. It is a purely subjective state and can be caused by a physical or functional abnormality of the eye, a physical or functional abnormality of the brain, or be purely psychological. Cyanopsia, if unaccompanied by any other sign or symptom, is not an indication of any disease or disorder. Unless it causes an impairment or significant distress, it is not in and of itself diagnostically relevant. Cyanopsia after cataract removal The eye's lens is normally tinted yellow. This reduces the intensity of blue light reaching the retina. When the lens is removed because of cataract, it is usually replaced by an artificial intraocular lens; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Surgery
Refractive eye surgery is optional eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea ( keratomileusis), lens implantation or lens replacement. The most common methods today use excimer lasers to reshape the curvature of the cornea. Refractive eye surgeries are used to treat common vision disorders such as myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia and astigmatism. History The first theoretical work on the potential of refractive surgery was published in 1885 by Hjalmar August Schiøtz, an ophthalmologist from Norway. In 1930, the Japanese ophthalmologist Tsutomu Sato made the first attempts at performing this kind of surgery, hoping to correct the vision of military pilots. His approach was to make radial cuts in the cornea, correcting effects by up to 6 diopters. The procedure unfortunately produced a high rate of corneal degeneration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Lenses
Contact lenses, or simply contacts, are thin lenses placed directly on the surface of the eyes. Contact lenses are ocular prosthetic devices used by over 150 million people worldwide, and they can be worn to correct vision or for cosmetic or therapeutic reasons. In 2010, the worldwide market for contact lenses was estimated at $6.1 billion, while the US soft lens market was estimated at $2.1 billion.Nichols, Jason J., et a"ANNUAL REPORT: Contact Lenses 2010" January 2011. Multiple analysts estimated that the global market for contact lenses would reach $11.7 billion by 2015. , the average age of contact lens wearers globally was 31 years old, and two-thirds of wearers were female.Morgan, Philip B., et al"International Contact Lens Prescribing in 2010" ''Contact Lens Spectrum''. October 2011. People choose to wear contact lenses for many reasons. Aesthetics and cosmetics are main motivating factors for people who want to avoid wearing glasses or to change the appearance or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses or spectacles, are vision eyewear, with lenses (clear or tinted) mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically utilizing a bridge over the nose and hinged arms (known as temples or temple pieces) that rest over the ears. Glasses are typically used for vision correction, such as with reading glasses and glasses used for nearsightedness; however, without the specialized lenses, they are sometimes used for cosmetic purposes. Safety glasses provide eye protection against flying debris for construction workers or lab technicians; these glasses may have protection for the sides of the eyes as well as in the lenses. Some types of safety glasses are used to protect against visible and near-visible light or radiation. Glasses are worn for eye protection in some sports, such as squash. Glasses wearers may use a strap to prevent the glasses from falling off. Wearers of glasses that are used only part of the time may have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplopia
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced horizontally or vertically in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occurring involuntarily, it results in impaired function of the extraocular muscles, where both eyes are still functional, but they cannot turn to target the desired object. Problems with these muscles may be due to mechanical problems, disorders of the neuromuscular junction, disorders of the cranial nerves (III, IV, and VI) that innervate the muscles, and occasionally disorders involving the supranuclear oculomotor pathways or ingestion of toxins. Diplopia can be one of the first signs of a systemic disease, particularly to a muscular or neurological process, and it may disrupt a person's balance, movement, or reading abilities. Causes Diplopia has a diverse range of ophthalmologic, infectious, autoimmune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisometropia
Anisometropia refers to a condition when two eyes have unequal refractive power. Generally, a difference in power of one diopter (1D) or more is the accepted threshold to label the condition anisometropia. Patients can tolerate 3 D of anisometropia before it becomes clinically symptomatic with headaches, asthenopia, double vision and photophobia. In certain types of anisometropia, the visual cortex of the brain will not process images from both eyes together ( binocular summation), and will instead suppress the central vision of one of the eyes. If this occurs often enough during the first 10 years of life while the visual cortex is developing, it can result in amblyopia, a condition where even when correcting the refractive error properly, the person's vision in the affected eye is still not correctable to 20/20. The name is from four Greek components: ''an-'' "not," ''iso-'' "same," ''metr-'' "measure," ''ops'' "eye." Antimetropia is a rare sub-type of anisometropia, in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
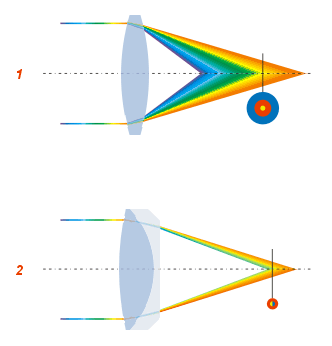
Optical Aberration
In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as lenses, that causes light to be spread out over some region of space rather than focused to a point. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred or distorted, with the nature of the distortion depending on the type of aberration. Aberration can be defined as a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements. An image-forming optical system with aberration will produce an image which is not sharp. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration. Aberration can be ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |