|
Ambo Remix
Ambo may refer to: Places * Ambo, Kiribati * Ambō (also spelled Anbō), Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan * Ambo Province, Huanuco Region, Peru ** Ambo District ** Ambo, Peru, capital of Ambo District * Ambo, Ethiopia, a capital of West Shewa Zone, Oromia Regional State, Ethiopia * Kom Ombo or , a town in Egypt known for its ancient Greek temple * Wendens Ambo, village in Essex, England Religion * Ambo (liturgy) or ambon, in Eastern orthodoxy the elevated area in front of the Iconostasis * Ambo, a pulpit or lectern in a church sanctuary (the official term for Catholic pulpits) Anthropology * Ovambo language, or Ambo language * Ovambo people, or Ambo people Arts, entertainment, and media * "Ambo", an episode of the American television series ''Animal Kingdom'' * Ambo, a music project of computer game designer Robyn Miller Other uses * Typhoon Ambo (other) * Ambo, in Australia, a term for an ambulance * Ambo, a variety of potato * Ambo, an operation in Conway polyhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambo, Kiribati
South Tarawa () is the capital and hub of the Republic of Kiribati and home to more than half of Kiribati's population. The South Tarawa population centre consists of all the small islets from Betio in the west to Bonriki and Tanaea in the north-east, connected by the South Tarawa main road, with a population of 63,439 . South Tarawa is home to most of the government, commercial and education facilities in Kiribati including the Port and the High Court at Betio, the State House, Government Ministries and foreign embassies and High Commissions in Bairiki, the University of the South Pacific campus in Teaoraereke, the House of Assembly in Ambo, the Kiribati Teacher College and King George V and Elaine Bernacchi School, the Government High School, is in Bikenibeu, and the Tungaru central hospital in Nawerewere. The Roman Catholic Diocese is based in Teaoraereke, the Kiribati Uniting Church in Antebuka, the National Spiritual Assembly of the Bahá’ís of Kiribati in Bikenibeu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovambo People
The Ovambo people (), also called Aawambo, Ambo, Aawambo (Ndonga, Nghandjera, Kwambi, Kwaluudhi, Kolonghadhi, Mbalantu, mbadja), or Ovawambo (Kwanyama), are a Bantu peoples, Bantu ethnic group native to Southern Africa, primarily modern Namibia. They are the single largest ethnic group in Namibia, accounting for about half of the population.Namibia: People and Society CIA Factbook, United States; "about 50% of the population belong to the Ovambo tribe", total population: 2.4 million Despite concerted efforts from Christian missionaries to wipe out what they believed to be 'pagan practices', the Ovambo have retained many aspects of their traditional cultural practices. They are also found in the southern Angolan province of Cunene Province, Cunene, where they are more commonly referred to as "Ambo". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
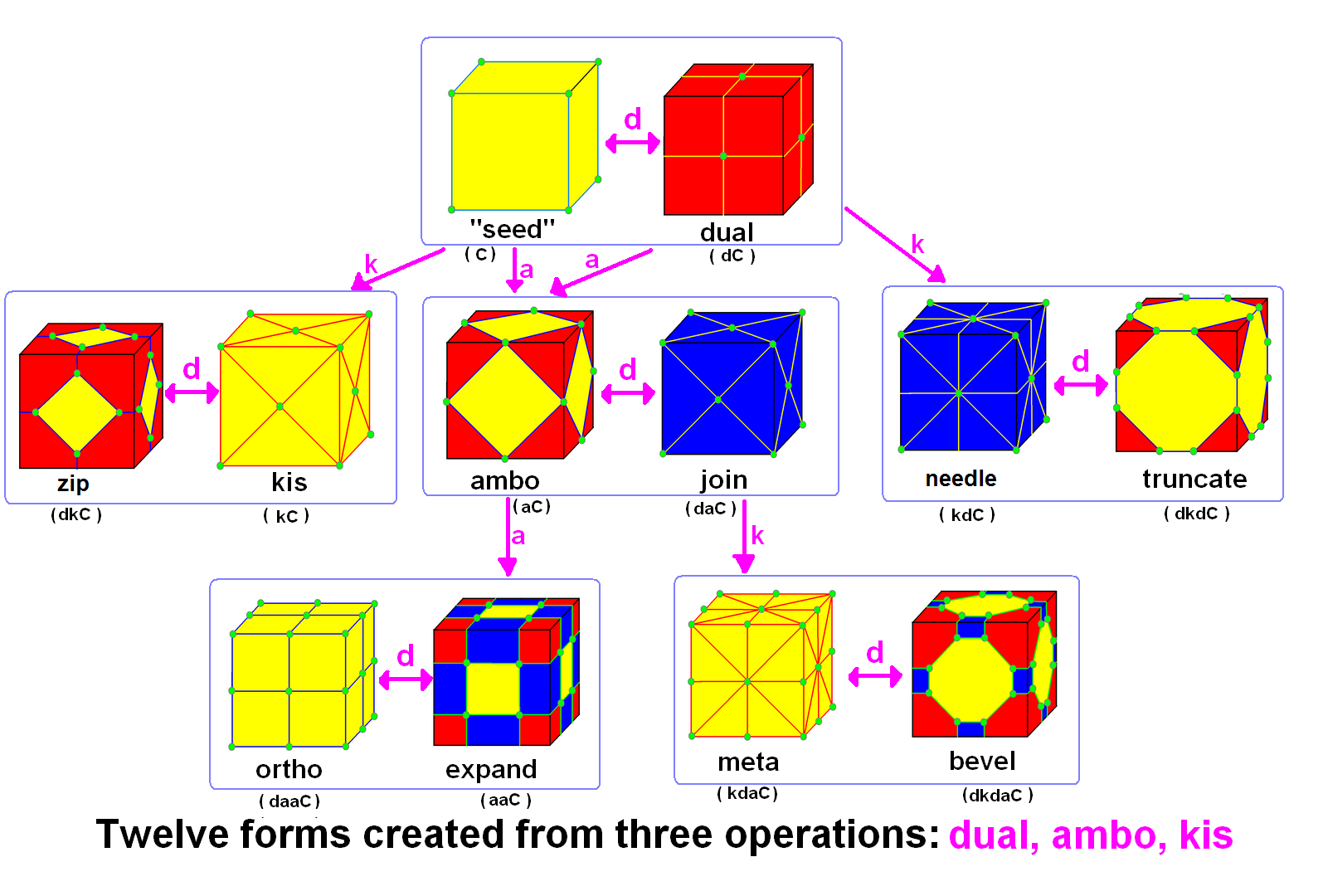
Conway Polyhedron Notation
In geometry and topology, Conway polyhedron notation, invented by John Horton Conway and promoted by George W. Hart, is used to describe polyhedra based on a seed polyhedron modified by various prefix operations. Conway and Hart extended the idea of using operators, like truncation as defined by Kepler, to build related polyhedra of the same symmetry. For example, represents a truncated cube, and , parsed as , is ( topologically) a truncated cuboctahedron. The simplest operator dual swaps vertex and face elements; e.g., a dual cube is an octahedron: . Applied in a series, these operators allow many higher order polyhedra to be generated. Conway defined the operators (ambo), (bevel), ( dual), (expand), (gyro), (join), (kis), (meta), (ortho), ( snub), and ( truncate), while Hart added ( reflect) and (propellor). Later implementations named further operators, sometimes referred to as "extended" operators. Conway's basic operations are sufficient to generate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae. Wild potato species can be found from the southern United States to southern Chile. Genetic studies show that the cultivated potato has a single origin, in the area of present-day southern Peru and extreme northwestern Bolivia. Potatoes were domesticated there about 7,000–10,000 years ago from a species in the '' S. brevicaule'' complex. Many varieties of the potato are cultivated in the Andes region of South America, where the species is indigenous. The Spanish introduced potatoes to Europe in the second half of the 16th century from the Americas. They are a staple food in many parts of the world and an integral part of much of the world's food supply. Following millennia of selective breeding, there are now over 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulance
An ambulance is a medically-equipped vehicle used to transport patients to treatment facilities, such as hospitals. Typically, out-of-hospital medical care is provided to the patient during the transport. Ambulances are used to respond to medical emergencies by emergency medical services (EMS), and can rapidly transport paramedics and other first responders, carry equipment for administering emergency care, and transport patients to hospital or other definitive care. Most ambulances use a design based on vans or pickup trucks, though others take the form of motorcycles, buses, hearses, aircraft and boats. Ambulances are generally considered emergency vehicles authorized to be equipped with emergency lights and sirens. Generally, vehicles count as an ambulance if they can transport patients. However, it varies by jurisdiction as to whether a non-emergency patient transport vehicle (also called an ambulette) is counted as an ambulance. These vehicles are not usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoon Ambo (other)
The name Ambo has been used for five tropical cyclones in the Philippines by the PAGASA in the Western Pacific Ocean. * Tropical Depression Ambo (2004) (01W, Ambo) – a tropical depression that was only recognized by PAGASA and JTWC. * Typhoon Neoguri (2008) (T0801, 02W, Ambo) – a rare April typhoon that struck China. * Typhoon Mawar (2012) (T1203, 04W, Ambo) – a strong typhoon that remained away from any landmass. * Tropical Depression Ambo (2016) (Ambo) – a tropical depression that was only recognized by PAGASA. * Typhoon Vongfong (2020) (T2001, 01W, Ambo) – a disastrous Category 3 storm that hit the Philippines, causing over damage. The name ''Ambo'' was retired from the PAGASA naming lists after the 2020 season. It was replaced by Aghon (a local ''Hiligaynon'' name means ''compass'' or ''mariner's compass'') in the 2024 season. * Typhoon Ewiniar (2024) Typhoon Ewiniar, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Aghon, was a fairly strong tropical cyclone that impacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robyn Miller
Robyn Charles Miller (born August 6, 1966) is an American video game designer who is the co-founder of Cyan Worlds with brother Rand Miller. He served as co-designer of the popular computer game ''Myst'', which held the title of best-selling computer game from its release in 1993 until the release of ''The Sims'' seven years later. He also co-directed and co-lead designed the sequel to ''Myst'', ''Riven'', which was the best-selling computer game of its year of release, 1997. Miller composed and performed the soundtracks to both games. He also acted in Myst, portraying one of the antagonists, Sirrus (with brother and Cyan-cofounder Rand appearing as Achenar and Atrus). He co-wrote the first Myst novel, ''The Book of Atrus''. After the release of ''Riven'', Miller left Cyan to pursue non-game interests, including films. He is the director of the 2013 film '' The Immortal Augustus Gladstone''. Early works Miller served as a designer on Cyan Worlds's early games '' The Manhole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Kingdom (TV Series)
''Animal Kingdom'' is an American crime drama television series developed by Jonathan Lisco. It is based on the 2010 Australian film of the same name, which in turn was inspired by the criminal Pettingill family. The series is produced by David Michôd, the film's writer and director, and Liz Watts, the film's producer. ''Animal Kingdom'' premiered on TNT on June 14, 2016, with the first season consisting of 10 episodes. Starting with the second season, each subsequent season consisted of 13 episodes. The second season premiered on May 30, 2017. The third season premiered on May 29, 2018. The fourth season premiered on May 28, 2019. The fifth season premiered on July 11, 2021. The sixth and final season premiered on June 19, 2022. The series concluded on August 28, 2022, after six seasons for a total of 75 episodes. It was the final scripted original series to air on TNT before the production of original programming ceased. Premise The series centers on Joshua "J" Cody who, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovambo Language
The Ovambo () language is a dialect cluster spoken by the Ovambo people in southern Angola and northern Namibia, of which the written standards are Kwanyama and Ndonga. The native name for the language is ''Oshiwambo'' (also written ''Oshivambo''), which is also used specifically for the Kwanyama and Ndonga dialects. It is the largest spoken local language in Namibia, particularly by the Ovambo people. The language is closely related to that of the Herero and Himba, the Herero language (''Otjiherero''). An obvious sign of proximity is the prefix used for language and dialect names, Proto-Bantu ''*ki-'' (class 7, as in the name of the Swahili language, ''Kiswahili''), which in Herero has evolved to ''Otji-'' and in Ovambo further to ''Oshi-''. History After Namibia's independence in 1990, the area previously known as Ovamboland was divided into the Ohangwena, Omusati, Oshana and Oshikoto Regions. The population, estimated at between 700,000 and 750,000, fluctuates rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anbō, Yakushima
, also spelled Ambō, is a port town and the major settlement of the island of Yakushima, in Japan. It is part of the municipality (with List of towns in Japan, town status) of Yakushima, Kagoshima, Yakushima, Kagoshima Prefecture. History Originally part of the municipality of Kamiyaku, Kagoshima, Kamiyaku, on October 1, 2007, it merged the municipality of Yaku, Kagoshima, Yaku (including Miyanoura) to create the current municipality of Yakushima. Geography Anbō is a coastal town on the Pacific Ocean, east of the island of Yakushima, below the mountains and crossed in the middle by Anbō River. It is 19 km southeast of the town of Miyanoura, and 13 km northeast of the village of Hiranai, Yakushima, Hiranai. A 13 km mountain road links it to the touristic natural areas Arakawa Waterfalls and Yakusugi Land. Transport The port of Anbō has passenger services to Kuchinoerabu-jima, Kuchinoerabu, Nishinoomote, Kagoshima, Nishinoomote (on Tanegashima island), Miyanoura and Kagoshima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulpit
A pulpit is a raised stand for preachers in a Christian church. The origin of the word is the Latin ''pulpitum'' (platform or staging). The traditional pulpit is raised well above the surrounding floor for audibility and visibility, accessed by steps, with sides coming to about waist height. From the late Middle Ages, late medieval period onwards, pulpits have often had a canopy known as the sounding board, ''tester'' or ''abat-voix'' above and sometimes also behind the speaker, normally in wood. Though sometimes highly decorated, this is not purely decorative, but can have a useful acoustic effect in projecting the preacher's voice to the Church (congregation), congregation below, especially prior to the invention of modern audio equipment. Most pulpits have one or more book-stands for the preacher to rest his bible, notes or texts upon. The pulpit is generally reserved for clergy. This is mandated in the regulations of the Catholic Church, and several others (though not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |