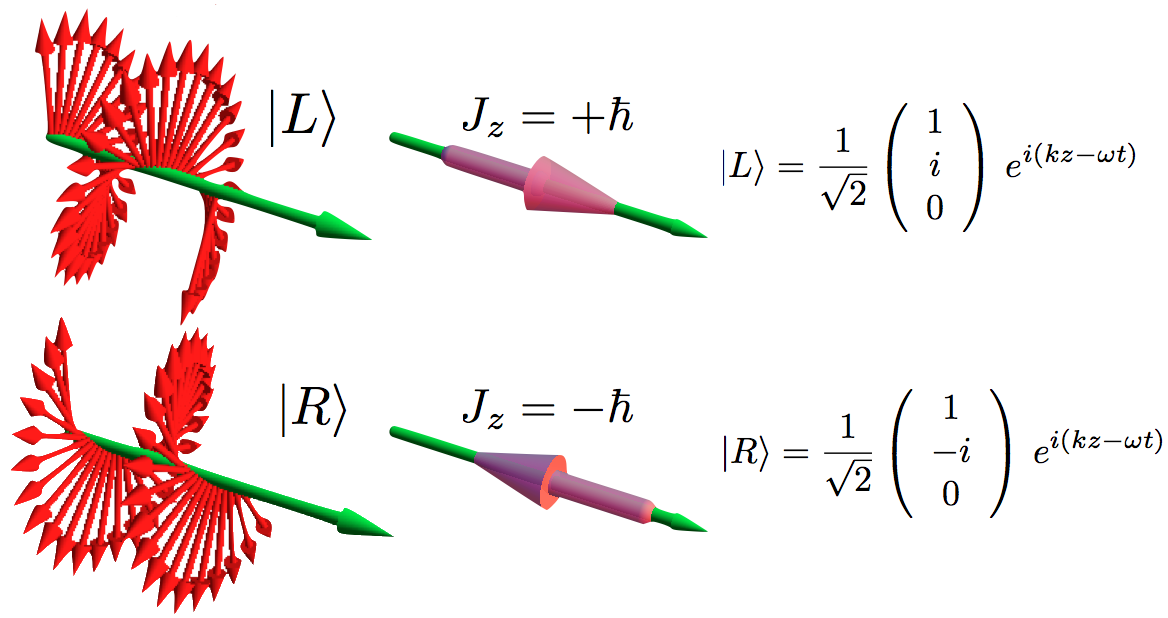|
Angular Momentum Of Light
The angular momentum of light is a vector quantity that expresses the amount of dynamical rotation present in the electromagnetic field of the light. While traveling approximately in a straight line, a beam of light can also be rotating (or "''spinning'', or "''twisting'') around its own axis. This rotation, while not visible to the naked eye, can be revealed by the interaction of the light beam with matter. There are two distinct forms of rotation of a light beam, one involving its polarization and the other its wavefront shape. These two forms of rotation are therefore associated with two distinct forms of angular momentum, respectively named light spin angular momentum (SAM) and light orbital angular momentum (OAM). The total angular momentum of light (or, more generally, of the electromagnetic field and the other force fields) and matter is conserved in time. Introduction Light, or more generally an electromagnetic wave, carries not only energy but also momentum, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OAM Vs Spin Video
OAM may refer to: Science and technology * Object access method, a function available in IBM's z/OS * OCP Accelerator Module, a computer hardware design specification published by the Open Compute Project * Operations, administration, and management, processes involved in maintaining a system, often a computer system * Oracle Access Manager, a software component of the Oracle Identity Management software suite * Orbital angular momentum (other) in physics Other uses * Medal of the Order of Australia, an Australian national honour * Oamaru Aerodrome, New Zealand * Observatorio Astronómico de Mallorca, an observatory in Spain * Office of Alternative Medicine, a U.S. government agency whose duties have been taken over by the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine * Office of Air and Marine, a federal law enforcement agency within the U.S. Customs and Border Protection * Official Museums of Amsterdam, Netherlands * On a Mission (other) * Ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, magnetism is one of two aspects of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt, nickel, and their alloys. All substances exhibit some type of magnetism. Magnetic materials are classified according to their bulk susceptibility. Ferromagnetism is responsible for most of the effects of magnetism encountered in everyday life, but there are actually several types of magnetism. Paramagnetic substances, such as aluminium and oxygen, are weakly attracted to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge Theory
In physics, a gauge theory is a type of field theory in which the Lagrangian, and hence the dynamics of the system itself, does not change under local transformations according to certain smooth families of operations (Lie groups). Formally, the Lagrangian is invariant under these transformations. The term "gauge" refers to any specific mathematical formalism to regulate redundant degrees of freedom in the Lagrangian of a physical system. The transformations between possible gauges, called gauge transformations, form a Lie group—referred to as the '' symmetry group'' or the gauge group of the theory. Associated with any Lie group is the Lie algebra of group generators. For each group generator there necessarily arises a corresponding field (usually a vector field) called the gauge field. Gauge fields are included in the Lagrangian to ensure its invariance under the local group transformations (called gauge invariance). When such a theory is quantized, the quanta of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Potential
In vector calculus, a vector potential is a vector field whose curl is a given vector field. This is analogous to a ''scalar potential'', which is a scalar field whose gradient is a given vector field. Formally, given a vector field \mathbf, a ''vector potential'' is a C^2 vector field \mathbf such that \mathbf = \nabla \times \mathbf. Consequence If a vector field \mathbf admits a vector potential \mathbf, then from the equality \nabla \cdot (\nabla \times \mathbf) = 0 (divergence of the curl is zero) one obtains \nabla \cdot \mathbf = \nabla \cdot (\nabla \times \mathbf) = 0, which implies that \mathbf must be a solenoidal vector field. Theorem Let \mathbf : \R^3 \to \R^3 be a solenoidal vector field which is twice continuously differentiable. Assume that \mathbf(\mathbf) decreases at least as fast as 1/\, \mathbf\, for \, \mathbf\, \to \infty . Define \mathbf (\mathbf) = \frac \int_ \frac \, d^3\mathbf where \nabla_y \times denotes curl with respect to variab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
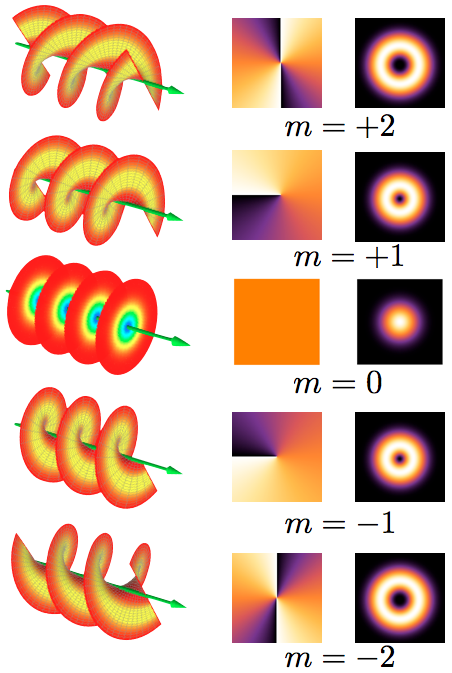
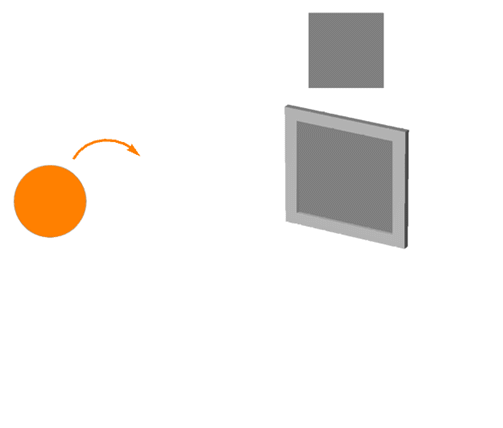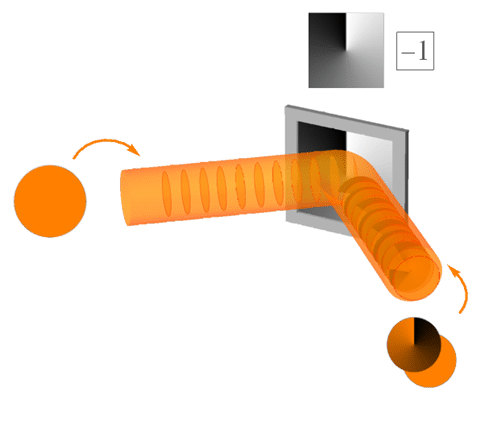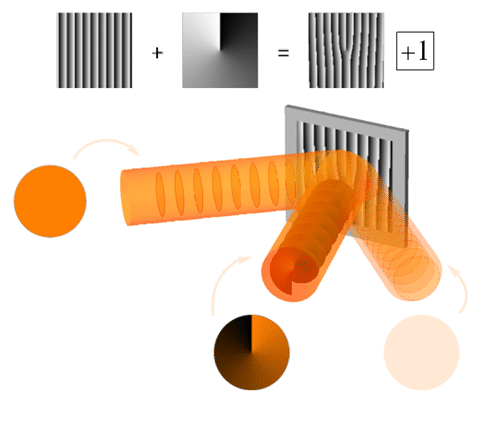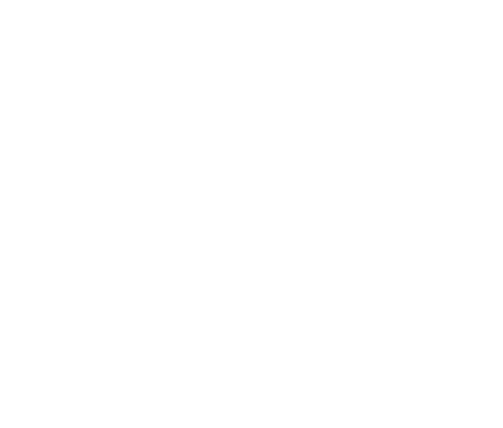
Orbital Angular Momentum Of Light
The orbital angular momentum of light (OAM) is the component of angular momentum of a light beam that is dependent on the field spatial distribution, and not on the polarization. OAM can be split into two types. The ''internal OAM'' is an origin-independent angular momentum of a light beam that can be associated with a helical or twisted wavefront. The ''external OAM'' is the origin-dependent angular momentum that can be obtained as cross product of the light beam position (center of the beam) and its total linear momentum. Concept A beam of light carries a linear momentum \mathbf, and hence it can be also attributed an external angular momentum \mathbf_e=\mathbf\times\mathbf. This external angular momentum depends on the choice of the origin of the coordinate system. If one chooses the origin at the beam axis and the beam is cylindrically symmetric (at least in its momentum distribution), the external angular momentum will vanish. The external angular momentum is a form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Angular Momentum Of Light
The spin angular momentum of light (SAM) is the component of angular momentum of light that is associated with the quantum spin and the rotation between the polarization degrees of freedom of the photon. Introduction Spin is the fundamental property that distinguishes the two types of elementary particles: fermions, with half-integer spins; and bosons, with integer spins. Photons, which are the quanta of light, have been long recognized as spin-1 gauge bosons. The polarization of the light is commonly accepted as its “intrinsic” spin degree of freedom. However, in free space, only two transverse polarizations are allowed. Thus, the photon spin is always only connected to the two circular polarizations. To construct the full quantum spin operator of light, longitudinal polarized photon modes have to be introduced. An electromagnetic wave is said to have circular polarization when its electric and magnetic fields rotate continuously around the beam axis during propagatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noether’s Theorem
Noether's theorem states that every continuous symmetry of the action of a physical system with conservative forces has a corresponding conservation law. This is the first of two theorems (see Noether's second theorem) published by the mathematician Emmy Noether in 1918. The action of a physical system is the integral over time of a Lagrangian function, from which the system's behavior can be determined by the principle of least action. This theorem applies to continuous and smooth symmetries of physical space. Noether's formulation is quite general and has been applied across classical mechanics, high energy physics, and recently statistical mechanics. Noether's theorem is used in theoretical physics and the calculus of variations. It reveals the fundamental relation between the symmetries of a physical system and the conservation laws. It also made modern theoretical physicists much more focused on symmetries of physical systems. A generalization of the formulations on c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Permittivity
Vacuum permittivity, commonly denoted (pronounced "epsilon nought" or "epsilon zero"), is the value of the absolute dielectric permittivity of classical vacuum. It may also be referred to as the permittivity of free space, the electric constant, or the distributed capacitance of the vacuum. It is an ideal (baseline) physical constant. Its CODATA value is: It is a measure of how dense of an electric field is "permitted" to form in response to electric charges and relates the units for electric charge to mechanical quantities such as length and force. For example, the force between two separated electric charges with spherical symmetry (in the vacuum of classical electromagnetism) is given by Coulomb's law: F_\text = \frac \frac Here, ''q''1 and ''q''2 are the charges, ''r'' is the distance between their centres, and the value of the constant fraction 1/(4π''ε''0) is approximately . Likewise, ''ε''0 appears in Maxwell's equations, which describe the properties of electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Angular Momentum Of Light
The orbital angular momentum of light (OAM) is the component of angular momentum of a light beam that is dependent on the field spatial distribution, and not on the polarization. OAM can be split into two types. The ''internal OAM'' is an origin-independent angular momentum of a light beam that can be associated with a helical or twisted wavefront. The ''external OAM'' is the origin-dependent angular momentum that can be obtained as cross product of the light beam position (center of the beam) and its total linear momentum. Concept A beam of light carries a linear momentum \mathbf, and hence it can be also attributed an external angular momentum \mathbf_e=\mathbf\times\mathbf. This external angular momentum depends on the choice of the origin of the coordinate system. If one chooses the origin at the beam axis and the beam is cylindrically symmetric (at least in its momentum distribution), the external angular momentum will vanish. The external angular momentum is a form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave. In electrodynamics, the strength and direction of an electric field is defined by its electric field vector. In the case of a circularly polarized wave, the tip of the electric field vector, at a given point in space, relates to the phase of the light as it travels through time and space. At any instant of time, the electric field vector of the wave indicates a point on a helix oriented along the direction of propagation. A circularly polarized wave can rotate in one of two possible senses: ''right-handed circular polarization (RHCP)'' in which the electric field vector rotates in a right-hand sense with respect to the direction of propagation, and ''left-handed circular polarization (LHCP)'' in which the vecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam Axis
An optical axis is an imaginary line that passes through the geometrical center of an optical system such as a camera lens, microscope or telescopic sight. Lens elements often have rotational symmetry about the axis. The optical axis defines the path along which light propagates through the system, up to first approximation. For a system composed of simple lenses and mirrors, the axis passes through the center of curvature of each surface, and coincides with the axis of rotational symmetry. The optical axis is often coincident with the system's mechanical axis, but not always, as in the case of off-axis optical systems. For an optical fiber, the optical axis is along the center of the fiber core, and is also known as the ''fiber axis''. See also * Ray (optics) * Cardinal point (optics) * Antenna boresight In telecommunications and radar engineering, the antenna boresight is the axis of maximum gain (maximum radiated power) of a directional antenna. For most antennas the bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field) is a physical field, varying in space and time, that represents the electric and magnetic influences generated by and acting upon electric charges. The field at any point in space and time can be regarded as a combination of an electric field and a magnetic field. Because of the interrelationship between the fields, a disturbance in the electric field can create a disturbance in the magnetic field which in turn affects the electric field, leading to an oscillation that propagates through space, known as an ''electromagnetic wave''. The way in which charges and currents (i.e. streams of charges) interact with the electromagnetic field is described by Maxwell's equations and the Lorentz force law. Maxwell's equations detail how the electric field converges towards or diverges away from electric charges, how the magnetic field curls around electrical currents, and how changes in the electric and magnetic fields influence each other. The L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |