|
Ankyrin
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that mediate the attachment of integral membrane proteins to the spectrin-actin based membrane cytoskeleton. Ankyrins have binding sites for the beta subunit of spectrin and at least 12 families of integral membrane proteins. This linkage is required to maintain the integrity of the plasma membranes and to anchor specific ion channels, ion exchangers and ion transporters in the plasma membrane. The name is derived from the Greek word ἄγκυρα (''ankyra'') for "anchor". Structure Ankyrins contain four functional domains: an N-terminal domain that contains 24 tandem ankyrin repeats, a central domain that binds to spectrin, a death domain that binds to proteins involved in apoptosis, and a C-terminal regulatory domain that is highly variable between different ankyrin proteins. Membrane protein recognition The 24 tandem ankyrin repeats are responsible for the recognition of a wide range of membrane proteins. These 24 repeats contain 3 struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANK2
Ankyrin-2, also known as Ankyrin-B, and Brain ankyrin, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''ANK2'' gene. Ankyrin-2 is ubiquitously expressed, but shows high expression in cardiac muscle. Ankyrin-2 plays an essential role in the localization and membrane stabilization of ion transporters and ion channels in cardiomyocytes, as well as in costamere structures. Mutations in ''ANK2'' cause a dominantly-inherited, cardiac Heart arrhythmia, arrhythmia syndrome known as Long QT syndrome, long QT syndrome 4 as well as sick sinus syndrome; mutations have also been associated to a lesser degree with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Alterations in ankyrin-2 expression levels are observed in human heart failure. Structure Ankyrin-B protein is around 220 kDa, with several isoforms. The ''ANK2'' gene is approximately 560 kb in size and consists of 53 exons on human chromosome 4; ''ANK2'' is also transcriptionally regulated via over 30 alternative splicing events with variable expression o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANK1
Ankyrin 1, also known as ANK-1, and erythrocyte ankyrin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ANK1'' gene. Tissue distribution The protein encoded by this gene, Ankyrin 1, is the prototype of the ankyrin family, was first discovered in erythrocytes, but since has also been found in brain and muscles. Genetics Complex patterns of alternative splicing in the regulatory domain, giving rise to different isoforms of ankyrin 1 have been described, however, the precise functions of the various isoforms are not known. Alternative polyadenylation accounting for the different sized erythrocytic ankyrin 1 mRNAs, has also been reported. Truncated muscle-specific isoforms of ankyrin 1 resulting from usage of an alternate promoter have also been identified. Disease linkage Mutations in erythrocytic ankyrin 1 have been associated in approximately half of all patients with hereditary spherocytosis. ANK1 shows altered methylation and expression in Alzheimer's disease. A gene exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankyrin Repeat
The ankyrin repeat is a 33-residue motif in proteins consisting of two alpha helices separated by loops, first discovered in signaling proteins in yeast Cdc10 and ''Drosophila'' Notch. Domains consisting of ankyrin tandem repeats mediate protein–protein interactions and are among the most common structural motifs in known proteins. They appear in bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic proteins, but are far more common in eukaryotes. Ankyrin repeat proteins, though absent in most viruses, are common among poxviruses. Most proteins that contain the motif have four to six repeats, although its namesake ankyrin contains 24, and the largest known number of repeats is 34, predicted in a protein expressed by '' Giardia lamblia''. Ankyrin repeats typically fold together to form a single, linear solenoid structure called ankyrin repeat domains. These domains are one of the most common protein–protein interaction platforms in nature. They occur in a large number of functionally div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANK3
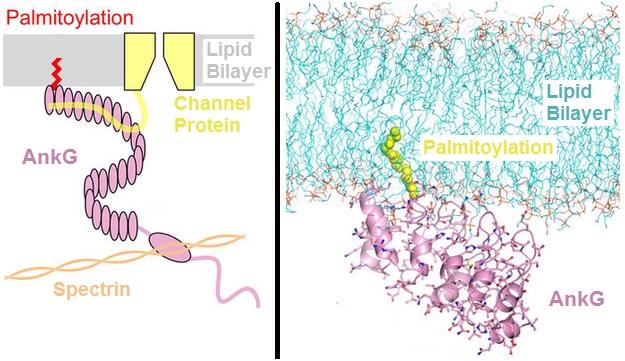
Ankyrin-3 (ANK-3), also known as ankyrin-G, is a protein from ankyrin family that in humans is encoded by the ''ANK3'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene, ankyrin-3 is an immunologically distinct gene product from ankyrins ANK1 and ANK2, and was originally found at the axonal initial segment and nodes of Ranvier of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Alternatively spliced variants may be expressed in other tissues. Although multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms have been found for this gene, the full-length nature of only two have been characterized. Within the nervous system, ankyrin-G is specifically localized to the neuromuscular junction, the axon initial segment and the Nodes of Ranvier. Within the nodes of Ranvier where action potentials are actively propagated, ankyrin-G has long been thought to be the intermediate binding partner to neurofascin and voltage-gated sodium channels. The genetic deletion of ankyrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DARPin
DARPins (an acronym for designed ankyrin repeat proteins) are genetically engineered antibody mimetic proteins typically exhibiting highly specific and high-affinity target protein binding. They are derived from natural ankyrin repeat proteins, one of the most common classes of binding proteins in nature, which are responsible for diverse functions such as cell signaling, regulation and structural integrity of the cell. DARPins consist of at least three, repeat motifs or modules, of which the most N- and the most C-terminal modules are referred to as "caps", since they shield the hydrophobic core of the protein. The number of internal modules is indicated as number (e.g. N1C, N2C, N3C, ...) while the caps are indicated with "N" or "C", respectively. The molecular mass of e.g. 14 or 18 kDa (kilodaltons) for four- (N2C) or five- (N3C) repeat DARPins is rather small for a biologic (ca 10% of the size of an IgG). DARPins constitute a new class of potent, specific and versatile s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Spherocytosis
Hereditary spherocytosis (HS) is a congenital hemolytic disorder, wherein a genetic mutation coding for a structural membrane protein phenotype leads to a spherical shaping of erythrocytic cellular morphology. As erythrocytes are sphere-shaped ( spherocytosis), rather than the normal biconcave disk-shaped, their morphology interferes with these cells' abilities to be flexible during circulation throughout the entirety of the body - arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, and organs. This difference in shape also makes the red blood cells more prone to rupture under osmotic and/or mechanical stress. Cells with these dysfunctional proteins are degraded in the spleen, which leads to a shortage of erythrocytes resulting in hemolytic anemia. HS was first described in 1871, and is the most common cause of inherited hemolysis in populations of northern European descent, with an incidence of 1 in 5000 births. The clinical severity of HS varies from mild (symptom-free carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrin
Spectrin is a cytoskeletal protein that lines the intracellular side of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells. Spectrin forms pentagonal or hexagonal arrangements, forming a scaffold and playing an important role in maintenance of plasma membrane integrity and cytoskeletal structure. The hexagonal arrangements are formed by tetramers of spectrin subunits associating with short actin filaments at either end of the tetramer. These short actin filaments act as junctional complexes allowing the formation of the hexagonal mesh. The protein is named spectrin since it was first isolated as a major protein component of human red blood cells which had been treated with mild detergents; the detergents lysed the cells and the hemoglobin and other cytoplasmic components were washed out. In the light microscope the basic shape of the red blood cell could still be seen as the spectrin-containing submembranous cytoskeleton preserved the shape of the cell in outline. This became known as a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KAHRP
KAHRP (knob-associated histidine-rich protein) is a protein expressed by ''Plasmodium falciparum'' infecting erythrocytes. KAHRP is a major component of knobs, feature found on Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes. It has been suggested that KAHRP may play a role in trafficking or docking PfEMP1, major malarial cytoadherence protein to the erythrocyte membrane; however, these findings were disputed by recent NMR and fluorescence anisotropy studies showing no interaction between PfEMP1 and KAHRP. Instead, KAHRP was shown to interact with Ankyrin, more precisely the D3 subunit of the Membrane-binding domain of Ankyrin type 1. This interaction was suggested via SPR, ELISA, and Pulldown studies, however, it has not been confirmed by NMR, ITC, crystallography Crystallography is the experimental science of determining the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids. Crystallography is a fundamental subject in the fields of materials science and solid-state physics (con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band 3
Band 3 anion transport protein, also known as anion exchanger 1 (AE1) or band 3 or solute carrier family 4 member 1 (SLC4A1), is a protein that is encoded by the gene in humans. Band 3 anion transport protein is a phylogenetically-preserved transport protein responsible for mediating the exchange of chloride (Cl−) with bicarbonate (HCO3−) across plasma membranes. Functionally similar members of the AE clade are AE2 and AE3. Function Band 3 is present in the basolateral face of the α-intercalated cells of the collecting ducts of the nephron, which are the main acid-secreting cells of the kidney. They generate hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions from carbon dioxide and water – a reaction catalysed by carbonic anhydrase. The hydrogen ions are pumped into the collecting duct tubule by vacuolar H+ ATPase, the apical proton pump, which thus excretes acid into the urine. kAE1 exchanges bicarbonate for chloride on the basolateral surface, essentially returning bicarbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly a protein) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample to be tested are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme and then any unbound antibodies are removed. In the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's substrate is added. If there was binding, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change. Performing an ELISA involves at lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPR (gene)
Sepiapterin reductase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SPR'' gene. Function Sepiapterin reductase (7,8-dihydrobiopterin:NADP+ oxidoreductase; EC 1.1.1.153) catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of various carbonyl substances, including derivatives of pteridines, and belongs to a group of enzymes called aldo-keto reductases. SPR plays an important role in the biosynthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin. Reaction Sepiapterin reductase (SPR) catalyzes the chemical reaction L-erythro-7,8-dihydrobiopterin + NADP+ \rightleftharpoons sepiapterin + NADPH + H+ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are L-erythro-7,8-dihydrobiopterin and NADP+, whereas its three products are sepiapterin, NADPH, and a single hydrogen ion (H+). This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, to be specific, those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 7,8-dihydrobiopterin:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |