|
Ancient Cappadocia
Cappadocia (; , from ) is a historical region in Central Anatolia region, Turkey. It is largely in the provinces of Nevşehir Province, Nevşehir, Kayseri Province, Kayseri, Aksaray Province, Aksaray, Kırşehir Province, Kırşehir, Sivas Province, Sivas and Niğde Province, Niğde. Today, the touristic Cappadocia Region is located in Nevşehir Province, Nevşehir province. According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revolt (499 BC), the Cappadocians were reported as occupying a region from the Taurus Mountains to the vicinity of the Euxine (Black Sea). Cappadocia, in this sense, was bounded in the south by the chain of mountains that separate it from Cilicia, to the east by the upper Euphrates, to the north by the Pontus (region), Pontus, and to the west by Lycaonia and eastern Galatia. Van Dam, R. ''Kingdom of Snow: Roman rule and Greek culture in Cappadocia.'' Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2002, p.13 The name, traditionally used in Christianity, Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevşehir Province
Nevşehir Province () is a Provinces of Turkey, province in central Turkey with its capital in Nevşehir. Its area is 5,485 km2, and its population is 317,952 (2024). Its adjacent provinces are Kırşehir Province, Kırşehir to the northwest, Aksaray Province, Aksaray to the southwest, Niğde Province, Niğde to the south, Kayseri Province, Kayseri to the southeast, and Yozgat Province, Yozgat to the northeast. Nevşehir includes the area called Cappadociaa tourist attraction in Turkey. The town of Göreme is also located in Nevşehir. Nevşehir was declared a World Peace City by the United Nations. Cappadocia once included the area now covered by this province. This province is notable for the fairy chimneys of Göreme, the Ortahisar, Nevşehir, Ortahisar (middle fortress), a number of old churches from the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine period. History Archaeology An approximately 5,000-year-old three-story underground town which referred as "Gir-Gör" (Enter and See) by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycaonia
Lycaonia (; , ''Lykaonia''; ) was a large region in the interior of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), north of the Taurus Mountains. It was bounded on the east by Cappadocia, on the north by Galatia, on the west by Phrygia and Pisidia, while to the south it extended to the chain of Mount Taurus, where it bordered on the country popularly called in earlier times Cilicia and in the Byzantine period Isauria; but its boundaries varied greatly at different times. The name is not found in Herodotus, but Lycaonia is mentioned by Xenophon as traversed by Cyrus the Younger on his march through Asia. That author describes Iconium as the last city of Phrygia; and in Acts 14:6 Paul, after leaving Iconium, crossed the frontier and came to Lystra in Lycaonia. Ptolemy, on the other hand, includes Lycaonia as a part of the province of Cappadocia, with which it was associated by the Romans for administrative purposes; but the two countries are clearly distinguished both by Strabo and Xenophon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontus (region)
Pontus or Pontos (; ,) is a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, located in the modern-day eastern Black Sea region of Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region and its mountainous hinterland (rising to the Pontic Alps in the east) by the Greeks who colonized the area in the Archaic Greece, Archaic period and derived from the Greek name of the Black Sea: (), 'Hospitable Sea', or simply ''Pontos'' () as early as the Aeschylus, Aeschylean ''The Persians, Persians'' (472 BC) and Herodotus' ''Histories (Herodotus), Histories'' (). Having originally no specific name, the region east of the river Halys River, Halys was spoken of as the country ''()'', , and hence it acquired the name of Pontus, which is first found in Xenophon's ''Anabasis (Xenophon), Anabasis'' (). The extent of the region varied through the ages but generally extended from the borders of Colchis (modern western Georgia (country), Georgia) until well into Paphlagonia in the west, with varying amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf. The Euphrates is the List of longest rivers of Asia, fifteenth-longest river in Asia and the longest in West Asia, at about , with a drainage area of that covers six countries. Etymology The term ''Euphrates'' derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Euphrátēs'' (), adapted from , itself from . The Elamite name is ultimately derived from cuneiform 𒌓𒄒𒉣; read as ''Buranun'' in Sumerian language, Sumerian and ''Purattu'' in Akkadian language, Akkadian; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilicia
Cilicia () is a geographical region in southern Anatolia, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilician plain (). The region includes the provinces of Mersin, Adana, Osmaniye and Hatay. Name The name of Cilicia () was derived from (), which was the name used by the Neo-Assyrian Empire to designate the western part of what would become Cilicia. The English spelling is the same as the Latin, as it was transliterated directly from the Greek form Κιλικία. The palatalization of c occurring in Western Europe in later Vulgar Latin () accounts for its modern pronunciation in English. Geography Cilicia extends along the Mediterranean coast east from Pamphylia to the Nur Mountains, which separate it from Syria. North and east of Cilicia stand the rugged Taurus Mountains, which separate it from the high central plateau of Anatolia, and which are pierced by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia (country), Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is Inflow (hydrology), supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper and Dniester. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea, not including the Sea of Azov, covers , has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taurus Mountains
The Taurus Mountains (Turkish language, Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar,'' Greek language, Greek'':'' Ταύρος) are a mountain range, mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coastal region from the central Anatolia#Anatolian plateau, Anatolian Plateau. The system extends along a curve from Lake Eğirdir in the west to the upper reaches of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the east. It is a part of the Alpide belt in Eurasia. Etymology The mountain range under the current name was mentioned in The Histories (Polybius), ''The Histories'' by Polybius as Ταῦρος (''Taûros''). Heinrich Kiepert writes in ''Lehrbuch der alten Geographie'' that the name was borrowed into Ancient Greek from the Semitic languages, Semitic (Old Aramaic) root wikt:טורא, טורא (''ṭūrā''), meaning "mountain". Geography The Taurus Mountains are divided into three chains from west to east as follows; * Western Taurus (Batı Torosla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris (Asia Minor), Doris, Ancient history of Cyprus, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Achaemenid Empire, Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfaction of the Greek cities of Asia Minor with the Tyranny, tyrants appointed by Persia to rule them, along with the individual actions of two Miletus, Milesian tyrants, Histiaeus and Aristagoras. The cities of Ionia had been conquered by Persia around 540 BC, and thereafter were ruled by native tyrants, nominated by the Persian satrap in Sardis. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, launched a joint expedition with the Persian satrap Artaphernes to conquer Naxos Island, Naxos, in an attempt to bolster his position. The mission was a debacle, and sensing his imminent removal as tyrant, Aristagoras chose to incite the whole of Ionia into rebellion against the Persian king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histories'', a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars, among other subjects such as the rise of the Achaemenid dynasty of Cyrus. He has been described as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero, and the " Father of Lies" by others. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus was criticized in his times for his inclusion of "legends an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niğde Province
Niğde Province () is a Provinces of Turkey, province in the southern part of Central Anatolia, Turkey. Its area is 7,234 km2, and its population is 365,419 (2022) of which 170,511 live in the city of Niğde. The population was 348,081 in 2000 and 305,861 in 1990. Neighbouring provinces are Kayseri Province, Kayseri, Adana Province, Adana, Mersin Province, Mersin, Konya Province, Konya, Aksaray Province, Aksaray and Nevşehir Province, Nevşehir. The province is surrounded on three sides by mountain ranges: the Taurus Mountains, Mount Hasan, and the Melendiz Mountains. Districts Niğde province is divided into 6 Districts of Turkey, districts (capital district in bold): * Altunhisar District, Altunhisar * Bor District, Niğde, Bor * Çamardı District, Çamardı * Çiftlik District, Çiftlik * Niğde District, Niğde * Ulukışla District, Ulukışla Some of the towns within these districts are Bademdere, Bahçeli, Niğde, Bahçeli, Çiftehan, Darboğaz, Fertek and Kemerhis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
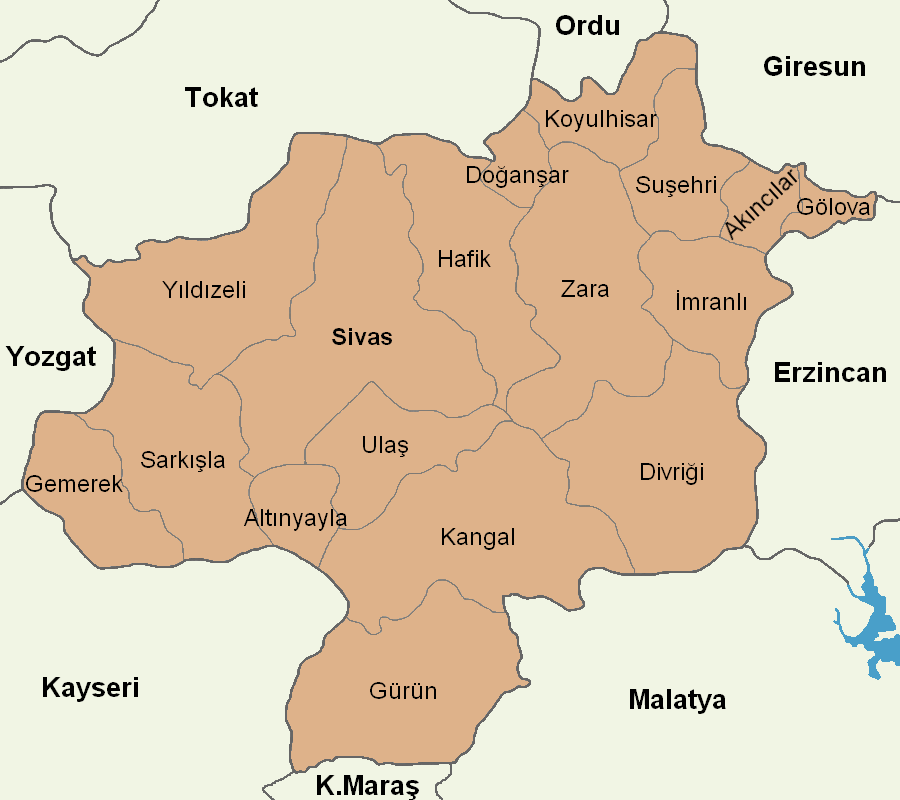
Sivas Province
Sivas Province () is a province of Turkey. It is located in the eastern part of the Central Anatolia region of Turkey. Its area is 28,164 km2 (the second largest province after Konya), and its population is 634,924 (2022). Its adjacent provinces are Yozgat to the west, Kayseri to the southwest, Kahramanmaraş to the south, Malatya to the southeast, Erzincan to the east, Giresun to the northeast, and Ordu to the north. Its capital is Sivas. Most of Sivas Province has the typical continental climate of the Central Anatolian Region, in which summer months are hot and dry, while winter months are cold and snowy. However, the northern part of the province shows some features of the oceanic/ humid subtropical Black Sea climate, while the eastern portion has influences of the Eastern Anatolian highland climate. This province is noted for its thermal springs. Districts Sivas province is divided into 17 districts (capital district in bold): History The route of the Silk R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |