|
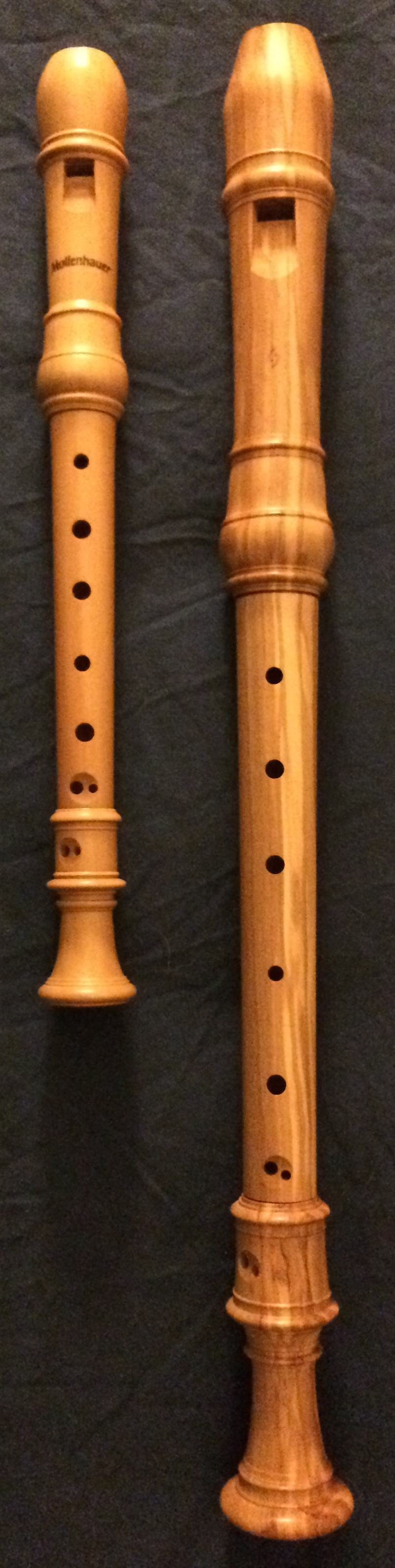
Alto Recorder
The alto recorder in F, also known as a treble (and, historically, as consort flute and common flute) is a member of the recorder family. Up until the 17th century the alto instrument was normally in G4 instead of F4. Its standard range is F4 to G6. The alto is between the soprano and tenor in size, and is correspondingly intermediate in pitch. It has the same general shape as a soprano, but is larger in all dimensions, resulting in a lower pitch for a given fingering. The F alto is a non-transposing instrument, though its basic scale is in F, that is, a fifth lower than the soprano recorder and a fourth higher than the tenor (both with a basic scale in C). So-called F fingerings are therefore used, as with the bassoon or the low register of the clarinet, in contrast to the C fingerings used for most other woodwinds. Its notation is usually at sounding pitch, but sometimes is written an octave lower than it sounds. History Recorders are known to have been made in diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Key Signature
In Western musical notation, a key signature is a set of sharp (), flat (), or rarely, natural () symbols placed on the staff at the beginning of a section of music. The initial key signature in a piece is placed immediately after the clef at the beginning of the first line. If the piece contains a section in a different key, the new key signature is placed at the beginning of that section. In a key signature, a sharp or flat symbol on a line or space of the staff indicates that the note represented by that line or space is to be played a semitone higher (sharp) or lower (flat) than it would otherwise be played. This applies through the rest of the piece or until another key signature appears. Each symbol applies to comparable notes in all octaves—for example, a flat on the fourth space of the treble staff (as in the diagram) indicates that all notes notated as Es are played as E-flats, including those on the bottom line of the staff. Most of this article addres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adrian Boult
Sir Adrian Cedric Boult, CH (; 8 April 1889 – 22 February 1983) was a British conductor. Brought up in a prosperous mercantile family, he followed musical studies in England and at Leipzig, Germany, with early conducting work in London for the Royal Opera House and Sergei Diaghilev's ballet company. His first prominent post was conductor of the City of Birmingham Orchestra in 1924. When the British Broadcasting Corporation appointed him director of music in 1930, he established the BBC Symphony Orchestra and became its chief conductor. The orchestra set standards of excellence that were rivalled in Britain only by the London Philharmonic Orchestra (LPO), founded two years later. Forced to leave the BBC in 1950 on reaching retirement age, Boult became principal conductor of the London Philharmonic Orchestra. The orchestra had declined from its peak of the 1930s, but under his guidance its fortunes were revived. He retired as its chief conductor in 1957, and later accepte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Michael Furter
Michael Furter (died 1516 or 1517) was a printer of incunabula in Basel. Printing career The first dated prints by Furter are from 1489. In 1494 he printed the ''Ship of Fools'' by Sebastian Brant for the publisher Jacob Bergmann von Olpe. Furter's workshop is notable for its illustrated prints and its large number of initial alphabets ( Haebler, ''Typenrepertorium'', 1905 lists twelve), including Etterlin's chronicle, ''Der Ritter vom Turm'' ( Marquard vom Stein) and the Apocalypse of Pseudo-Methodius. In 1508 Furter and Gregor Schott jointly printed the third edition of the ''Margarita Philosophica'' by Gregor Reisch. Further also produced numerous popular works on grammar, jurisprudence, theology and morals. He was for a short while considered the first printer of Basel due to a typo in his prints and was the first to have depicted a coat of arms of Basel jointly with two Basilisks. Personal life Furter is recorded as buying a house in ''Ryngasse'', Lesser Basel on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The New Grove Dictionary Of Music And Musicians
''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' is an encyclopedic dictionary of music and musicians. Along with the German-language '' Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', it is one of the largest reference works on the history and theory of music. Earlier editions were published under the titles ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', and ''Grove's Dictionary of Music and Musicians''; the work has gone through several editions since the 19th century and is widely used. In recent years it has been made available as an electronic resource called ''Grove Music Online'', which is now an important part of ''Oxford Music Online''. ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' was first published in London by Macmillan and Co. in four volumes (1879, 1880, 1883, 1889) edited by George Grove with an Appendix edited by J. A. Fuller Maitland in the fourth volume. An Index edited by Mrs. E. Wodehouse was issued as a separate volume in 189 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Georg Rhau
Georg Rhau (Rhaw) (1488 – 6 August 1548) was a German publisher and composer. He was one of the most significant music printers in Germany in the first half of the 16th century, during the early period of the Protestant Reformation. He was principally active in Wittenberg, Saxony, the town where Martin Luther is said to have nailed the Ninety-five Theses to the door of the Castle Church, initiating the Reformation. Rhau's support as a printer was critical to Luther's success.Mattfield, Grove online Life Born in the Thuringian town of Eisfeld, then part of Ernestine Saxony, Rhau from 1513 onwards studied philosophy at the newly established University of Wittenberg. From 1518 he continued his studies at the University of Leipzig where he also worked as a tutor. He was the cantor of Leipzig Thomanerchor from 1518 to 1520. During Luther's Leipzig Debate, he performed his mass ''Missa de Sancto Spiritu'' for twelve voices on 27 June 1519. In 1520 Rhau had to leave Leipzi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Transverse Flute
A transverse flute or side-blown flute is a flute which is held horizontally when played.Powell, A. (2001). Transverse flute. Grove Music Online. Retrieved 6 Feb. 2024 The player blows across the embouchure hole, in a direction perpendicular to the flute's body length. Transverse flutes include the Western concert flute, the Irish flute, the Indian classical flutes (the bansuri and the venu), the Chinese dizi, the Western fife, a number of Japanese fue, and Korean flutes such as daegeum, junggeum and sogeum. See also *End-blown flute thumb , Notched flute, showing U-shaped notch in the instrument’s rim. The end-blown flute (also called an edge-blown flute or rim-blown flute) is a woodwind instrument played by directing an airstream against the sharp edge of the upper en ... References {{Flute-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Johann Christoph Denner
Johann Christoph Denner (13 August 1655 – 26 April 1707)Martin Kirnbauer. "Denner", ''Grove Music Online'', ed. L. Macy (accessed 13 October 2006)grovemusic.com (subscription access). was a German woodwind instrument maker of the Baroque era, to whom the invention of the clarinet is attributed. Denner was born in Leipzig to a family of horn-tuners. With his father, Heinrich Denner, a maker of game whistles and hunting horns, he moved to Nuremberg in 1666. J. C. Denner went into business as an instrument maker in 1678 and was granted rights for the “manufacture of French musical instruments consisting chiefly of oboes and recorders landadois�� in 1697. Two of his sons, Jacob and Johann David, also became instrument builders. At least sixty-eight instruments attributed to J. C. Denner have survived to the present day, although the surviving instruments with his name are believed to have come from his sons' workshops. Denner died in 1707 and was buried in Nuremberg. In 1730, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jean Hotteterre
Jean Hotteterre (1677–1720) was a French composer and musician of the Hotteterre family. Hotteterre worked at the family workshop on the Rue de Harlay, Paris until his death at the court of Louis XIV of France. He and his brothers Jacques-Martin and Nicolas made many enhancements to the oboe, creating an "indoor" version similar to the shawm The shawm () is a Bore (wind instruments)#Conical bore, conical bore, double-reed woodwind instrument made in Europe from the 13th or possibly 12th century to the present day. It achieved its peak of popularity during the medieval and Renaissanc .... References 1677 births 1720 deaths 18th-century French classical composers 18th-century French composers 18th-century French male musicians French male classical composers French Baroque composers French classical oboists French male oboists 17th-century French male musicians {{france-composer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
All Fifths Tuning
Among guitar tunings, all-fifths tuning refers to the set of tunings in which each interval between consecutive open strings is a perfect fifth. All-fifths tuning is also called fifths, perfect fifths, or mandoguitar. The conventional " standard tuning" consists of perfect fourths and a single major third between the ''g'' and ''b'' strings: :E-A-d-g-b-e' All-fifths tuning has the set of open strings :C-G-d-a-e'-b' or G'-D-A-e-b-f', which have intervals of 3 octaves minus a half-step between the lowest and highest string. The conventional tuning has an interval of 2 octaves between lowest and highest string. All-fifths tuning is a tuning in intervals of perfect fifths like that of a mandolin or a violin. It has a wide range. It was used by jazz guitarist Carl Kress in the form : B'-F-c-g-d'-a'. An approximation: new standard tuning All-fifths tuning has been approximated with tunings that avoid the high b' replacing it with a g' in the New Standard Tuning of King&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Martin Agricola
Martin Agricola (6 January 1486 – 10 June 1556) was a German composer of Renaissance music and a music theorist. Biography Agricola was born in Świebodzin, a town in Western Poland, and took the name Agricola later in life, a common practice among Lutherans often meant to emphasize humble, peasant origins. From 1524 until his death, he lived in the German city of Magdeburg, where he was a teacher or cantor in the Protestant school. Georg Rhau, a publisher and senator in Wittenberg, was Agricola's close friend and publisher. Agricola's theoretical writing was valuable in expounding the change from the old to the new system of musical notation. His ''Musica instrumentalis deudsch'' (English: ''German Instrumental Music''), published in 1528, 1530, 1532 and 1542, and then heavily revised in 1545, was one of the most important early works in organology and on the elements of music. Agricola was the first to harmonize in four parts Martin Luther's famous chorale A chorale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Octave
In music, an octave (: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is an interval between two notes, one having twice the frequency of vibration of the other. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music", the use of which is "common in most musical systems". The interval between the first and second harmonics of the harmonic series is an octave. In Western music notation, notes separated by an octave (or multiple octaves) have the same name and are of the same pitch class. To emphasize that it is one of the perfect intervals (including unison, perfect fourth, and perfect fifth), the octave is designated P8. Other interval qualities are also possible, though rare. The octave above or below an indicated note is sometimes abbreviated ''8a'' or ''8va'' (), ''8va bassa'' (, sometimes also ''8vb''), or simply ''8'' for the octave in the direction indicated by placing this mark above or below the staff. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |