|
Antheridium
An antheridium is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes (called ''antherozoids'' or sperm). The plural form is antheridia, and a structure containing one or more antheridia is called an androecium. The androecium is also the collective term for the stamens of flowering plants. Antheridia are present in the gametophyte phase of cryptogams like bryophytes and ferns. Many algae and some fungi, for example, ascomycetes and water moulds, also have antheridia during their reproductive stages. In gymnosperms and angiosperms, the male gametophytes have been reduced to pollen grains, and in most of these, the antheridia have been reduced to a single generative cell within the pollen grain. During pollination, this generative cell divides and gives rise to sperm cells. The female counterpart to the antheridium in cryptogams is the archegonium, and in flowering plants is the gynoecium. An antheridium typically consists of sterile cells and spermatogenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chara (alga)
''Chara'' is a genus of charophyte green algae in the family Characeae. They are multicellular and superficially resemble land plants because of stem-like and leaf-like structures. They are found in freshwater, particularly in limestone areas throughout the northern temperate zone, where they grow submerged, attached to the muddy bottom. They prefer less oxygenated and hard water and are not found in waters where mosquito larvae are present. They are covered with calcium carbonate (CaCO3) deposits and are commonly known as stoneworts. Cyanobacteria have been found growing as epiphytes on the surfaces of ''Chara'', where they may be involved in fixing nitrogen, which is important to plant nutrition. Structure The branching system of ''Chara'' species is complex with branches derived from apical cells which cut off segments at the base to form nodal and internodal cells alternately.Round, F.E. 1965.''The Biology of the algae.'' Ernest Arnold. The main axes bear whorls of bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycete
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of Ascomycota are asexual and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as '' Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (containing all of the descendants of a common ancestor). Previously placed in the Basidiomycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomycetes are now identified and classified based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
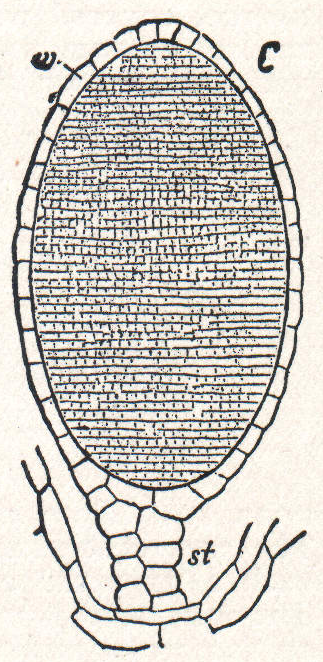
Archegonium
An archegonium (: archegonia), from the Ancient Greek ''ἀρχή'' ("beginning") and ''γόνος'' ("offspring"), is a multicellular structure or organ of the gametophyte phase of certain plants, producing and containing the ovum or female gamete. The corresponding male organ is called the antheridium. The archegonium has a long neck canal or venter and a swollen base. Archegonia are typically located on the surface of the plant thallus, although in the hornworts they are embedded. __TOC__ Bryophytes In bryophytes and other cryptogams, sperm reach the archegonium by swimming in water films, whereas in Pinophyta and angiosperms, the pollen are delivered by wind or animal vectors and the sperm are delivered by means of a pollen tube. In the moss ''Physcomitrella patens'', archegonia are not embedded but are located on top of the leafy gametophore (s. Figure). The Polycomb protein FIE is expressed in the unfertilized egg cell (right) as the blue colour after GUS staining revea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. The name gamete was introduced by the German cytologist Eduard Strasburger in 1878. Gametes of both mating individuals can be the same size and shape, a condition known as isogamy. By contrast, in the majority of species, the gametes are of different sizes, a condition known as anisogamy or heterogamy that applies to humans and other mammals. The human ovum has approximately 100,000 times the volume of a single human sperm cell. The type of gamete an organism produces determines its sex and sets the basis for the sexual roles and sexual selection. In humans and other species that produce two Morphology (biology), morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which Gonochorism, each individual produces only one type, a femal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plants contain non-motile sperm inside pollen, while some more basal plants like ferns and some gymnosperms have motile sperm. Sperm cells form during the process known as spermatogenesis, which in amniotes (reptiles and mammals) takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles. This process involves the production of several successive sperm cell precursors, starting with spermatogonia, which Cellular differentiation, differentiate into spermatocytes. The spermatocytes then undergo meiosis, reducing their Ploidy, chromosome number by half, which produces spermatids. The sper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marchantia Polymorpha
''Marchantia polymorpha'' is a species of large thalloid liverwort in the class Marchantiopsida. ''M. polymorpha'' is highly variable in appearance and contains several subspecies. This species is dioicous, having separate male and female plants. ''M. polymorpha'' has a wide distribution and is found worldwide.Matthews, Robin F. 1993. Marchantia polymorpha. In: Fire Effects Information System, nline U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: https://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/plants/bryophyte/marpol/all.html 017, December 8 Common names include common liverwort or umbrella liverwort. Distribution ''Marchantia polymorpha'' subsp. ''ruderalis'' has a circumpolar boreo-arctic cosmopolitan distribution, found worldwide on all continents except Antarctica. Habitat ''Marchantia polymorpha'' grows on shaded moist soil and rocks in damp habitats such as the banks of streams and pools, bogs, fens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynoecium
Gynoecium (; ; : gynoecia) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl (botany), whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) ''#Pistil, pistils'' and is typically surrounded by the pollen-producing plant reproductive morphology, reproductive organs, the stamens, collectively called the androecium. The gynoecium is often referred to as the "female" portion of the flower, although rather than directly producing female gametes (i.e. egg cells), the gynoecium produces megaspores, each of which develops into a female gametophyte which then produces egg cells. The term gynoecium is also used by botanists to refer to a cluster of archegonia and any associated modified leaves or stems present on a gametophyte shoot in mosses, Marchantiophyta, liverworts, and hornworts. The corresponding terms for the male parts of those plants are clusters of antheridiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oogonium
An oogonium (: oogonia) is a small diploid cell which, upon maturation, forms a primordial follicle in a female fetus or the female (haploid or diploid) gametangium of certain thallophytes. In the mammalian fetus Oogonia are formed in large numbers by mitosis early in fetus, fetal development from germ cell, primordial germ cells. In humans they start to develop between weeks 4 and 8 and are present in the fetus between weeks 5 and 30. Structure Normal oogonia in human ovary, ovaries are spherical or ovoid in shape and are found amongst neighboring somatic (biology), somatic cells and oocytes at different phases of development. Oogonia can be distinguished from neighboring somatic cells, under an electron microscope, by observing their Cell nucleus, nuclei. Oogonial nuclei contain randomly dispersed fibrillar and granular material whereas the somatic cells have a more condensed nucleus that creates a darker outline under the microscope. Oogonial nuclei also contain dense p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients, and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaf, leaves called megaphylls that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled Fiddlehead fern, fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate (Polypodiidae (plant), Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, Psilotaceae, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid ferns. The fern crown group, consisting of the leptosporangiates and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue (biology)
In biology, tissue is an assembly of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same embryonic origin that together carry out a specific function. Tissues occupy a Biological organisation#Levels, biological organizational level between cell (biology), cells and a complete organ (biology), organ. Accordingly, organs are formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" Morphological derivation, derives from the French word "", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is Studied Space Shuttle designs, studied in both plant anatomy and Plant physiology, physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the Microtome#Applications, paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the staining, histological stain, and the Microscope, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |