|
Anti-Brahmanism
Anti-Brahminism is a term used in opposition to caste based hierarchal social order which places Brahmins at its highest position. Initial expressions of Anti-Brahminism emerged from instances of pre-colonial opposition to the caste system in India, ideological influences during the colonial period, and from a colonialist Protestant Christian understanding of religion in the 19th century, which viewed "Brahminism" as a corrupted religion imposed on the Indian population. Ambedkar and some Hindu Reformists structured their criticism along similar lines following the 19th century criticism of "Brahminism," opposing the dominant position Brahmins had acquired by the time of British rule in the 19th century. However, anti-Brahminism has also manifested as an anti-Brahmin sentiment, notably during the Dravidian movement and the Self-Respect Movement in the 20th century, and even in the 21st century among some followers of Periyar. Definitions "Brahminism" refers both to the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caste System
A caste is a fixed social group into which an individual is born within a particular system of social stratification: a caste system. Within such a system, individuals are expected to marry exclusively within the same caste (endogamy), follow lifestyles often linked to a particular occupation, hold a ritual status observed within a hierarchy, and interact with others based on cultural notions of exclusion, with certain castes considered as either more pure or more polluted than others. The term "caste" is also applied to morphological groupings in eusocial insects such as ants, bees, and termites. The paradigmatic ethnographic example of caste is the division of India's Hindu society into rigid social groups. Its roots lie in South Asia's ancient history and it still exists; however, the economic significance of the caste system in India seems to be declining as a result of urbanisation and affirmative action programs. A subject of much scholarship by sociologists and ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periyar E
Erode Venkatappa Ramasamy (17 September 187924 December 1973), commonly known as Periyar, was an Indian social activist and politician. He was the organizer of the Self-Respect Movement and Dravidar Kazhagam and is considered the architect of Dravidian politics. Periyar joined the Indian National Congress in 1919 and participated in the Vaikom Satyagraha, during which he was imprisoned twice. He resigned from the Congress in 1925, believing that they only served the interests of Brahmins. From 1929 to 1932, he toured British Malaya, Europe and the Soviet Union which later influenced his Self-Respect Movement in favor of caste equality. In 1939, he became the head of the Justice Party, which he transformed into a social organisation named ''Dravidar Kazhagam'' in 1944. The party later split with one group led by C. N. Annadurai forming the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK) in 1949. While continuing the Self-Respect Movement, he advocated for an independent Dravida Nadu (land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrimination In India
Discrimination is the process of making unfair or prejudicial Distinction (sociology), distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong, such as Racial discrimination, race, Sexism, gender, Ageism, age, Class discrimination, class, Religious discrimination, religion, or Sexual orientation discrimination, sexual orientation. Discrimination typically leads to groups being unfairly treated on the basis of perceived statuses based on ethnic, racial, gender or religious categories. It involves depriving members of one group of opportunities or privileges that are available to members of another group. Discriminatory traditions, policies, ideas, practices and laws exist in many countries and institutions in all parts of the world, including some, where such discrimination is generally decried. In some places, countervailing measures such as quotas have been used to redress the balance in favor of those who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics Of India
The Politics and Government of India works within the framework of the country's Constitution, which was adopted in 1950. India is a parliamentary secular democratic republic, described as a “sovereign, socialist, secular democratic republic” in its constitution, in which the president of India is the head of state & first citizen of India and the Prime Minister of India is the head of government. It is based on the federal structure of government, although the word is not used in the Constitution itself. India follows the dual polity system, i.e. federal in nature, that consists of the central authority at the centre and states at the periphery. The Constitution defines the organizational powers and limitations of both central and state governments; it is well recognised, fluid (with the Preamble of the Constitution, fundamental rights, and principles of liberty, equality, justice, and fraternity, being rigid and to dictate further amendments to the Constitution) and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
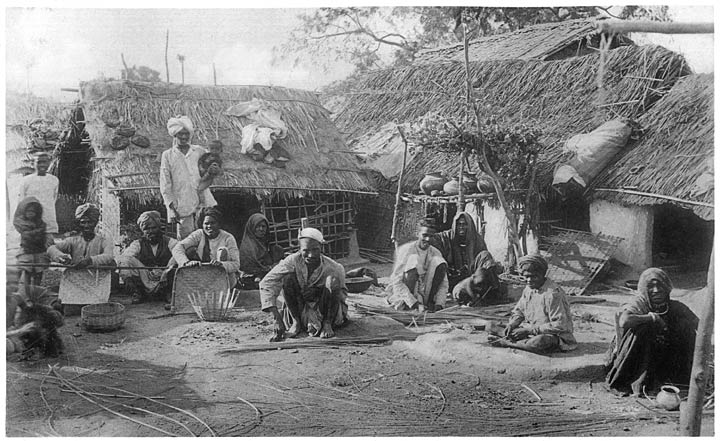
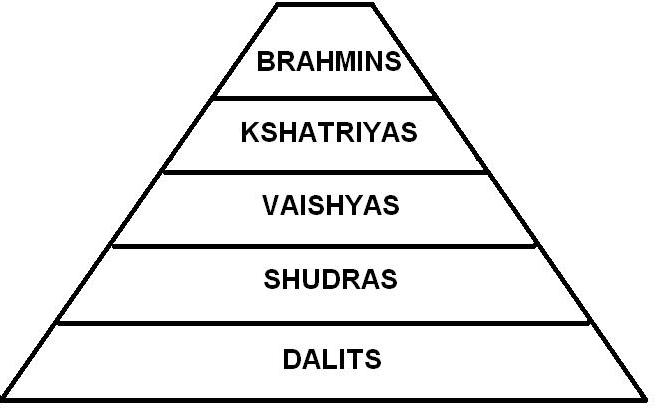
Caste System In India
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic instance of social classification based on castes. It has its origins in ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, especially in the aftermath of the collapse of the Mughal Empire and the establishment of the British Raj. Beginning in ancient India, the caste system was originally centered around '' varna'', with ''Brahmins'' (priests) and, to a lesser extent, ''Kshatriyas'' (rulers and warriors) serving as the elite classes, followed by '' Vaishyas'' (traders, merchants, and farmers) and finally '' Shudras'' (labourers). Outside of this system are the oppressed, marginalised, and persecuted '' Dalits'' (also known as " Untouchables") and '' Adivasis'' (tribals). Over time, the system became increasingly rigid, and the emergence of '' jati'' led to further entrenchment, introducing thousands of new castes and sub-castes. With the arrival of Islamic rule, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Indian Express
''The Indian Express'' is an English-language Indian daily newspaper founded in 1932 by P. Varadarajulu Naidu. It is headquartered in Noida, owned by the ''Indian Express Group''. It was later taken over by Ramnath Goenka. In 1999, eight years after Goenka's death in 1991, the group was split between the family members. The southern editions took the name '' The New Indian Express'', while the northern editions, based in Mumbai, retained the original ''Indian Express'' name with ''The'' prefixed to the title. History In 1932, the ''Indian Express'' was started by an Ayurvedic doctor, P. Varadarajulu Naidu, at Chennai, being published by his Tamil Nadu press. Soon under financial difficulties, he sold the newspaper to Swaminathan Sadanand, the founder of '' The Free Press Journal'', a national news agency. In 1933, the ''Indian Express'' opened its second office in Madurai, launching the Tamil edition, '' Dinamani''. Sadanand introduced several innovations and reduced t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California Press
The University of California Press, otherwise known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish scholarly and scientific works by faculty of the University of California, established 25 years earlier in 1868. As the publishing arm of the University of California system, the press publishes over 250 new books and almost four dozen multi-issue journals annually, in the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences, and maintains approximately 4,000 book titles in print. It is also the digital publisher of Collabra and Luminos open access (OA) initiatives. The press has its administrative office in downtown Oakland, California, an editorial branch office in Los Angeles, and a sales office in New York City, New York, and distributes through marketing offices in Great Britain, Asia, Australia, and Latin America. A Board consisting of senior officers of the University of Cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservations In India
Reservation is a system of affirmative action in India that was established during the British Raj. Based on provisions in the Indian Constitution, it allows the Union Government and the States and Territories of India to allocate a specific percentage of 'reserved quotas' or 'seats', in higher education admissions, employment, political bodies, etc., for "Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Backward Classes and Economically Weaker Sections". Since its implementation, reservation has been a subject of massive debates and controversies over its impact, execution and effectiveness, significantly shaping the agendas of political parties and the actions of social groups. History of Reservation Before independence Quota systems favouring certain castes and other communities existed before independence in the British raj. Demands for various forms of positive discrimination has been made, for example, in 1881 and 1891. Chatrapati Shahu, the Maharaja of the princely state of Kolhapu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caste Politics
In India, a caste although it's a western stratification arrived from Portuguese word Casta and Latin word castus, is a (usually endogamous) social group where membership is decided by birth. Broadly, Indian castes are divided into the Forward Castes, Other Backward Classes, Scheduled Castes, and Scheduled Tribes. Indian Christians and Indian Muslims are also function as castes (a full list of castes can be found at the end of this article). With castes separating individuals into different social groups, it follows that each group will have conflicting interests; oftentimes putting those with lower social standing in less favorable positions. An attempt to address this inequality has been the reservation system, which essentially acts as affirmative action to provide representation to caste groups that have been systematically disadvantaged. There have also been other cases where political parties, like the Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP), was formed to challenge the power o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserved Political Positions In India
In India, a number of political positions and university posts are held for specific groups of the population, including Scheduled Castes(SC) and Scheduled Tribes(ST), and women in some cases. There are reserved constituencies both Parliamentary and State Assembly elections. Scheduled Castes (usually abbreviated as SC), and Scheduled Tribes (usually abbreviated as ST) are castes and tribes included in the schedules published by the government to indicate these castes' and tribes' backward status. All voters, including Non-SC, Non-ST community voters, have the right to vote for these candidates belonging to SC or ST candidate, if contesting from their constituency. About 25% of Indian population belongs to SC/ST communities. About the same ratio of seats are reserved for them in the Parliament. In each state, that number will depend on the percentage of population and percentage of SC/ST amongst them. In local body elections, like municipal polls, in addition to SC/ST, othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caste-related Violence In India
Caste-related violence in India has occurred and continues to occur in various forms. According to a report by Human Rights Watch: inhuman, and degrading treatment of over 165 million people in India has been justified on the basis of caste. Caste is descent-based and hereditary in nature. It is a characteristic determined by one's birth into a particular caste, irrespective of the faith practiced by the individual. Caste denotes a traditional system of rigid social stratification into ranked groups defined by descent and occupation. Caste divisions in India dominate in housing, marriage, employment, and general social interaction-divisions that are reinforced through the practice and threat of social ostracism, economic boycotts, and physical violence. Quoting about the atrocities that are committed by land holding communities on Untouchables, Author Dr. C. P. Yadav states that, "Atrocities are committed on the 'Untouchables' in the villages and small towns and the incidents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |