|
Anterior Atlantooccipital Membrane
The anterior atlantooccipital membrane (anterior atlantooccipital ligament) is a broad, dense membrane extending between the anterior margin of the foramen magnum (superiorly), and (the superior margin of) the anterior arch of atlas (inferiorly). The membrane helps limit excessive movement at the atlanto-occipital joints. Anatomy Structure It is composed of broad, densely woven fibers; especially towards the midline where the membrane is continuous medially with the anterior longitudinal ligament. It is innervated by the cervical spinal nerve 1. Relations Medially, it is continuous with the anterior longitudinal ligament. Laterally, it is blends with either articular capsule In anatomy, a joint capsule or articular capsule is an envelope surrounding a synovial joint. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Atlantoaxial Ligament
The anterior atlantoaxial ligament is a strong membrane, fixed above the lower border of the anterior arch of the atlas; below, to the front of the body of the axis. It is strengthened in the middle line by a rounded cord, which connects the tubercle on the anterior arch of the atlas to the body of the axis. It is a continuation upward of the anterior longitudinal ligament. Structure Anatomical relations The anterior atlantoaxial ligament is situated anterior to the longus capitis muscle The longus capitis muscle (Latin for ''long muscle of the head'', alternatively rectus capitis anticus major) is broad and thick above, narrow below, and arises by four tendinous slips, from the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of t .... See also * Atlanto-axial joint References External links Description at spineuniverse.com Ligaments of the head and neck Bones of the vertebral column {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen Magnum
The foramen magnum () is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes through the foramen magnum as it exits the cranial cavity. Apart from the transmission of the medulla oblongata and its membranes, the foramen magnum transmits the vertebral arteries, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the tectorial membranes and alar ligaments. It also transmits the accessory nerve into the skull. The foramen magnum is a very important feature in bipedal mammals. One of the attributes of a biped's foramen magnum is a forward shift of the anterior border of the cerebellar tentorium; this is caused by the shortening of the cranial base. Studies on the foramen magnum position have shown a connection to the functional influences of both posture and locomotion. The forward shift of the foramen magnum is apparent in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Arch Of Atlas
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. The bone is named for Atlas of Greek mythology, just as Atlas bore the weight of the heavens, the first cervical vertebra supports the head. However, the term atlas was first used by the ancient Romans for the seventh cervical vertebra (C7) due to its suitability for supporting burdens. In Greek mythology, Atlas was condemned to bear the weight of the heavens as punishment for rebelling against Zeus. Ancient depictions of Atlas show the globe of the heavens resting at the base of his neck, on C7. Sometime around 1522, anatomists decided to call the first cervical vertebra the atlas. Scholars believe that by switching the designation atlas from the seventh to the first cervical vertebra Renaissance anatomists were commenting that the point of man's burden had shifted from his shoulders to his head—that man's true burden was not a physical load, but rather, his min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas (anatomy)
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. The bone is named for Atlas of Greek mythology, just as Atlas bore the weight of the heavens, the first cervical vertebra supports the head. However, the term atlas was first used by the ancient Romans for the seventh cervical vertebra (C7) due to its suitability for supporting burdens. In Greek mythology, Atlas was condemned to bear the weight of the heavens as punishment for rebelling against Zeus. Ancient depictions of Atlas show the globe of the heavens resting at the base of his neck, on C7. Sometime around 1522, anatomists decided to call the first cervical vertebra the atlas. Scholars believe that by switching the designation atlas from the seventh to the first cervical vertebra Renaissance anatomists were commenting that the point of man's burden had shifted from his shoulders to his head—that man's true burden was not a physical load, but rather, his m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlanto-occipital Joint
The atlanto-occipital joint (''Articulatio atlantooccipitalis'') is an articulation between the atlas bone and the occipital bone. It consists of a pair of condyloid joints. It is a synovial joint. Structure The atlanto-occipital joint is an articulation between the atlas bone and the occipital bone. It consists of a pair of condyloid joints. It is a synovial joint. Ligaments The ligaments connecting the bones are: * Two articular capsules * Posterior atlanto-occipital membrane * Anterior atlanto-occipital membrane Capsule The capsules of the atlantooccipital articulation surround the condyles of the occipital bone, and connect them with the articular processes of the atlas: they are thin and loose. Variation Atlantooccipital fusion, also known as occipitalization of the atlas, is a congenital or acquired anomaly characterized by the partial or complete fusion of the atlas to the base of the occipital bone. It is found in 0.12% to 0.72% of the population. This fusio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
The anterior longitudinal ligament is a ligament that extends across the anterior/ventral aspect of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs the spine. It may be partially cut to treat certain abnormal curvatures in the vertebral column, such as kyphosis. Anatomy The anterior longitudinal ligament extends superoinferiorly between the basiocciput of the skull and the anterior tubercle of the atlas (cervical vertebra C1) superiorly, and the superior part of the sacrum inferiorly; inferiorly, it ends at the sacral promontory. It broadens inferiorly. Inferiorly, it becomes continuous with the anterior sacrococcygeal ligament. Superiorly, between the skull and atlas, the ligament is continuous laterally with the anterior atlantooccipital membrane. The ligament is thick and slightly more narrow over the vertebral bodies and thinner but slightly wider over the intervertebral discs. It tends to be narrower and thicker around thoracic vertebrae, and wider and thinner around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Spinal Nerve 1
The cervical spinal nerve 1 (C1) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment. from spinalcordinjuryzone.com. Published February 23, 2004 Archived Dec 23, 2011. Retrieved June 12, 2018. C1 carries predominantly motor fibres, but also a small meningeal branch that supplies sensation to parts of the dura around the foramen magnum (via dorsal rami). It originates from the spinal column from above the (C1). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
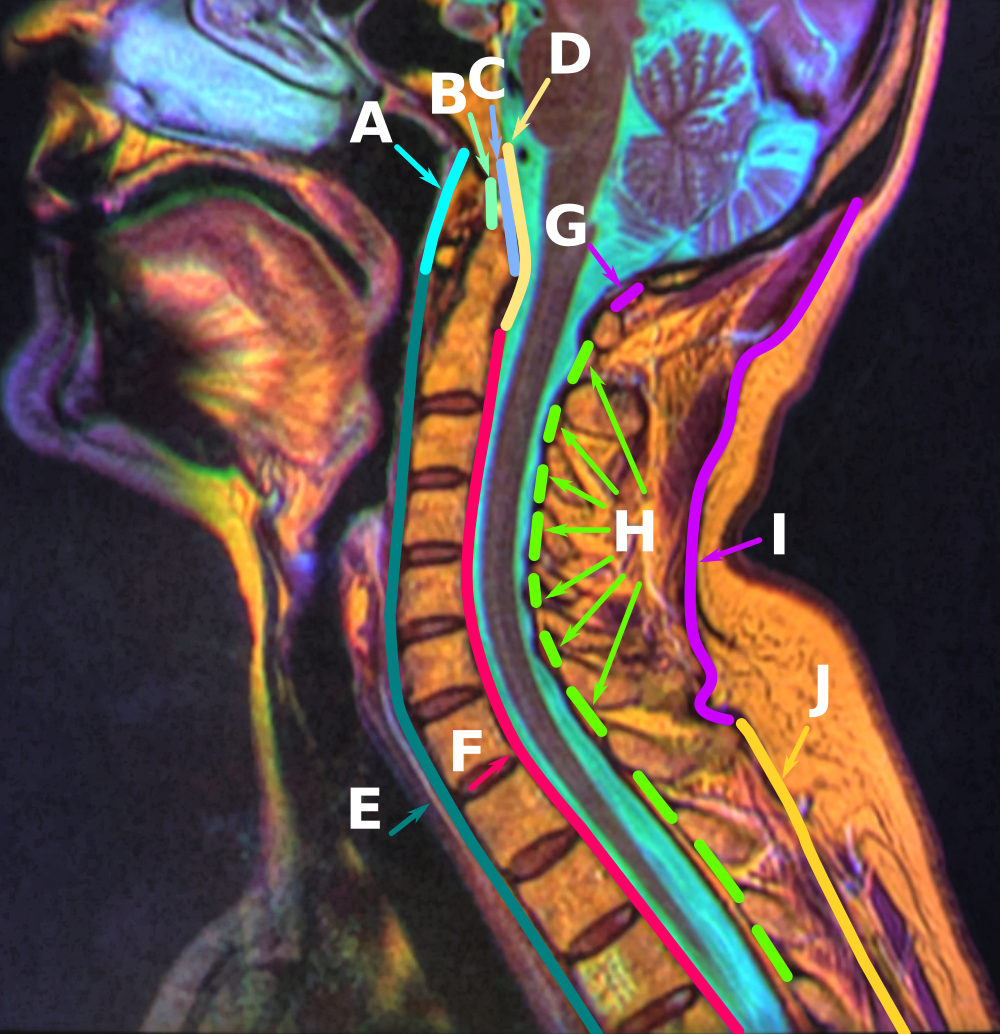
Anatomy Of The Neck Sagittal Color MRI
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine, and is often studied alongside physiology. Anatomy is a complex and dynamic field that is constantly evolving as discoveries are made. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the use of advanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articular Capsules
In anatomy, a joint capsule or articular capsule is an envelope surrounding a synovial joint. Each joint capsule has two parts: an outer fibrous layer or membrane, and an inner synovial layer or membrane. Membranes Each capsule consists of two layers or membranes: * an outer (fibrous membrane, ''fibrous stratum'') composed of avascular white fibrous tissue * an inner ('''', ''synovial stratum'') which is a secreting layer On the inside of the capsule, articular cartilage covers the end surfaces of the bones that articulate within ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectus Capitis Anterior Muscle
The rectus capitis anterior (rectus capitis anticus minor) is a short, flat muscle, situated immediately behind the upper part of the Longus capitis. It arises from the anterior surface of the lateral mass of the atlas, and from the root of its transverse process, and passing obliquely upward and medialward, is inserted into the inferior surface of the basilar part of the occipital bone immediately in front of the foramen magnum. action: aids in flexion of the head and the neck; nerve supply: C1, C2. Additional images File:Rectus capitis anterior muscle - animation01.gif, Animation. Position of rectus capitis anterior muscle. Some bones around the muscle are shown in semi-transparent. File:Rectus capitis anterior muscle - animation02.gif, Skull has been removed (except for occipital bone The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alar Ligaments
In anatomy, the alar ligaments are ligaments which connect the dens (a bony protrusion on the second cervical vertebra) to tubercles on the medial side of the occipital condyle. They are short, tough, fibrous cords that attach on the skull and on the axis, and function to check side-to-side movements of the head when it is turned. Because of their function, the alar ligaments are also known as the "check ligaments of the odontoid". Structure The alar ligaments are two strong, rounded cords of about 0.5 cm in diameter that run from the sides of the foramen magnum of the skull to the dens of the axis, the second cervical vertebra. They span almost horizontally, creating an angle between them of at least 140°. Development The alar ligaments, along with the transverse ligament of the atlas, derive from the axial component of the first cervical sclerotome. Function The function of the alar ligaments is to limit the amount of rotation of the head, and by their action on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Atlantooccipital Membrane
The posterior atlantooccipital membrane (posterior atlantooccipital ligament) is a broad but thin membrane extending between the posterior margin of the foramen magnum above, and posterior arch of atlas (first cervical vertebra) below. It forms the floor of the suboccipital triangle. The membrane helps limit excessive movement of the atlanto-occipital joints. Anatomy Attachments The superior attachment of the membrane at the posterior margin of the foramen magnum, and its inferior attachment is at the superior margin of the posterior arch of atlas (cervical vertebra C1). The membrane additionally attaches posteriorly (by a soft tissue bridge which may contain muscle or tendon fibres) to the recti capitis posteriores minores mucles, and anteriorly to the dura mater. Innervation The membrane is innervated by the spinal nerve C1. Relations At either lateral extremity, the membrane is pierced by the vertebral artery and cervical spinal nerve C1. The free border of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |