|
Alloenzyme
Alloenzymes (or also called allozymes) are variant forms of an enzyme which differ structurally but not functionally from other allozymes coded for by different alleles at the same locus. These are opposed to isozymes, which are enzymes that perform the same function, but which are coded by genes located at different loci. Alloenzymes are common biological enzymes that exhibit high levels of functional evolutionary conservation throughout specific phyla and kingdoms. They are used by phylogeneticists as molecular markers to gauge evolutionary histories and relationships between different species. This can be done because allozymes do not have the same structure. They can be separated by capillary electrophoresis. However, some species are monomorphic for many of their allozymes which would make it difficult for phylogeneticists to assess the evolutionary histories of these species. In these instances, phylogeneticists would have to use another method to determine the evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparative Genomics
Comparative genomics is a branch of biological research that examines genome sequences across a spectrum of species, spanning from humans and mice to a diverse array of organisms from bacteria to chimpanzees. This large-scale holistic approach compares two or more genomes to discover the similarities and differences between the genomes and to study the biology of the individual genomes. Comparison of Whole genome sequencing, whole genome sequences provides a highly detailed view of how organisms are related to each other at the gene level. By comparing whole genome sequences, researchers gain insights into Genetics, genetic relationships between organisms and study Evolutionary biology, evolutionary changes. The major principle of comparative genomics is that common features of two organisms will often be encoded within the DNA that is evolutionarily Conserved sequence, conserved between them. Therefore, Comparative genomics provides a powerful tool for studying evolutionary chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes such as natural selection, common descent, and speciation that produced the diversity of life on Earth. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biology emerged through what Julian Huxley called the Modern synthesis (20th century), modern synthesis of understanding, from previously unrelated fields of biological research, such as genetics and ecology, systematics, and paleontology. The investigational range of current research has widened to encompass the genetic architecture of adaptation, molecular evolution, and the different forces that contribute to evolution, such as sexual selection, genetic drift, and biogeography. The newer field of evolutionary developmental biology ("evo-devo") investigates how embryogenesis is controlled, thus yielding a wider synthesis that integrates developmental biology with the fields of study covered by the earlier evolutionary synthesis. Subfields ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. Though cells and other microscopic structures had been observed in living organisms as early as the 18th century, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms and interactions governing their behavior did not emerge until the 20th century, when technologies used in physics and chemistry had advanced sufficiently to permit their application in the biological sciences. The term 'molecular biology' was first used in 1945 by the English physicist William Astbury, who described it as an approach focused on discerning the underpinnings of biological phenomena—i.e. uncovering the physical and chemical structures and properties of biological molecules, as well as their interactions with other molecules and how these interactions explain observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
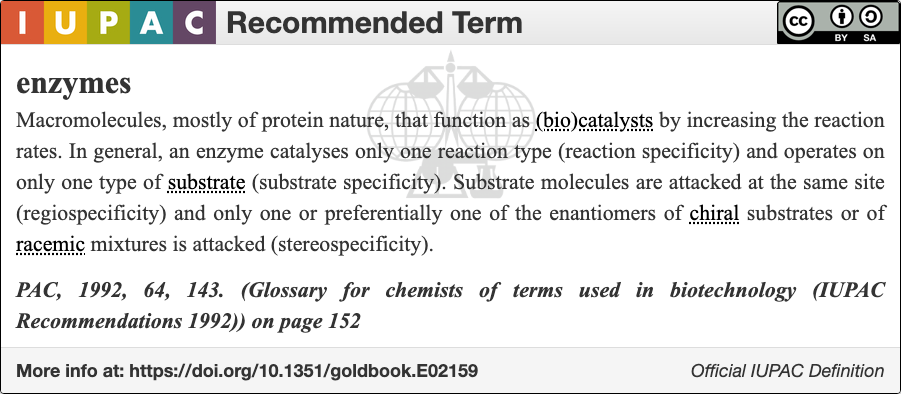
Enzymes
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes described as a ''type'' of enzyme rather than being ''like'' an enzyme, but even in the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity in anatomical structures or genes between organisms of different taxa due to shared ancestry, ''regardless'' of current functional differences. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures as retained heredity from a common descent, common ancestor after having been subjected to adaptation (biology), adaptive modifications for different purposes as the result of natural selection. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this from Aristotle's biology onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the bat wing development, wings of bats and origin of avian flight, birds, the arms of primates, the front flipper (anatomy), flippers of whales, and the forelegs of quadrupedalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Evolution
Molecular evolution describes how Heredity, inherited DNA and/or RNA change over evolutionary time, and the consequences of this for proteins and other components of Cell (biology), cells and organisms. Molecular evolution is the basis of phylogenetics, phylogenetic approaches to describing the Tree of life (biology), tree of life. Molecular evolution overlaps with population genetics, especially on shorter timescales. Topics in molecular evolution include the origins of new genes, the genetic nature of complex traits, the genetic basis of adaptation and speciation, the Evolutionary developmental biology, evolution of development, and patterns and processes underlying genome, genomic changes during evolution. History The history of molecular evolution starts in the early 20th century with comparative biochemistry, and the use of "fingerprinting" methods such as immune assays, gel electrophoresis, and paper chromatography in the 1950s to explore homologous proteins. The advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogeny
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in taxonomy and biogeography. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular evolution correlate. Molecular evolution is the process of selective changes (mutations) at a molecular level (genes, proteins, etc.) throughout various branches in the tree of life (evolution). Molecular phylogenetics makes inferences of the evolutionary relationships that arise due to molecular evolution and results in the construction of a phylogenetic tree. History The theoretical framew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in question. In addition to their use for inferring phylogenetic pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alleles
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or locus, on a DNA molecule. Alleles can differ at a single position through single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), but they can also have insertions and deletions of up to several thousand base pairs. Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function or amount of the gene product(s) they code or regulate for. However, sometimes different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation. A notable example of this is Gregor Mendel's discovery that the white and purple flower colors in pea plants were the result of a single gene with two alleles. Nearly all multicellular organisms have two sets of chromosomes at some point in their biological life cycle; that is, they are diploid. For a given locus, if the two chromosomes contain the same allele, they, and the organism, are homozygous with respect to that allele. If the alleles are differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalysis, catalyze the chemical reaction : deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNAn pyrophosphate + DNAn+1. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the Directionality (molecular biology), three prime (3')-end of a DNA strand, one nucleotide at a time. Every time a Cell division, cell divides, DNA polymerases are required to duplicate the cell's DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each daughter cell. In this way, genetic information is passed down from generation to generation. Before replication can take place, an enzy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |