|
Ambulacrarian
Ambulacraria , or Coelomopora , is a clade of invertebrate phyla that includes echinoderms and hemichordates; a member of this group is called an ambulacrarian. Phylogenetic analysis suggests the echinoderms and hemichordates separated around 533 million years ago. The Ambulacraria are part of the deuterostomes, a clade that also includes the many Chordata, and the few extinct species belonging to the Vetulicolia. Phylogeny The two living clades with representative organisms are: * Echinodermata (sea stars, sea urchins, brittle stars, sea cucumbers, feather stars, sea lilies, etc.) * Hemichordata (acorn worms (Enteropnuesta) and Pterobranchia (including Graptolithina)) (These together sometimes are called the ''lower deuterostomes''.) Whether the Xenacoelomorpha clade is the sister group to the Ambulacraria remains a contentious issue, with some authors arguing that the former should be placed more basally among metazoans, and other authors asserting that the best choices of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as larvae, as adults echinoderms are recognisable by their usually five-pointed radial symmetry (pentamerous symmetry), and are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,600 living species, making it the second-largest group of deuterostomes after the chordates, as well as the largest marine-only phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian. Echinoderms are important both ecologically and geologically. Ecologically, there are few other groupings so abundant in the deep sea, as well as shallower oceans. Most echinoderms are able to reproduce asexually and regenerate tissue, organs and limbs; in some cases, they can undergo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinodermata
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as larvae, as adults echinoderms are recognisable by their usually five-pointed radial symmetry (pentamerous symmetry), and are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,600 living species, making it the second-largest group of deuterostomes after the chordates, as well as the largest marine animal, marine-only phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian. Echinoderms are important both ecologically and geologically. Ecologically, there are few other groupings so abundant in the deep sea, as well as continental shelf, shallower oceans. Most echinoderms are able to asexual reproduction, reproduce asexually and regeneration (biology), regenerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterostome
Deuterostomes (from Greek: ) are bilaterian animals of the superphylum Deuterostomia (), typically characterized by their anus forming before the mouth during embryonic development. Deuterostomia comprises three phyla: Chordata, Echinodermata, Hemichordata, and the extinct clade Cambroernida. In deuterostomes, the developing embryo's first opening (the blastopore) becomes the anus and cloaca, while the mouth is formed at a different site later on. This was initially the group's distinguishing characteristic, but deuterostomy has since been discovered among protostomes as well. The deuterostomes are also known as enterocoelomates, because their coelom develops through pouching of the gut, enterocoely. Deuterostomia's sister clade is Protostomia, animals that develop mouth first and whose digestive tract development is more varied. Protostomia includes the ecdysozoans and spiralians, as well as the extinct '' Kimberella''. Together with the Xenacoelomorpha, these constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
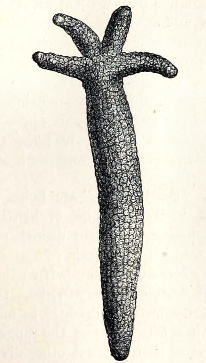
Yanjiahella
''Yanjiahella biscarpa'' is an extinct species of Early Cambrian deuterostome which may represent the earliest stem group echinoderm. This species is known from the Fortunian Yanjiahe Formation (~541.0–534.6 Ma) in Hubei province, China and was first described by Guo et al. who had difficulty in assigning a taxonomy to the animal due to the shared nature of its features between the hemichordates and echinoderms. Etymology The ''Yanjiahella'' genus takes its name from the Yanjiahe Formation combined with the Latin diminutive "-ella" in reference to the small size of the species with the species name ''biscarpa'' deriving from the Latin "''bis''" meaning two, and Greek "''carpa''" meaning arms. Guo et al. originally divided the Yanjiahella genus into three species based on the number of feeding appendages, ''Y. ancarpa'' (meaning "no armed") ''Y. monocarpa'' (meaning "single armed") and ''Y. biscarpa''. However, analysis by Topper et al. showed identical morphological feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vetulicolia
Vetulicolia is a group of bilaterian marine animals encompassing several extinct species from the Cambrian, and possibly Ediacaran, periods. As of 2023, the majority of workers favor placing Vetulicolians in the stem group of the Chordata, but some continue to favor a more crownward placement as a sister group to the Tunicata. It was initially erected as a monophyletic clade with the rank of phylum in 2001, with subsequent work supporting its monophyly. However, more recent research suggests that vetulicolians may be paraphyletic and form a basal evolutionary grade of stem chordates. Etymology The taxon name, Vetulicolia, is derived from the type genus, '' Vetulicola'', which is a compound Latin word composed of ''vetuli'' "old" and ''cola'' "inhabitant". It was named after '' Vetulicola cuneata'', the first species of the group described in 1987. Description The vetulicolian body plan comprises two parts: a voluminous rostral (anterior) forebody, tipped with an anteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
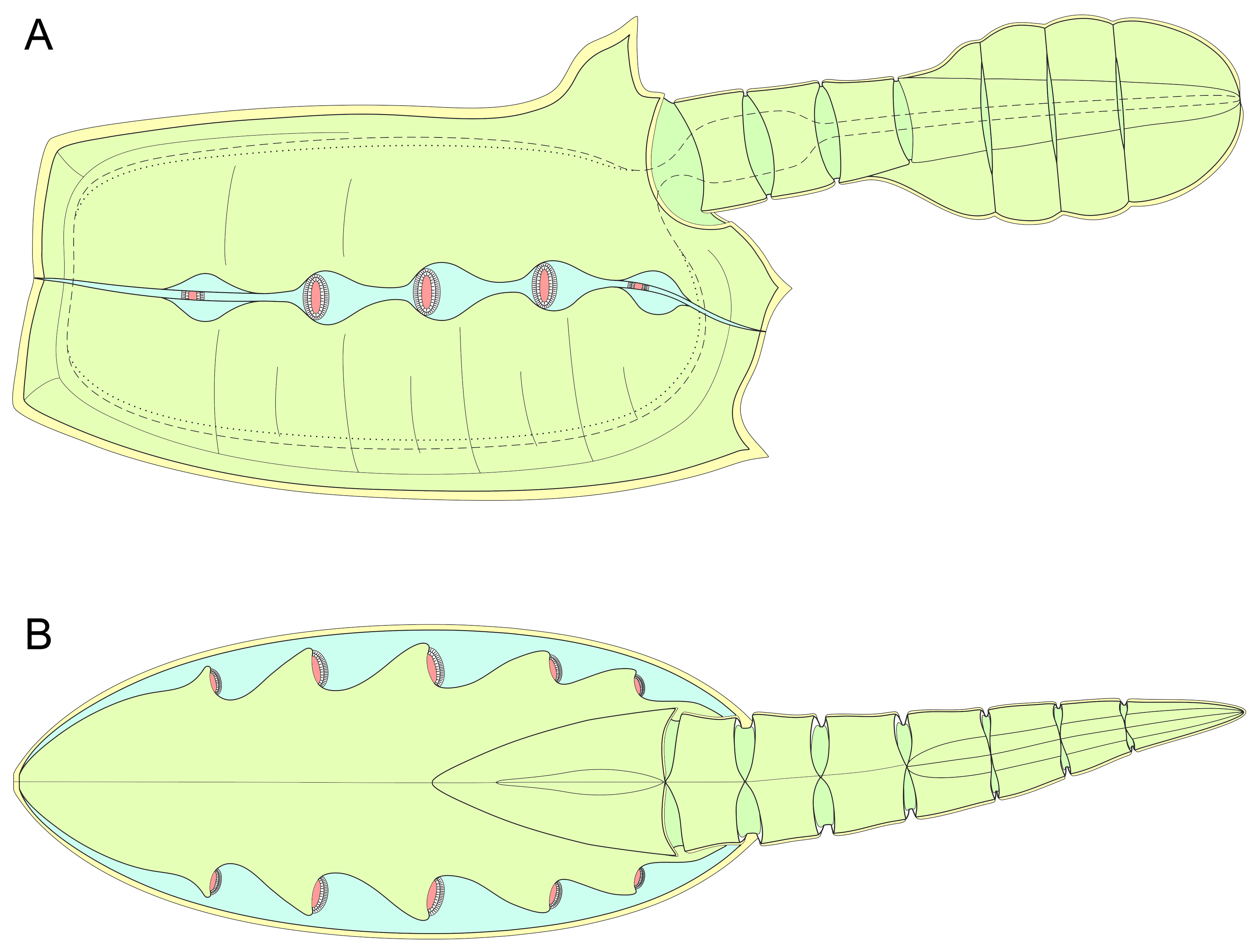
Vetulocystida
Vetulocystidae is the only family of the taxon Vetulocystida, which is a group of extinct deuterostomes of uncertain phylogenetic position. Vetulocystidae is made up of the genera ''Vetulocystis'', '' Dianchicystis'' and '' Thylacocercus''. Etymology The latin ''vetus'' means "old," while ''cystis'' refers to the organisms' bag-like shape. Description The body consists of a voluminous thecal-shaped section (similar to the outer shape of the pterobranchs), where there are two cone-shaped structures (anterior and posterior) and a lenticular respiratory organ; and another small section attached to the substrate. The anterior cone-shaped structure is believed to have constituted the mouth, due to its similarity to primitive echinoderms (such as stylophorans and blastoids); while the posterior structure (similar to that of the cystoids and eocrinoids) fulfilled the functions of anus and gonopore. Furthermore, and unlike many other echinoderms, these animals lacked a calcified skele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpetogaster Collinsi Reconstruction
''Herpetogaster'' is an extinct cambroernid genus of animal from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang biota of China, Blang Formation of China, Pioche Formation of Nevada and Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of Canada containing the species ''Herpetogaster collinsi'' and ''Herpetogaster haiyanensis''. Description '' H. collinsi'' is known from over 160 specimens. It possessed a pair of branching tentacles and a tough but flexible body that curved helically to the right like a ram's horn and was divided into at least 13 segments. A flexible, extensible stolon emerged from the body at about the ninth segment and secured the animal to the sea floor, often by attaching to the sponge '' Vauxia.'' It is not known whether the attachment was permanent. A mouth opened between the tentacles, leading internally to a pharynx, a large lentil-shaped stomach, a narrower straight intestine, and an anus at the end of the "tail." The tentacles were softer than the body and probably extensible. A dark li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vetulocystidae
Vetulocystidae is the only family of the taxon Vetulocystida, which is a group of extinct deuterostomes of uncertain phylogenetic position. Vetulocystidae is made up of the genera '' Vetulocystis'', '' Dianchicystis'' and '' Thylacocercus''. Etymology The latin ''vetus'' means "old," while ''cystis'' refers to the organisms' bag-like shape. Description The body consists of a voluminous thecal-shaped section (similar to the outer shape of the pterobranchs), where there are two cone-shaped structures (anterior and posterior) and a lenticular respiratory organ; and another small section attached to the substrate. The anterior cone-shaped structure is believed to have constituted the mouth, due to its similarity to primitive echinoderms (such as stylophorans and blastoids); while the posterior structure (similar to that of the cystoids and eocrinoids) fulfilled the functions of anus and gonopore. Furthermore, and unlike many other echinoderms, these animals lacked a calcified sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenambulacraria
Xenambulacraria is a proposed clade of animals with bilateral symmetry as an embryo, consisting of the Xenacoelomorpha (i.e., ''Xenoturbella'' and acoelomorphs) and the Ambulacraria (i.e., echinoderms and hemichordates). If confirmed, the clade would either be the sister group to the chordates (if deuterostomes are monophyletic) or the sister group to all the other bilaterians, grouped together in Centroneuralia (with deuterostomes being paraphyletic). Although the validity of the clade relies mostly on phylogenomics, molecular genetics studies have proposed pigment cell clusters expressing polyketide synthase (PKS) and sulfotransferase as a synapomorphy of Xenambulacraria. Phylogeny Xenambulacraria has usually been recovered as a clade inside of either of two distinct phylogenies. Basal Xenambulacraria The following phylogeny assumes a paraphyletic Deuterostomia, with Xenambulacraria at the base of Bilateria. Xenambulacraria inside Deuterostomia The following ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordates
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics ( synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post- anal tail. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and inner mitochondrial membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSIs provide molecular means to reliably distinguish chordates from all other animals. Chordates are divided into three subphyla: Vertebrata (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals), whose notochords are replaced by a cartilaginous/ bony axial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterobranchia
Pterobranchia, members of which are often called pterobranchs, is a class of small worm-shaped animals. They belong to the Hemichordata, and live in secreted tubes on the ocean floor. Pterobranchia feed by filtering plankton out of the water with the help of cilia attached to tentacles. There are about 25 known living pterobranch species in three genera, which are '' Rhabdopleura'', '' Cephalodiscus'', and '' Atubaria''. On the other hand, there are several hundred extinct genera, some of which date from the Cambrian Period. The class Pterobranchia was established by Ray Lankester in 1877. It contained, at that time, the single genus '' Rhabdopleura''. ''Rhabdopleura'' was at first regarded as an aberrant polyzoon, but when the ''Challenger'' report on '' Cephalodiscus'' was published in 1887, it became clear that ''Cephalodiscus'', the second genus now included in the order, had affinities with the Enteropneusta. Electron microscope studies have suggested that pterobranch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Communications
''Nature Communications'' is a peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio since 2010. It is a multidisciplinary journal that covers the natural sciences, including physics, chemistry, earth sciences, medicine, and biology. The journal has editorial offices in London, Berlin, New York City, and Shanghai. The founding editor-in-chief was Lesley Anson, followed by Joerg Heber, Magdalena Skipper, and Elisa De Ranieri. the editors are Nathalie Le Bot for health and clinical sciences, Stephane Larochelle for biological sciences, Enda Bergin for chemistry and biotechnology, and Prabhjot Saini for physics and earth sciences. Starting October 2014, the journal only accepted submissions from authors willing to pay an article processing charge. Until the end of 2015, part of the published submissions were only available to subscribers. In January 2016, all content became freely accessible. Starting from 2017, the journal offers a deposition ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |