|
Amylomaize
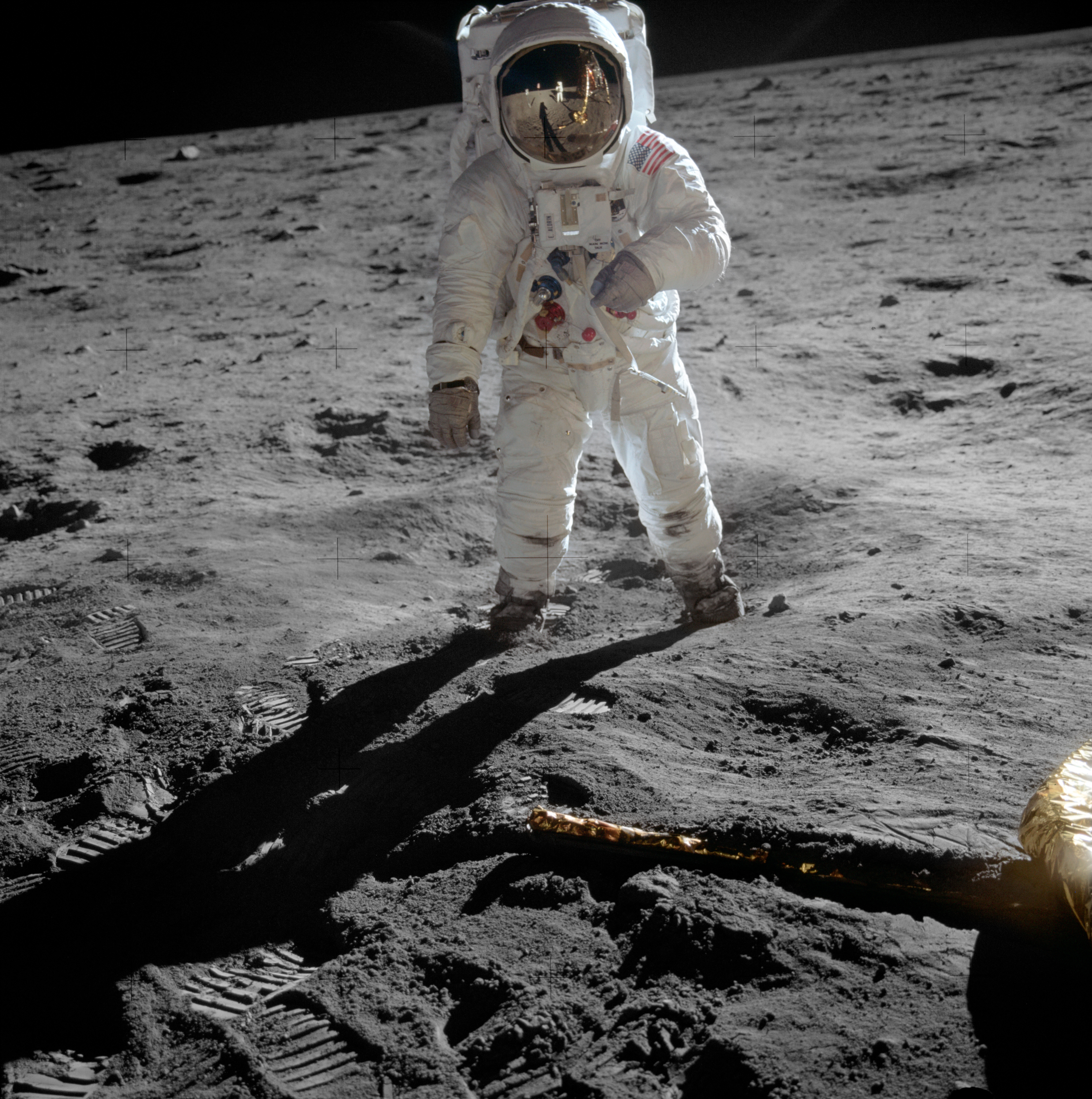
Amylomaize was a term coined in the late 1940s by Robert P. Bear of Bear Hybrids Corn Company in Decatur, Illinois to describe his discovery and commercial breeding of a cornstarch with high (>50%) amylose content, also called high amylose starch. The discovery of amylomaize occurred as a mutation in a normal inbred line; from that one mutation an entire new kind of maize (corn) was developed. Amylomaize starch is principally used in making biodegradable plastics (or bioplastics). It is also used in edible and digestible coatings. The food consumed on Apollo Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ... space flights from 1969 to 1972 were coated with an amylomaize film to prevent crumbs from floating around the space capsule. Several years earlier Robert P. Bear had disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornstarch
Cornflour, cornstarch, maize starch, or corn starch (American English) is the starch derived from corn (maize) grain. The starch is obtained from the endosperm of the kernel. Corn starch is a common food ingredient, often used to thicken sauces or soups, and to make corn syrup and other sugars. Corn starch is versatile, easily modified, and finds many uses in industry such as adhesives, in paper products, as an anti-sticking agent, and textile manufacturing. It has medical uses as well, such as to supply glucose for people with glycogen storage disease. Like many products in dust form, it can be hazardous in large quantities due to its flammability—see dust explosion. When mixed with a fluid, corn starch can rearrange itself into a non-Newtonian fluid. For example, adding water transforms corn starch into a material commonly known as oobleck while adding oil transforms corn starch into an electrorheological (ER) fluid. The concept can be explained through the mixtur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
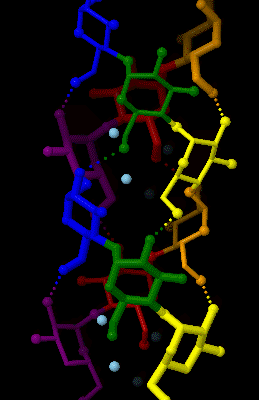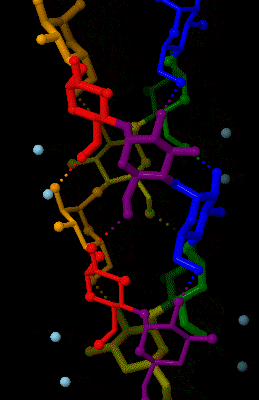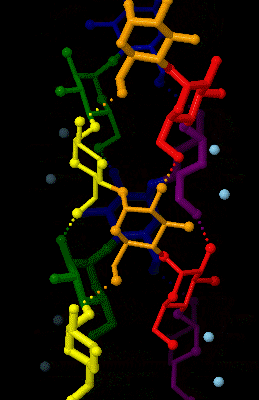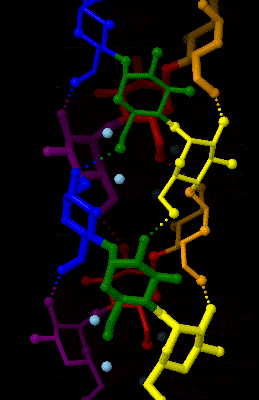
Amylose
Amylose is a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is one of the two components of starch, making up approximately 20–25% of it. Because of its tightly packed Helix, helical structure, amylose is more resistant to digestion than other starch molecules and is therefore an important form of resistant starch. Structure Amylose is made up of α(1→4) bound glucose molecules. The carbon atoms on glucose are numbered, starting at the aldehyde (C=O) carbon, so, in amylose, the 1-carbon on one glucose molecule is linked to the 4-carbon on the next glucose molecule (α(1→4) bonds). The structural formula of amylose is pictured at right. The number of repeated glucose subunits (n) is usually in the range of 300 to 3000, but can be many thousands. There are three main forms of amylose chains can take. It can exist in a disordered amorphous conformation, found both in starch granules and in hydrated amylose (when starch i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioplastic
Bioplastics are plastic materials produced from renewable biomass sources. Timeline of plastic development, Historically, bioplastics made from natural materials like shellac or Celluloid, cellulose had been the first plastics. Since the end of the 19th century they have been increasingly superseded by fossil-fuel plastics derived from petroleum or natural gas (''fossilized'' biomass is not considered to be Renewable resource, renewable in reasonable short time). Today, in the context of bioeconomy and circular economy, bioplastics are gaining interest again. Conventional petro-based polymers are increasingly blended with bioplastics to manufacture "bio-attributed" or "mass-balanced" plastic products - so the difference between bio- and other plastics might be difficult to define. Bioplastics can be produced by: * processing directly from Biopolymer, natural biopolymers including polysaccharides (e.g., corn starch or rice starch, cellulose, chitosan, and alginate) and proteins ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waxy Corn
Waxy corn or glutinous corn is a type of corn characterized by its sticky texture when cooked. It has big round kernels that have endosperms that are almost universally white, though the aleurone layers can sometimes be purple or red which cause some cultivars to be multi-colored or even deep purple to black. Waxy corn is absent in the Americas and is believed to have originated from a single chromosome, chromosomal mutation soon after the introduction of corn to Asia from the Americas. They include a large number of genetically diverse cultivars from various countries that have adapted to a wide range of tropical to temperate environments. It is common throughout Southeast Asia (the Philippines, eastern Indonesia, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and Myanmar) and East Asia (China, Taiwan, Japan, and South Korea) The stickiness of waxy corn cultivars is the result of the presence of larger amounts of amylopectin starch in contrast to regular corn (which has larger amounts of amylose star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waxy Maize
Waxy corn or glutinous corn is a type of corn characterized by its sticky texture when cooked. It has big round kernels that have endosperms that are almost universally white, though the aleurone layers can sometimes be purple or red which cause some cultivars to be multi-colored or even deep purple to black. Waxy corn is absent in the Americas and is believed to have originated from a single chromosomal mutation soon after the introduction of corn to Asia from the Americas. They include a large number of genetically diverse cultivars from various countries that have adapted to a wide range of tropical to temperate environments. It is common throughout Southeast Asia (the Philippines, eastern Indonesia, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and Myanmar) and East Asia (China, Taiwan, Japan, and South Korea) The stickiness of waxy corn cultivars is the result of the presence of larger amounts of amylopectin starch in contrast to regular corn (which has larger amounts of amylose starch). See a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert P
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decatur, Illinois
Decatur ( ) is the largest city in Macon County, Illinois, United States, and its county seat. The city was founded in 1829 and is situated along the Sangamon River and Lake Decatur in Central Illinois. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it had a population of 70,522. It is the List of municipalities in Illinois, 17th-most populous city in Illinois and the sixth-most populous outside the Chicago metropolitan area. Decatur has an economy based on industrial and agricultural commodity processing and production. The city is home to Millikin University and Richland Community College. History 19th century The city is named after War of 1812 naval hero Stephen Decatur. The Potawatomi Trail of Death passed through the city in 1838. Post No. 1 of the Grand Army of the Republic was founded by Civil War veterans in Decatur on April 6, 1866. Decatur was the first home in Illinois of Abraham Lincoln, who settled just west of Decatur with his family in 1830. At the age of 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat, potatoes, maize (corn), rice, and cassava (manioc). Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helix, helical amylose and the branched amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malting. These sugars may be fermentation, fermented to produce ethanol in the manufacture of beer, whisky and biofuel. In addition, sugars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradable Plastic
Biodegradable plastics are plastics that can be decomposed by the action of living organisms, usually microbes, into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. Biodegradable plastics are commonly produced with renewable raw materials, micro-organisms, petrochemicals, or combinations of all three. While the words "bioplastic" and "biodegradable plastic" are similar, they are not synonymous. Not all bioplastics (plastics derived partly or entirely from biomass) are biodegradable, and some biodegradable plastics are fully petroleum based. As more companies are keen to be seen as having "green" credentials, solutions such as using bioplastics are being investigated and implemented more. The definition of bioplastics is still up for debate. The phrase is frequently used to refer to a wide range of diverse goods that may be biobased, biodegradable, or both. This could imply that polymers made from oil can be branded as "bioplastics" even if they have no biological components at all. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Apollo
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in space. It was conceived in 1960 as a three-person spacecraft during President Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower, Dwight D. Eisenhower's administration. Apollo was later dedicated to President John F. Kennedy's national goal for the 1960s of "landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth" in an address to United States Congress, Congress on May 25, 1961. It was the third American human spaceflight program to fly, preceded by Project Gemini conceived in 1961 to extend spaceflight capability in support of Apollo. Kennedy's goal was accomplished on the Apollo 11 mission when astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin landed their Apollo Lunar Module (LM) on July 20, 1969, and walked on the lunar surface, while Michael Collins ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |