|
Angiolipoma
Angiolipoma is a subcutaneous nodule with vascular structure, having all other features of a typical lipoma. They are commonly painful.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . Angiolipomas manifest as multiple painful subcutaneous nodules commonly on the upper limbs. The can occur sporadically, with a family history or after trauma. Angiolipomas can be seen on CT scans and MRI but are diagnosed based on histopathology. Total excision or liposuction is used to treat angiolipomas. They are more common in men and usually appear in third and second decades of life. Signs and symptoms Angiolipoma typically manifests as many, painful subcutaneous nodules (solitary in only one-third of patients), most commonly originating in the upper limbs (of which the forearm accounts for around two thirds), trunk, and lower limbs. These lesions are well-defined, usually measuring less than 4 cm. Caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, or superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's Dermatome (anatomy), dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the Epidermis (botany), epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of Pinna (anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoma
A lipoma is a benign tumor made of adipose tissue, fat tissue. They are generally soft to the touch, movable, and painless. They usually occur just under the skin, but occasionally may be deeper. Most are less than in size. Common locations include upper back, shoulders, and abdomen. It is possible to have several lipomas. The cause is generally unclear. Risk factors include family history, obesity, and lack of exercise. Diagnosis is typically based on a physical exam. Occasionally medical imaging or tissue biopsy is used to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment is typically by watchful waiting, observation or surgical removal. Rarely, the condition may recur following removal, but this can generally be managed with repeat surgery. Lipomas are not generally associated with a future risk of cancer. Lipomas have a prevalence of roughly 2 out of every 100 people. Lipomas typically occur in adults between 40 and 60 years of age. Males are more often affected than females. They are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodule (medicine)
In medicine, nodules are small firm lumps, usually greater than 1 cm in diameter. If filled with fluid they are referred to as cysts. Smaller (less than 0.5 cm) raised soft tissue bumps may be termed papules. The evaluation of a skin nodule includes a description of its appearance, its location, how it feels to touch and any associated symptoms which may give clues to an underlying medical condition. Nodules in skin include dermatofibroma and pyogenic granuloma. Nodules may form on tendons and muscles in response to injury, and are frequently found on vocal cords. They may occur in organs such as the lung, or thyroid, or be a sign in other medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Characteristics Nodules are small firm lumps usually greater than 1 cm in diameter, found in skin and other organs. If filled with fluid they are usually softer and referred to as cysts. Smaller (less than 0.5 cm) raised soft tissue bumps may be termed papules. Eva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: 'tissue', 'suffering', and '' -logia'' 'study of') is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks "). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buffered saline). Preparation for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liposuction
Liposuction, or simply lipo, is a type of fat-removal procedure used in plastic surgery. Evidence does not support an effect on weight beyond a couple of months and does not appear to affect obesity-related problems. In the United States, liposuction is the most common cosmetic surgery. The procedure may be performed under general, regional, or local anesthesia. It involves using a cannula and negative pressure to suck out fat. As a cosmetic procedure it is believed to work best on people with a normal weight and good skin elasticity. While the suctioned fat cells are permanently gone, after a few months overall body fat generally returns to the same level as before treatment. This is despite maintaining the previous diet and exercise regimen. While the fat returns somewhat to the treated area, most of the increased fat occurs in the abdominal area. Visceral fat—the fat surrounding the internal organs—increases, and this condition has been linked to life-shortening ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow ( brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the forearm can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PRKD2
Serine/threonine-protein kinase D2 or PKD2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKD2'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the protein kinase D (PKD) family of serine/threonine protein kinases, a subfamily of protein kinase C. This kinase can be activated by phorbol esters as well as by gastrin via the cholecystokinin B receptor (CCKBR) in gastric cancer cells. It can bind to diacylglycerol (DAG) in the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and may regulate basolateral membrane protein exit from TGN. Alternative splicing Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene ma ... results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * EC 2.7.11 {{gene-19-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignancy
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties, but may still be harmful to health. The term benign in more general medical use characterizes a condition or growth that is not cancerous, i.e. does not spread to other parts of the body or invade nearby tissue. Sometimes the term is used to suggest that a condition is not dangerous or serious. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their entire genomes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
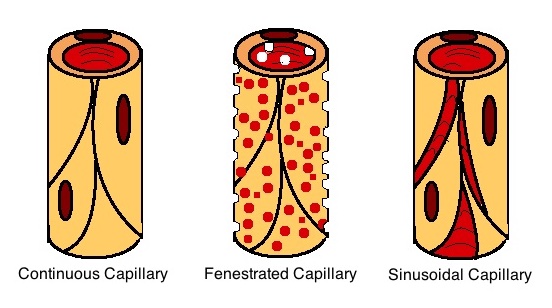
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |