|
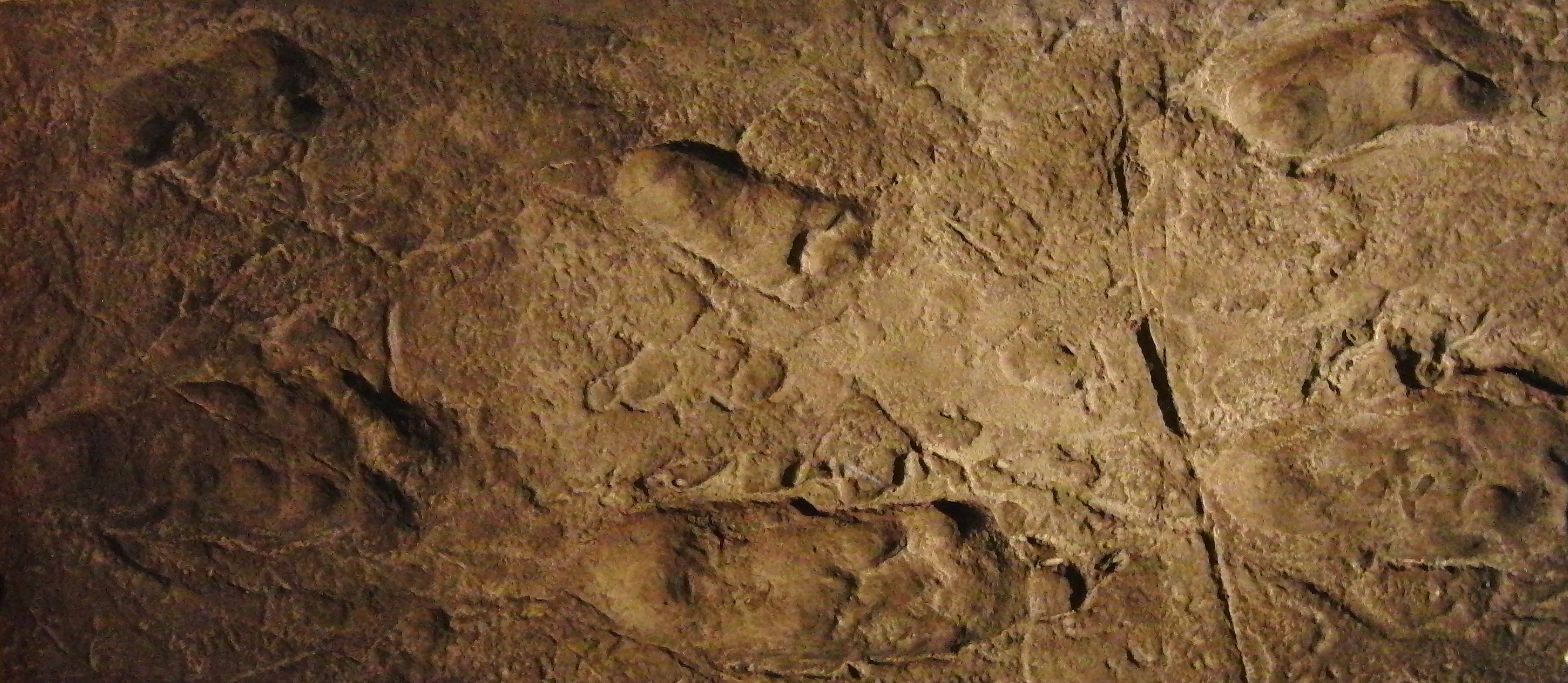
Ancient Footprints Of Acahualinca
The Ancient footprints of Acahualinca (; ) exist in Managua, Nicaragua near the southern shore of Lake Managua. The region was once called "El Cauce". The tracks are fossil Late Holocene human footprints left behind in volcanic ash and mud, which solidified about 2,120±120 years ago, shortly after the group of up to 15 people passed by. It is sometimes reported that the people were running to escape from a volcanic explosion, but the distance between the footprints indicates a walking gait. Fossilized footprints of several animals are also present, but the fact that they intersect the human footprints shows they were not traveling with the people. Scientific analysis of the footprints In 1874, construction workers discovered the footprints. The United States medical doctor and archaeological collector, Earl Flint, brought the footprints to the attention of the international science community and media in 1884. The Carnegie Institution of Washington began the first scientific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eve's Footprint
Eve's footprint is the popular name for a set of fossilised footprints discovered on the shore of Langebaan, Langebaan Lagoon, South Africa in 1995. They are thought to be those of a female human and have been dated to approximately 117,000 years ago. This makes them the oldest known footprints of an Archaic humans, anatomically modern human. The estimated age of Eve's footprint means that the individual who left the tracks in the soil, thought to be female, would have lived within the current wide range of estimates for the date of Mitochondrial Eve. History The three footprints were found in 1995 by geologist David Roberts from the Council for Geoscience and announced at a press conference with paleoanthropologist Lee R. Berger of the University of the Witwatersrand at Johannesburg, South Africa, at the National Geographic Society in Washington, D.C. The discovery was documented in the August 1997 issue of the ''South African Journal of Science''. Berger and Roberts say the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the Federal government of the United States#branches, three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. The Smithsonian Institution has historical holdings of over 157 million items, 21 museums, 21 libraries, 14 education and research centers, a zoo, and historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in Washington, D.C. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York (state), New York, and Virg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
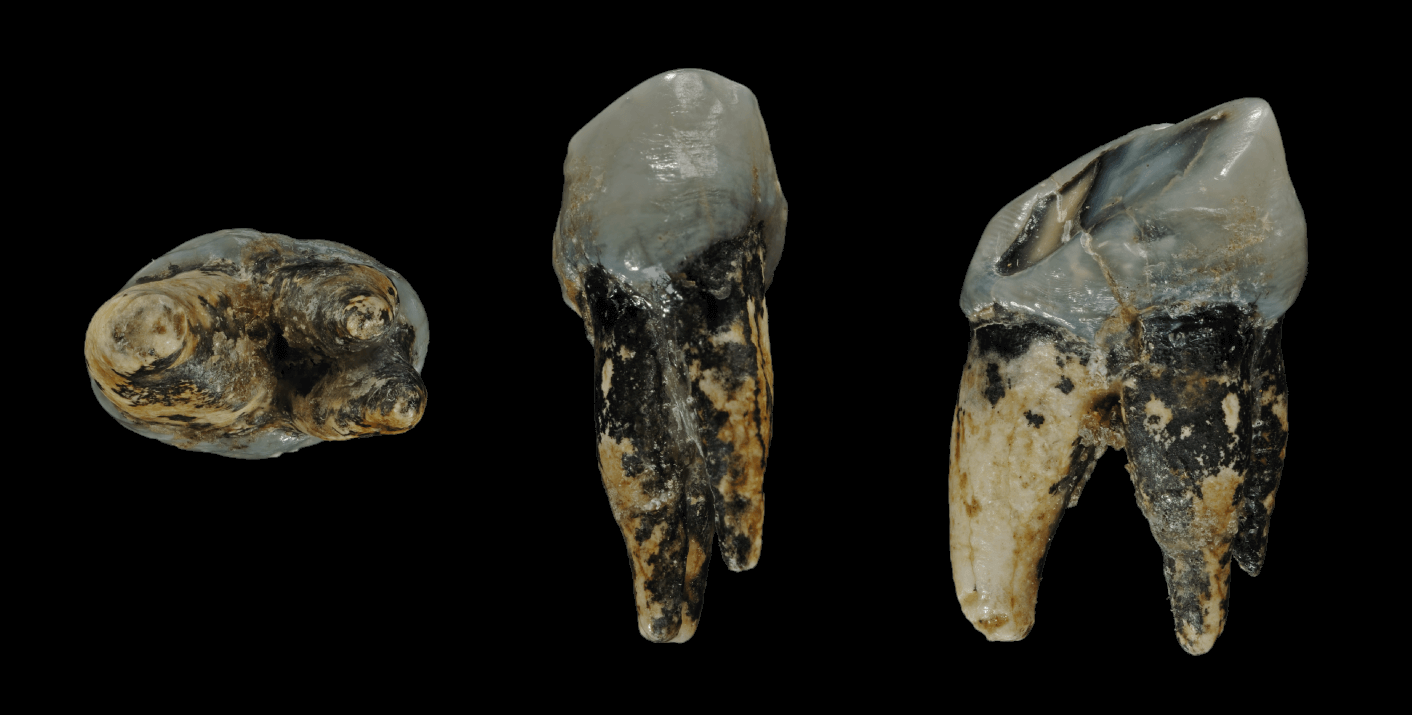
List Of Hominina Fossils
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of hominin fossils and remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but shows some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million years ago (extinction of ''Paranthropus''), all fossils sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossil Sites
This list of fossil sites is a worldwide list of localities known well for the presence of fossils. Some entries in this list are notable for a single, unique find, while others are notable for the large number of fossils found there. Many of the entries in this list are considered Lagerstätten (sedimentary deposits that exhibits extraordinary fossils with exceptional preservation—sometimes including preserved soft tissues). Lagerstätten are indicated by a note () in the noteworthiness column. Fossils may be found either associated with a geological formation or at a single geographic site. Geological formations consist of rock that was deposited during a specific period of time. They usually extend for large areas, and sometimes there are different important sites in which the same formation is exposed. Such sites may have separate entries if they are considered to be more notable than the formation as a whole. In contrast, extensive formations associated with large areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Leakey
Mary Douglas Leakey, Fellow of the British Academy, FBA (née Nicol, 6 February 1913 – 9 December 1996) was a British paleoanthropologist who discovered the first fossilised ''Proconsul (mammal), Proconsul'' skull, an extinct ape which is now believed to be ancestral to humans. She also discovered the robust ''Zinjanthropus'' skull at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania, eastern Africa. For much of her career she worked with her husband, Louis Leakey, at Olduvai Gorge, where they uncovered fossils of ancient hominines and the earliest hominins, as well as the stone tools produced by the latter group. Mary Leakey developed a system for Taxonomy, classifying the stone tools found at Olduvai. She discovered the Laetoli footprints, and at the Laetoli site she discovered hominin fossils that were more than 3.75 million years old. During her career, Leakey discovered fifteen new species of animal. She also brought about the naming of a new genus. In 1972, after the death of her husband, Leake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. According to a 2024 estimate, Tanzania has a population of around 67.5 million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania. In the Stone and Bronze Age, prehistoric migrations into Tanzania included South Cushitic languages, Southern Cushitic speakers similar to modern day Iraqw people who moved south from present-day Ethiopia; Eastern Cushitic people who moved into Tanzania from north of Lake Turkana about 2,000 and 4,000 years ago; and the Southern Nilotic languages, Southern Nilotes, including the Datooga people, Datoog, who originated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hominidae
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic Family (biology), family of primates that includes eight Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant species in four Genus, genera: ''Orangutan, Pongo'' (the Bornean orangutan, Bornean, Sumatran orangutan, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the Eastern gorilla, eastern and western gorilla); ''Pan (genus), Pan'' (the chimpanzee and the bonobo); and ''Homo'', of which only Human, modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') remain. Numerous revisions in classifying the great apes have caused the use of the term ''hominid'' to change over time. The original meaning of "hominid" referred only to humans (''Homo'') and their closest extinct relatives. However, by the 1990s humans and other apes were considered to be "hominids". The earlier restrictive meaning has now been largely assumed by the term ''Hominini, hominin'', which comprises all members of the human clade after the split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laetoli
Laetoli is a pre-historic site located in Enduleni ward of Ngorongoro District in Arusha Region, Tanzania. The site is dated to the Plio-Pleistocene and famous for its Hominina footprints, preserved in volcanic ash. The site of the Laetoli footprints (Site G) is located 45 km south of Olduvai gorge. The location and tracks were discovered by archaeologist Mary Leakey and her team in 1976, and were excavated by 1978. Based on analysis of the footfall impressions "The Laetoli Footprints" provided convincing evidence for the theory of bipedalism in Pliocene Hominina and received significant recognition by scientists and the public. Since 1998, paleontological expeditions have continued under the leadership of Amandus Kwekason of the National Museum of Tanzania and Terry Harrison of New York University, leading to the recovery of more than a dozen new Hominina finds, as well as a comprehensive reconstruction of the paleoecology. The site is a registered National Historic Sites of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. Kenya's capital and largest city is Nairobi. Its second-largest and oldest city is Mombasa, a major port city located on Mombasa Island. Other major cities within the country include Kisumu, Nakuru & Eldoret. Going clockwise, Kenya is bordered by South Sudan to the northwest (though much of that border includes the disputed Ilemi Triangle), Ethiopia to the north, Somalia to the east, the Indian Ocean to the southeast, Tanzania to the southwest, and Lake Victoria and Uganda to the west. Kenya's geography, climate and population vary widely. In western, rift valley counties, the landscape includes cold, snow-capped mountaintops (such as Batian, Nelion and Point Lenana on Mount Kenya) with vast surrounding forests, wildlife and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Erectus
''Homo erectus'' ( ) is an extinction, extinct species of Homo, archaic human from the Pleistocene, spanning nearly 2 million years. It is the first human species to evolve a humanlike body plan and human gait, gait, to early expansions of hominins out of Africa, leave Africa and colonize Asia and Europe, and to Control of fire by early humans, wield fire. ''H. erectus'' is the ancestor of later human species, including ''Homo heidelbergensis, H. heidelbergensis'' — the last common ancestor of human, modern humans, Neanderthals, and Denisovans. As such a widely distributed species both geographically and temporally, ''H. erectus'' anatomy varies considerably. Subspecies are sometimes recognized: ''Java Man, H. e. erectus'', ''Peking Man, H. e. pekinensis'', ''Solo Man, H. e. soloensis'', ''Homo ergaster, H. e. ergaster'', ''Dmanisi hominins, H. e. georgicus'', and ''Tautavel Man, H. e. tautavelensis''. The species was first species description, described by Eugène Dubois i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ileret
Ileret (also spelled Illeret) is a village in Marsabit County, Kenya. It is located in Northern Kenya, on the eastern shore of Lake Turkana, north of Sibiloi National Park and near the Ethiopian border. Numerous hominin fossils have been found near Ileret, including ''Homo erectus'' footprints dating back to about 1.5 million years ago, making them the second oldest hominin footprints ever found after those at Laetoli, Tanzania. Hominin fossils found near Ileret Besides the ''Homo erectus'' footprints, numerous other fossils have been found near the Ileret site. In 2012–2013, a team of researchers from Stony Brook University found new hominin fossils near Ileret, in two sites within the Kolom Odiet area. The fossils were representative of three different individuals, composing of two partial skeletons – KNM-ER ( Kenya National Museum – East Rudolf) 64061 and KNM-ER 64062 – and an almost entirely completed mandible, KNM-ER 64060. KNM-ER 64060 and KNM-ER 64061 dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |