|
Alluvion
Alluvion, is a Roman law method of acquisition of heritable property (land). The typical cause is sediment (alluvium) deposited by a river. This sediment, legally termed ''the accessory, accreses'' (i.e., merges with) a piece of land, the principal (operating a subtype of the Roman mode of acquisition by accession) and thus accedes to the ownership of the principal land over time. It continues to have relevance in the modern age from adopting Roman property law by modern legal systems, primarily civil law jurisdictions. Scots law is a notable example of the usage of alluvion within the law of accession (accesio). Public international law also recognises the acquisition of sovereignty of virgin territory by operation of nature, such as sediment deposits, again following the Roman law principles of alluvion. See also *Alluvial fan *Alluvial plain An alluvial plain is a plain (an essentially flat landform) created by the deposition of sediment over a long period by one or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
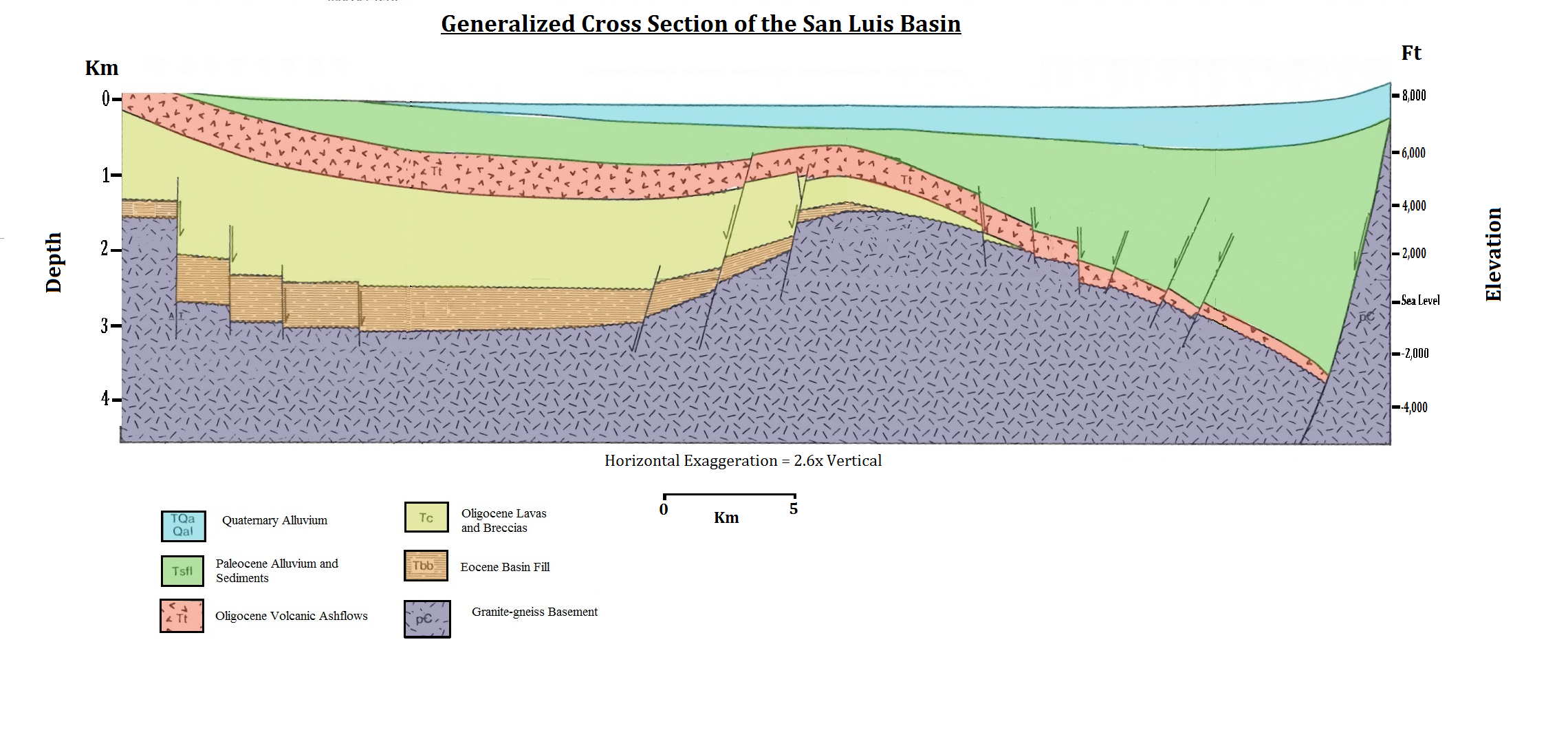
Alluvium
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not Consolidation (geology), consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present Scientific consensus, consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined ''alluvion'' (the French term for al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessio (Roman Law)
''Accessio'' is a concept from Roman property law for acquiring ownership of property (the accessory) which is ''merged'', or ''acceded to'', another piece of property (the principal). Generally, the owner of the principal, whatever it may be, also became the owner of the accessory. Its usage continues in modern times in legal systems around the world incorporating Roman property law, primarily civilian legal systems. ''Accessio'' was not a specific rule of original acquisition of property in itself; instead, it served as the principle underlying the modes of acquisition that had their own particular guidelines for determination of ownership. Roman accession ''Accession'' might also be (from Latin ''accedere'', to go to, approach), in law, a method of acquiring property adopted from Roman law, by which, in things that have a close connection with or dependence on one another, the property of the principal draws after it the property of the accessory, according to the principle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessio (Scots Law)
Accession (Latin ''accessio'') is a method of original acquisition of property under Scots property law. It operates to allow property (the accessory) to ''merge with (or accede to)'' another object (the principal), either moveable or heritable. Accession derives from the Roman-law concept of the same name. Other jurisdictions employ similar rules. The leading case in this area is said to be ''Brand's Trustees v Brand's Trustees'' (1876) 3 R (HL) 16. A common example is a tree (the accessory) acceding to the land (the principal), thereby the tree is owned by the owner of the land on which it is planted by the operation of accession. Accession may appear similar to other modes of original acquisition, but each mode has discrete differences. Importantly, accession does not produce a new object (''nova species'') in itself, such as with '' specificatio''; accession merely attaches one object (the accessory) to another (the principal). Types of accession There are broadly two types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acquisition Of Sovereignty
A number of methods of acquisition of sovereignty are or have been recognised by international law as lawful methods by which a state may acquire sovereignty over territory. International law adopts much of Roman property law in regards to acquisition of sovereignty due to the underlying European civil law at the time of early discovery voyages such as Christopher Columbus. The basis of acquisition of states ownership of vacant territory therefore continues to apply, (and was often applied historically to land already possessed by indigenous populations). Accretion Accretion refers to the physical expansion of an existing territory through geological processes, such as alluvion (the deposit of sediment) or vulcanism. Cession A state may acquire sovereignty over territory if that sovereignty is ceded (transferred) to it by another state. Cession is typically effected by treaty. Examples of cession include the cession of Hong Kong Island and Kowloon, purchases such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (), to the (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I. Roman law also denoted the legal system applied in most of Western Europe until the end of the 18th century. In Germany, Roman law practice remained in place longer under the Holy Roman Empire (963–1806). Roman law thus served as a basis for Civil law (legal system), legal practice throughout Western continental Europe, as well as in most former colonies of these European nations, including Latin America, and also in Ethiopia. English and Anglo-American common law were influenced also by Roman law, notably in their Latinate legal glossary. Eastern Europe was also influenced by the jurisprudence of the , especially in countries such as medieval Romania, which created a new legal system comprising a mixture of Roman and local law. After the dissolution of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human History
Human history or world history is the record of humankind from prehistory to the present. Early modern human, Modern humans evolved in Africa around 300,000 years ago and initially lived as hunter-gatherers. They Early expansions of hominins out of Africa, migrated out of Africa during the Last Ice Age and had spread across Earth's continental land except Antarctica by the end of the Ice Age 12,000 years ago. Soon afterward, the Neolithic Revolution in West Asia brought the first systematic Agriculture, husbandry of plants and animals, and saw many humans transition from a nomadic life to a Sedentism, sedentary existence as farmers in Civilization, permanent settlements. The growing complexity of human societies necessitated systems of accounting and writing. These developments paved the way for the Cradle of civilization, emergence of early civilizations in Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, Egypt, the Indus Valley, and History of China, China, marking the beginning of the ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Law (legal System)
Civil law is a legal system rooted in the Roman Empire and was comprehensively codified and disseminated starting in the 19th century, most notably with France's Napoleonic Code (1804) and Germany's (1900). Unlike common law systems, which rely heavily on judicial precedent, civil law systems are characterized by their reliance on legal codes that function as the primary source of law. Today, civil law is the world's most common legal system, practiced in about 150 countries. The civil law system is often contrasted with the common law system, which originated in medieval England. Whereas the civil law takes the form of legal codes, the common law comes from uncodified case law that arises as a result of judicial decisions, recognising prior court decisions as legally binding precedent. Historically, a civil law is the group of legal ideas and systems ultimately derived from the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'', but heavily overlain by Napoleonic, Germanic, canonical, feuda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Law
Scots law () is the List of country legal systems, legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing Civil law (legal system), civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different historical sources. Together with English law and Northern Irish law, it is one of the three legal systems of the United Kingdom.Stair, General Legal Concepts (Reissue), para. 4 (Online) Retrieved 2011-11-29 Scots law recognises four sources of law: legislation, legal precedent, specific academic writings, and custom. Legislation affecting Scotland and Scots law is passed by the Scottish Parliament on all areas of devolved responsibility, and the United Kingdom Parliament on reserved matters. Some legislation passed by the pre-1707 Parliament of Scotland is still also valid. History of Scots law, Early Scots law before the 12th century consisted of the different legal traditions of the various cultural groups who inhabited the country at the time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public International Law
International law, also known as public international law and the law of nations, is the set of Rule of law, rules, norms, Customary law, legal customs and standards that State (polity), states and other actors feel an obligation to, and generally do, obey in their mutual relations. In international relations, actors are simply the individuals and collective entities, such as states, International organization, international organizations, and non-state groups, which can make behavioral choices, whether lawful or unlawful. Rules are formal, typically written expectations that outline required behavior, while norms are informal, often unwritten guidelines about appropriate behavior that are shaped by custom and social practice. It establishes norms for states across a broad range of domains, including war and diplomacy, Trade, economic relations, and human rights. International law differs from state-based List of national legal systems, domestic legal systems in that it operates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial Fan
An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to Semi-arid climate, semiarid climates, but are also found in more humid environments subject to intense rainfall and in areas of modern glaciation. They range in area from less than to almost . Alluvial fans typically form where a flow of sediment or rocks emerge from a confined channel and are suddenly free to spread out in many directions. For example, many alluvial fans form when steep mountain valleys meet a flat plain. The transition from a narrow channel to a wide open area reduces the carrying capacity of flow and results in Deposition (geology), deposition of sediments. The flow can take the form of infrequent debris flows like in a landslide, or can be carried by an intermittent stream or creek. The reduction of flow is key to the formation of alluvial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial Plain
An alluvial plain is a plain (an essentially flat landform) created by the deposition of sediment over a long period by one or more rivers coming from highland regions, from which alluvial soil forms. A ''floodplain'' is part of the process, being the smaller area over which the rivers flood at a particular time. In contrast, the alluvial plain is the larger area representing the region over which the floodplains have shifted over geological time. As the highlands erode due to weathering and water flow, the sediment from the hills is transported to the lower plain. Various creeks will carry the water further to a river, lake, bay, or ocean. As the sediments are deposited during flood conditions in the floodplain of a creek, the elevation of the floodplain will be raised. As this reduces the channel floodwater capacity, the creek will, over time, seek new, lower paths, forming a meander (a curved path). The leftover higher locations, typically natural levees at the margins of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Property Law
Scots property law governs the rules relating to property found in the legal jurisdiction of Scotland. In Scots law, the term 'property' does not solely describe land. Instead the term 'a person's property' is used when describing objects or 'things' (in Latin ''res'') that an individual holds a right of ownership in. It is the rights that an individual holds in a 'thing' that are the subject matter of Scots property law. The terms objects or 'things' is also a wide-ranging definition, and is based on Roman law principles. Objects (or things) can be physical (such as land, a house, a car, a statue or a keyring) or they can also be unseen but still capable of being owned, (e.g. a person can have a right to payment under a contract, a lease in a house, or intellectual property rights in relation to works (s)he produced). While this may appear to encompass a wide range of 'things', they can be classified and sorted according to a legal system's rules. In Scots property law, all 'thin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |