|
Antibiotics In Animal Husbandry
The use of antibiotics in the husbandry of livestock includes treatment when ill (therapeutic), treatment of a group of animals when at least one is diagnosed with clinical infection (metaphylaxis), and preventative treatment (prophylaxis). Antibiotics are an important tool to treat animal as well as human disease, safeguard animal health and welfare, and support food safety. However, used irresponsibly, this may lead to antibiotic resistance which may impact human, animal and environmental health. While levels of use vary dramatically from country to country, for example some Northern European countries use very low quantities to treat animals compared with humans, worldwide an estimated 73% of antimicrobials (mainly antibiotics) are consumed by farm animals. Furthermore, a 2015 study also estimates that global agricultural antibiotic usage will increase by 67% from 2010 to 2030, mainly from increases in use in developing BRIC countries. Increased antibiotic use is a matter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
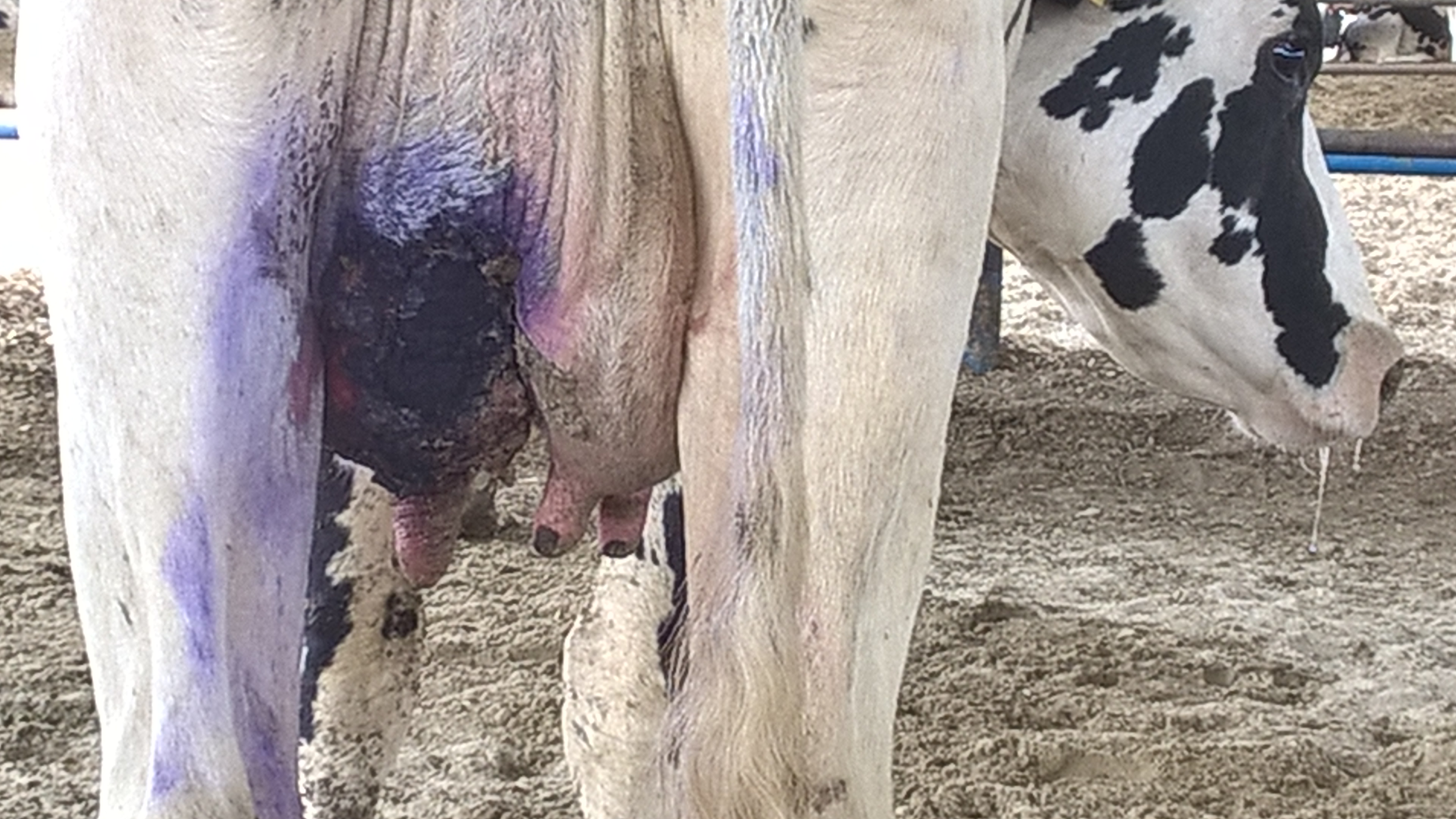
Bovine Mastitis
Bovine mastitis is the persistent, inflammatory reaction of the udder tissue due to physical trauma or microorganisms infections. Mastitis, a potentially fatal mammary gland infection, is the most common disease in dairy cattle in the United States and worldwide. It is also the most costly disease to the dairy industry. Milk from cows suffering from mastitis has an increased somatic cell count. Prevention and control of mastitis requires consistency in sanitizing the cow barn facilities, proper milking procedure and segregation of infected animals. Treatment of the disease is carried out by penicillin injection in combination with sulphar drug. Definition Mastitis occurs when white blood cells (leukocytes) are released into the mammary gland, usually in response to bacteria invading the teat canal or occasionally by chemical, mechanical, or thermal trauma on the udder. Milk-secreting tissue and various ducts throughout the mammary gland are damaged due to toxins released by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merial
Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health is a Multinational corporation, multinational animal health company, formed in January 2017 when Merial was acquired by Boehringer Ingelheim and merged with Boehringer Ingelheim's existing animal health assets. Overview In August 1997, Merial started as a joint venture between the animal health subsidiaries of Merck & Co. (MSD AgVet) and Sanofi-Aventis (Rhône-Mérieux). Merial became the animal health division of Sanofi, when Sanofi bought out Merck's 50% share of the joint venture. On December 30, 2016 Boehringer Ingelheim completed a swap of their OTC business for Sanofi's animal health business. Merial is now owned by Boehringer Ingelheim and combined with their animal health business, Boehringer Ingelheim Vetmedica, to form Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health. Merial produces many products and vaccines for domestic pets, farm animals and wildlife. Merial has about 6,900 employees and is present in more than 150 countries in the world. Their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck & Co
Merck & Co., Inc. is an American Multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Rahway, New Jersey. The company does business as Merck Sharp & Dohme or MSD outside the United States and Canada. It is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world, generally ranking in the global top five by revenue. Merck & Co. was originally established as the American affiliate of Merck Group in 1891. Merck develops and produces medicines, vaccines, biologic therapies and animal health products. It has several blockbuster products, including cancer immunotherapy, anti-diabetic medications, and vaccines for HPV and chickenpox, each generating significant revenue as of 2020. The company is ranked 71st on the 2022 Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 and 87th on the 2022 Forbes Global 2000, ''Forbes'' Global 2000, both based on 2021 revenues. In 2023, the company’s seat in the ''Forbes'' Global 2000 was 73. Products The company develops medicines, vaccines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bambermycin
Bambermycin (flavomycin) is a complex of antibiotics obtained from '' Streptomyces bambergiensis'' and '' Streptomyces ghanaensis'' used as a food additive for beef cattle, dairy cattle, poultry and swine. The complex consists mainly of moenomycins A and C. Bambermycin is a performance-enhancing antibiotic intended and available solely for use in animal nutrition. Its mechanism of action is to inhibit the synthesis of the bacterial wall. Bambermycin is predominantly effective against Gram-positive pathogenic bacteria. However, it does not have significant action against ''Lactobacillus'', ''Bifidobacterium ''Bifidobacterium'' is a genus of gram-positive, nonmotile, often branched anaerobic bacteria. They are ubiquitous inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tract though strains have been isolated from the vagina and mouth ('' B. dentium'') of mamma ...'', and other protective bacteria. Bambermycin has no precautions or warnings to humans on its label pertaining to mixing an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (carboxyl g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacitracin
Bacitracin is a polypeptide antibiotic. It is a mixture of related cyclic peptides produced by '' Bacillus licheniformis'' bacteria, that was first isolated from the variety "Tracy I" ( ATCC 10716) in 1945. These peptides disrupt Gram-positive bacteria by interfering with cell wall and peptidoglycan synthesis. Bacitracin is primarily used as a topical preparation, as it can cause kidney damage when used internally. It is generally safe when used topically, but in rare cases may cause hypersensitivity, allergic or anaphylactic reactions, especially in people allergic to neomycin. In 2022, it was the 323rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 100,000 prescriptions. Medical uses Bacitracin is used in human medicine as a polypeptide antibiotic and is "approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in chickens and turkeys," though use in animals contributes to antibiotic resistance. As bacitracin zinc salt, in combination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccidiostat
A coccidiostat is an antiprotozoal agent that acts upon Coccidia parasites. Examples include: * Amprolium * Arprinocid * Artemether * Clazuril * Clopidol * Decoquinate * Diclazuril * Dinitolmide * Ethopabate * Halofuginone * Lasalocid * Maduramicin * Monensin * Narasin * Nicarbazin * Oryzalin * Ponazuril * Robenidine * Roxarsone * Salinomycin * Spiramycin * Sulfadiazine * Sulfadimethoxine * Toltrazuril Toltrazuril is an antiparasitic medication used primarily to treat coccidiosis in animals. Coccidiosis is a parasitic disease caused by coccidia, which are microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to ... References Antiprotozoal agents {{antiinfective-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionophore
In chemistry, an ionophore () is a chemical species that reversibly binds ions. Many ionophores are lipid-soluble entities that transport ions across the cell membrane. Ionophores catalyze ion transport across hydrophobic membranes, such as liquid polymeric membranes (carrier-based ion selective electrodes) or lipid bilayers found in the living cells or synthetic vesicles ( liposomes). Structurally, an ionophore contains a hydrophilic center and a hydrophobic portion that interacts with the membrane. Some ionophores are synthesized by microorganisms to import ions into their cells. Synthetic ion carriers have also been prepared. Ionophores selective for cations and anions have found many applications in analysis. These compounds have also shown to have various biological effects and a synergistic effect when combined with the ion they bind. Classification Biological activities of metal ion-binding compounds can be changed in response to the increment of the metal concentr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut Flora
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses, that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut microbiota. The gut is the main location of the human microbiome. The gut microbiota has broad impacts, including effects on colonization, resistance to pathogens, maintaining the intestinal epithelium, metabolizing dietary and pharmaceutical compounds, controlling immune function, and even behavior through the gut–brain axis. The microbial composition of the gut microbiota varies across regions of the digestive tract. The colon contains the highest microbial density of any human-associated microbial community studied so far, representing between 300 and 1000 different species. Bacteria are the largest and to date, best studied component and 99% of gut bacteria come from about 30 or 40 species. About 55% of the dry mass of feces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feed Conversion Efficiency
In animal husbandry, feed conversion ratio (FCR) or feed conversion rate is a ratio or rate measuring of the efficiency with which the bodies of livestock convert animal feed into the desired output. For dairy cows, for example, the output is milk, whereas in animals raised for meat (such as beef cows,Dan Shike, University of IllinoiBeef Cattle Feed Efficiency/ref> pigs, chickens, and fish) the output is the flesh, that is, the body mass gained by the animal, represented either in the final mass of the animal or the mass of the dressed output. FCR is the mass of the input divided by the output (thus mass of feed per mass of milk or meat). In some sectors, feed efficiency, which is the output divided by the input (i.e. the inverse of FCR), is used. These concepts are also closely related to efficiency of conversion of ingested foods (ECI). Background Feed conversion ratio (FCR) is the ratio of inputs to outputs; it is the inverse of "feed efficiency" which is the ratio of output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Concerned Scientists
The Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS) is a nonprofit science advocacy organization based in the United States. The UCS membership includes many private citizens in addition to professional scientists. Anne Kapuscinski, Professor of Environmental Studies and Director of the Coastal Science and Policy Program at the University of California, Santa Cruz, chairs the UCS Board of Directors , having replaced James J. McCarthy, Professor of Biological Oceanography at Harvard University and past president of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. History The Union of Concerned Scientists was founded in 1969 by faculty and students of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The organization's founding document says it was formed to "initiate a critical and continuing examination of governmental policy in areas where science and technology are of actual or potential significance" and to "devise means for turning research applications away from the present emphasis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |