|
Antenatal Steroid
Antenatal steroids, also known as antenatal corticosteroids, are medications administered to pregnant women expecting a preterm birth. When administered, these steroids accelerate the maturation of the fetus' lungs, which reduces the likelihood of infant respiratory distress syndrome and infant mortality. The effectiveness of this corticosteroid treatment on humans was first demonstrated in 1972 by Sir Graham Liggins and Ross Howie, during a randomized control trial using betamethasone. Uses Preterm birth Antenatal steroids have been shown to reduce the occurrence and mortality of infant respiratory distress syndrome, a life-threatening condition caused by underdeveloped lungs. Current evidence suggests that giving antenatal corticosteroids reduces risk of late miscarriages and baby deaths. The baby is also less likely to develop respiratory distress syndrome or die during or after birth. They are also less likely to have intraventricular hemorrhage (bleeding of the brain), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone () (cortisone and aldosterone are isomers). The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. The etymology of the '' cortico-'' part of the name refers to the adrenal cortex, which makes these steroid hormones. Thus a corticosteroid is a "cortex steroid". Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometritis
Endometritis is inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). Symptoms may include fever, lower abdominal pain, and abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge. It is the most common cause of infection after childbirth. It is also part of spectrum of diseases that make up pelvic inflammatory disease. Endometritis is divided into acute and chronic forms. The acute form is usually from an infection that passes through the cervix as a result of an abortion, during menstruation, following childbirth, or as a result of douching or placement of an IUD. Risk factors for endometritis following delivery include Caesarean section and prolonged rupture of membranes. Chronic endometritis is more common after menopause. The diagnosis may be confirmed by endometrial biopsy. Ultrasound may be useful to verify that there is no retained tissue within the uterus. Treatment is usually with antibiotics. Recommendations for treatment of endometritis following delivery includes cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetric Drugs
Obstetric medicine, similar to maternal medicine, is a sub-specialty of internal medicine, general internal medicine and obstetrics that specializes in process of prevention, diagnosing, and treating medical disorders in with pregnant women. It is closely related to the specialty of maternal-fetal medicine, although obstetric medicine does not directly care for the fetus. The practice of obstetric medicine, or previously known as "obstetric intervention," primarily consisted of the extraction of the baby during instances of duress, such as obstructed labor or if the baby was positioned in breech. Obstetric physicians may provide care for chronic medical conditions that precede the pregnancy (such as epilepsy, asthma or heart disease), or for new medical problems that develop while the pregnancy is already in progress (such as gestational diabetes, and hypertension). By the 19th century, obstetrics had become recognized as a medical discipline in Europe and the United States. Formal t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
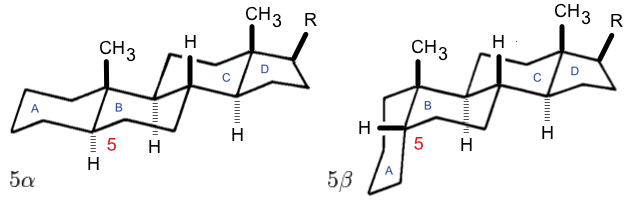
Steroids
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterol: cholesterol (animals), lanosterol ( opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus ( core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four fused rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word ''surfactant'' is a Blend word, blend of "surface-active agent", coined in 1950. As they consist of a water-repellent and a water-attracting part, they enable water and oil to mix; they can form foam and facilitate the detachment of dirt. Surfactants are among the most widespread and commercially important chemicals. Private households as well as many industries use them in large quantities as detergent, detergents and cleaning agents, but also for example as emulsion#Emulsifiers, emulsifiers, wetting agents, foaming agents, Antistatic agent, antistatic additives, or dispersants. Surfactants occur naturally in traditional plant-based detergents, e.g. Aesculus, horse chestnuts or Sapindus, soap nuts; they can also be found in the secretions of some caterpillars. Today one of the most commonly used anionic surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
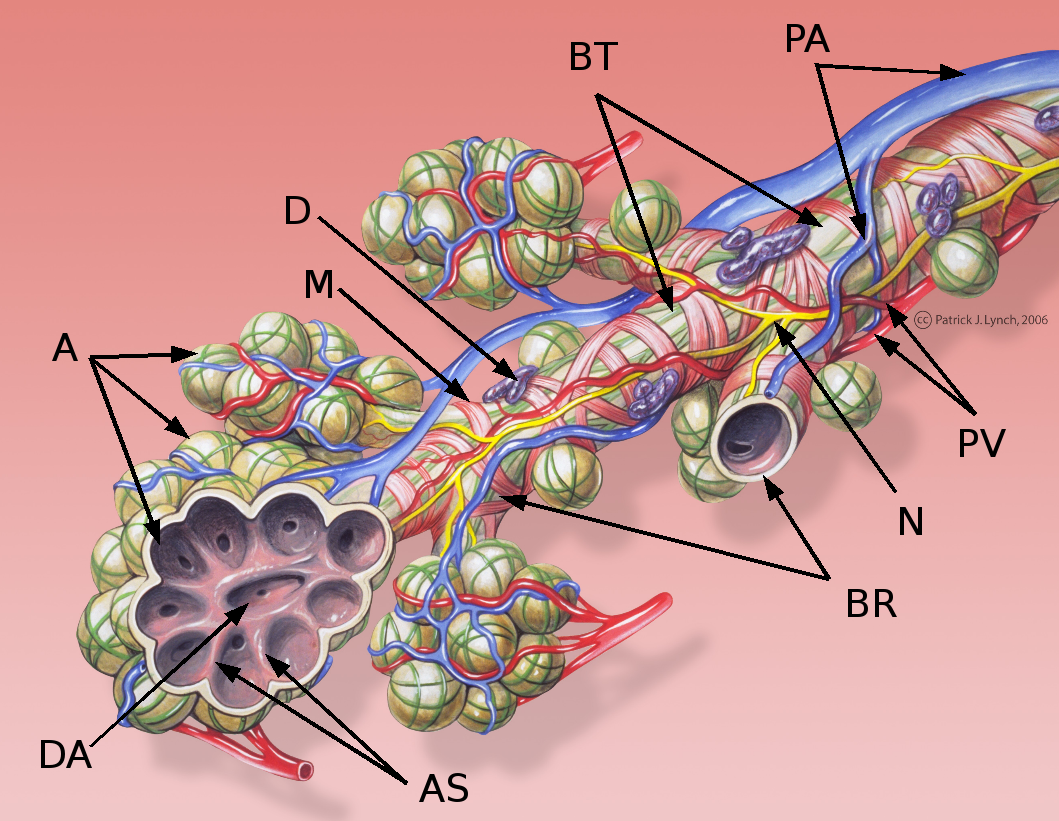
Pulmonary Alveolus
A pulmonary alveolus (; ), also called an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air barrier between the alveolar air and the pulmonary capillary. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Oxygen is diffused across the membrane into the capillaries and carbon dioxide is released fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a fluorinated glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena cava syndrome (a complication of some forms of cancer), and along with antibiotics in tuberculosis. In adrenocortical insufficiency, it may be used in combination with a mineralocorticoid medication such as fludrocortisone. In preterm labor, it may be used to improve outcomes in the baby. It may be given by mouth, as an injection into a muscle, as an injection into a vein, as a topical cream or ointment for the skin or as a topical ophthalmic solution to the eye. The effects of dexamethasone are frequently seen within a day and last for about three days. The long-term use of dexamethasone may result in thrush, bone loss, cataracts, easy bruising, or muscle weakness. It is in pregnancy category C in the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
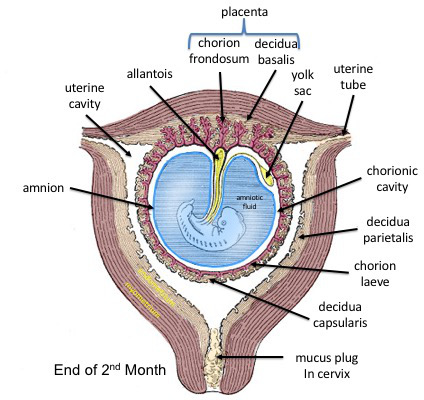
Fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature distinguishing an embryo from a fetus. However, in general a fetus is characterized by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet be fully developed and functional, and some may not yet be situated in their final Anatomy, anatomical location. In human prenatal development, fetal development begins from the ninth week after Human fertilization, fertilization (which is the eleventh week of Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age) and continues until the childbirth, birth of a newborn. Etymology The word ''wikt:fetus#English, fetus'' (plural ''wikt:fetuses#English, fetuses'' or rarely, the solecism ''wikt:feti#English, feti''''Oxford English Dict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes Animal communication#Auditory, vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premature Rupture Of Membranes
Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), previously known as premature rupture of membranes, is breakage of the amniotic sac before the onset of labour. Women usually experience a painless gush or a steady leakage of fluid from the vagina. Complications in the baby may include premature birth, cord compression, and infection. Complications in the mother may include placental abruption and postpartum endometritis. Risk factors include infection of the amniotic fluid, prior PROM, bleeding in the later parts of pregnancy, smoking, and a mother who is underweight. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms and speculum exam and may be supported by testing the vaginal fluid or by ultrasound. If it occurs before 37 weeks it is known as PPROM (preterm prelabor rupture of membranes) otherwise it is known as term PROM. Treatment is based on how far along a woman is in pregnancy and whether complications are present. In those at or near term without any complications, induction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorioamnionitis
Chorioamnionitis, also known as amnionitis and intra-amniotic infection (IAI), is inflammation of the fetal membranes (amnion and chorion), usually due to bacterial infection. In 2015, a National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Workshop expert panel recommended use of the term "triple I" to address the heterogeneity of this disorder. The term triple I refers to intrauterine infection or inflammation or both and is defined by strict diagnostic criteria, but this terminology has not been commonly adopted although the criteria are used. Chorioamnionitis results from an infection caused by bacteria ascending from the vagina into the uterus and is associated with premature or prolonged labor. It triggers an inflammatory response to release various inflammatory signaling molecules, leading to increased prostaglandin and metalloproteinase release. These substances promote uterine contractions and cervical ripening, causations of premature birth. The risk of developing ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medicine, medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are Drug class, classified in many ways. One of the key divisions is by level of controlled substance, control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the medical prescription) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Medicines may be classified by mode of action, route of administration, biological system affected, or therapeutic effects. The World Health Organization keeps a list of essential medicines. Drug discovery and drug development are complex and expensive endeavors undertake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |