|
Anhydrides
An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is also an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the parent acid is a carboxylic acid, the formula of the anhydride being (RC(O))2O. Symmetrical acid anhydrides of this type are named by replacing the word ''acid'' in the name of the parent carboxylic acid by the word ''anhydride''. Thus, (CH3CO)2O is called ''acetic anhydride.'' ''Mixed'' (or ''unsymmetrical'') acid anhydrides, such as acetic formic anhydride (see below), are known, whereby reaction occurs between two different carboxylic acids. Nomenclature of unsymmetrical acid anhydrides list the names of both of the reacted carboxylic acids before the word "anhydride" (for example, the dehydration reaction between benzoic acid and propanoic acid would yield "benzoic propanoic anhydride"). One or both acyl groups of an acid anhydride ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . Commonly abbreviated , it is one the simplest organic acid anhydride, anhydrides of a carboxylic acid and is widely used in the production of cellulose acetate as well as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air. Structure and properties Acetic anhydride, like most organic acid anhydrides, is a flexible molecule with a nonplanar structure. The C=O and C-O distances are 1.19 and 1.39 Å. The Pi bond, pi system linkage through the central oxygen offers very weak resonance stabilization compared to the dipole, dipole-dipole repulsion between the two carbonyl oxygens. The energy barriers to bond rotation between each of the optimal aplanar conformations are quite low. Production Acetic anhydride was first synthesized in 1852 by the French chemist Charles Frédéric Gerhardt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Chloride
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride (or acid chloride) is an organic compound with the functional group . Their formula is usually written , where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids (). A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, . Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides. Nomenclature Where the acyl chloride Moiety (chemistry), moiety takes priority, acyl chlorides are named by taking the name of the parent carboxylic acid, and substituting ''-yl chloride'' for ''-ic acid''. Thus: : : :Butyric acid, butyr''ic acid'' (C3H7COOH) → Butyryl chloride, butyr''yl chloride'' (C3H7COCl) (Idiosyncratically, for some trivial names, ''-oyl chloride'' substitutes ''-ic acid''. For example, pival''ic acid'' becomes pival''oyl chloride'' and acryl''ic acid'' becomes acryl''oyl chloride.'' The names pivalyl chloride and acrylyl chloride are less commonly used, although they are arguably more logical.) When other fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phthalic Anhydride
Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used commercially. This white solid is an important industrial chemical, especially for the large-scale production of plasticizers for plastics. In 2000, the worldwide production volume was estimated to be about 3 million tonnes per year. Synthesis and production Phthalic anhydride was first reported in 1836 by Auguste Laurent. Early procedures involved liquid-phase mercury-catalyzed oxidation of naphthalene. The modern industrial variant process instead uses vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) as the catalyst in a gas-phase reaction with naphthalene using molecular oxygen. The overall process involves oxidative cleavage of one of the rings and loss of two of the carbon atoms as carbon dioxide. An alternative process involves oxidation of the two m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maleic Anhydride
Maleic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula . It is the acid anhydride of maleic acid. It is a colorless or white solid with an acrid odor. It is produced industrially on a large scale for applications in coatings and polymers. Structure and bonding Maleic anhydride is a planar molecule. By virtue of the acid anhydride group, the alkene is electrophilic. On account of its cycle of 4 π electrons in an array of 5 atoms with p orbitals, maleic anhydride was long thought to exhibit antiaromaticity. However, a thermochemical study concluded that only 8 kJ/mol of destabilization energy can be ascribed to this effect, making it weakly antiaromatic at best. Production Maleic anhydride is produced by vapor-phase oxidation of butane, ''n''-butane. The overall process converts the methyl groups to carboxylate and dehydrogenation, dehydrogenates the backbone. The selectivity of the process reflects the robustness of maleic anhydride, with its conjugated double-bond system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g., alkyl, alkenyl, aryl), or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They often have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid () is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Anhydride
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid. In organic chemistry, organic acid anhydrides contain the functional group . Organic acid anhydrides often form when one equivalent of water is removed from two equivalents of an organic acid in a dehydration reaction. In inorganic chemistry, an acid anhydride refers to an acidic oxide, an oxide that reacts with water to form an oxyacid (an inorganic acid that contains oxygen or carbonic acid), or with a base to form a salt. See also * Base anhydride, an oxide that reacts with water to form a hydroxide Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It ... salt References {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
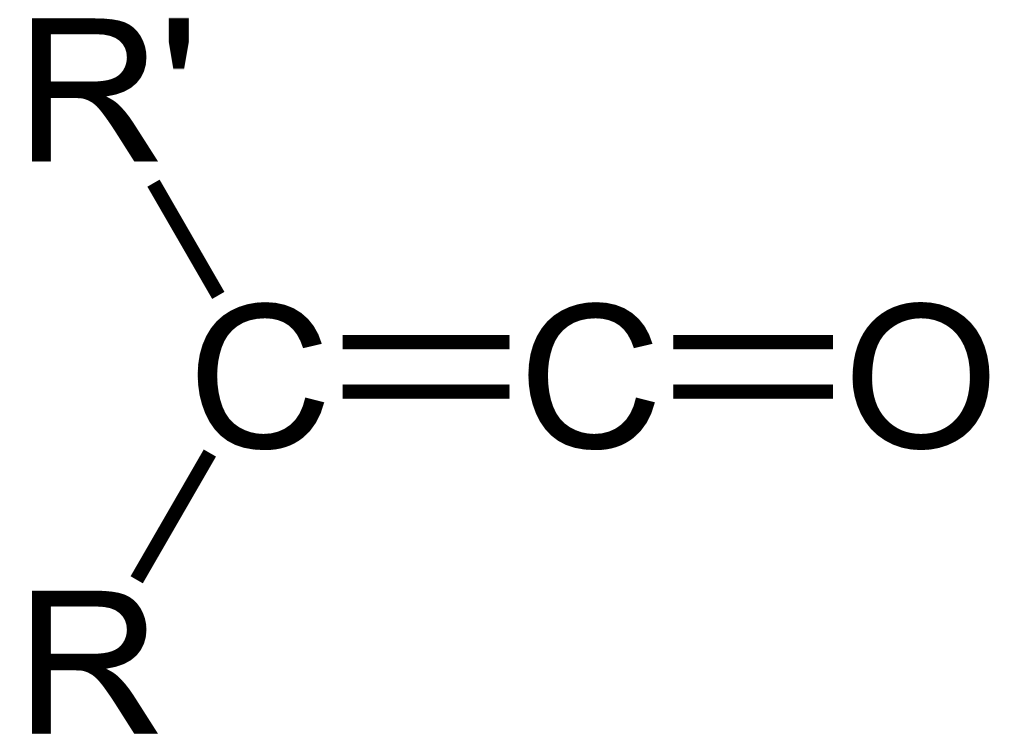
Ketene
In organic chemistry, a ketene is an organic compound of the form , where R and R' are two arbitrary valence (chemistry), monovalent functional group, chemical groups (or two separate Substituent, substitution sites in the same molecule). The name may also refer to the specific compound ethenone , the simplest ketene. Although they are highly useful, most ketenes are chemical stability, unstable. When used as reagents in a chemical procedure, they are typically generated when needed, and consumed as soon as (or while) they are produced. History Ketenes were first studied as a class by Hermann Staudinger before 1905. Ketenes were systematically investigated by Hermann Staudinger in 1905 in the form of diphenylketene (conversion of \alpha-chlorodiphenyl acetyl chloride with zinc). Staudinger was inspired by the first examples of reactive organic intermediates and stable radicals discovered by Moses Gomberg in 1900 (compounds with triphenylmethyl group). Properties Ketenes are h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Formic Anhydride
Acetic formic anhydride is an organic compound with the chemical formula , which can be viewed as the mixed anhydride of acetic acid and formic acid. It is used on a laboratory-scale as a formylating agent. Preparation Acetic formic anhydride can be produced by reacting sodium formate with acetyl chloride in anhydrous diethyl ether between 23–27 °C. It can also be prepared by the reaction of acetic anhydride and formic acid at 0 °C. Properties While more stable than formic anhydride, acetic formic anhydride is thermally unstable and gradually decomposes above about 60 °C, with the evolution of carbon monoxide. Impurities such as pyridine or residual acid can promote this, resulting in decomposition commencing as low as 0 °C. Crude material has been successfully purified by distillation at ≤30 °C under reduced pressure. Applications Acetic formic anhydride is a formylation agent for amines, amino acids, and alcohols. It is also a starting material for ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acyl Group
In chemistry, an acyl group is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids. It contains a double-bonded oxygen atom and an organyl group () or hydrogen in the case of formyl group (). In organic chemistry, the acyl group (IUPAC name alkanoyl if the organyl group is alkyl) is usually derived from a carboxylic acid, in which case it has the formula , where R represents an organyl group or hydrogen. Although the term is almost always applied to organic compounds, acyl groups can in principle be derived from other types of acids such as sulfonic acids and phosphonic acids. In the most common arrangement, acyl groups are attached to a larger molecular fragment, in which case the carbon and oxygen atoms are linked by a double bond. Reactivity trends There are five main types of acyl derivatives. Acid halides are the most reactive towards nucleophiles, followed by anhydrides, esters, and amides. Carboxylate ions are esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redistribution Reaction
In chemistry, redistribution usually refers to the exchange of anionic ligands bonded to metal and metalloid centers. The conversion does not involve redox Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is t ..., in contrast to disproportionation reactions. Some useful redistribution reactions are conducted at higher temperatures; upon cooling the mixture, the product mixture is kinetically frozen and the individual products can be separated. In cases where redistribution is rapid at mild temperatures, the reaction is less useful synthetically but still important mechanistically. Examples Redistribution reactions are exhibited by methylboranes. Thus monomethyldiborane rapidly converts at room temperature to diborane and trimethylborane:. The authors refer to redistributions as "dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |