|
Algorithmic Game Theory
Algorithmic game theory (AGT) is an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of game theory and computer science, focused on understanding and designing algorithms for environments where multiple strategic agents interact. This research area combines computational thinking with economic principles to address challenges that emerge when algorithmic inputs come from self-interested participants. In traditional algorithm design, inputs are assumed to be fixed and reliable. However, in many real-world applications—such as online auctions, internet routing, digital advertising, and resource allocation systems—inputs are provided by multiple independent agents who may strategically misreport information to manipulate outcomes in their favor. AGT provides frameworks to analyze and design systems that remain effective despite such strategic behavior. The field can be approached from two complementary perspectives: * ''Analysis'': Evaluating existing algorithms and systems throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Game Theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which a participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by the losses and gains of the other participant. In the 1950s, it was extended to the study of non zero-sum games, and was eventually applied to a wide range of Human behavior, behavioral relations. It is now an umbrella term for the science of rational Decision-making, decision making in humans, animals, and computers. Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum games and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics. His paper was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
PPAD (complexity)
In computer science, PPAD ("Polynomial Parity Arguments on Directed graphs") is a complexity class introduced by Christos Papadimitriou in 1994. PPAD is a subclass of TFNP based on functions that can be shown to be total by a parity argument. The class attracted significant attention in the field of algorithmic game theory because it contains the problem of computing a Nash equilibrium: this problem was shown to be complete for PPAD by Daskalakis, Goldberg and Papadimitriou with at least 3 players and later extended by Chen and Deng to 2 players.*. Definition PPAD is a subset of the class TFNP, the class of function problems in FNP that are guaranteed to be total. The TFNP formal definition is given as follows: :A binary relation P(''x'',''y'') is in TFNP if and only if there is a deterministic polynomial time algorithm that can determine whether P(''x'',''y'') holds given both ''x'' and ''y'', and for every ''x'', there exists a ''y'' such that P(''x'',''y'') holds. Subclasses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessment to form Cambridge University Press and Assessment under Queen Elizabeth II's approval in August 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 countries, it published over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publications include more than 420 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also published Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Sports and Social Centre. It also served as the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press, as part of the University of Cambridge, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Multi-agent Systems
A multi-agent system (MAS or "self-organized system") is a computerized system composed of multiple interacting intelligent agents.H. Pan; M. Zahmatkesh; F. Rekabi-Bana; F. Arvin; J. HuT-STAR: Time-Optimal Swarm Trajectory Planning for Quadrotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025. Multi-agent systems can solve problems that are difficult or impossible for an individual agent or a monolithic system to solve.Hu, J.; Turgut, A.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Robust Formation Coordination of Robot Swarms with Nonlinear Dynamics and Unknown Disturbances: Design and Experiments IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2021. Intelligence may include methodic, functional, procedural approaches, algorithmic search or reinforcement learning. With advancements in large language models (LLMs), LLM-based multi-agent systems have emerged as a new area of research, enabling more sophisticated interactions and coordination among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fair Division
Fair division is the problem in game theory of dividing a set of resources among several people who have an Entitlement (fair division), entitlement to them so that each person receives their due share. The central tenet of fair division is that such a division should be performed by the players themselves, without the need for external arbitration, as only the players themselves really know how they value the goods. There are many different kinds of fair division problems, depending on the nature of goods to divide, the criteria for fairness, the nature of the players and their preferences, and other criteria for evaluating the quality of the division. The archetypal fair division algorithm is divide and choose. The research in fair division can be seen as an extension of this procedure to various more complex settings. Description In game theory, fair division is the problem of dividing a set of resources among several people who have an Entitlement (fair division), entitlem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
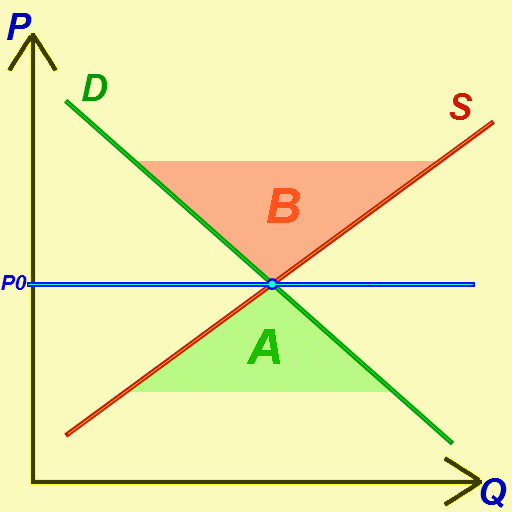
Market Equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which the economic forces of supply and demand are balanced, meaning that economic variables will no longer change. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. Understanding economic equilibrium An economic equilibrium is a situation when the economic agent cannot change the situation by adopting any strategy. The concept has been borrowed from the physical sciences. Take a system where physical forces are balanced for instance.This economically interpreted means no further change ensues. Properties of equilibrium Three basic properti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Correlated Equilibrium
In game theory, a correlated equilibrium is a solution concept that is more general than the well known Nash equilibrium. It was first discussed by mathematician Robert Aumann in 1974. The idea is that each player chooses their action according to their private observation of the value of the same public signal. A strategy assigns an action to every possible observation a player can make. If no player would want to deviate from their strategy (assuming the others also don't deviate), the distribution from which the signals are drawn is called a correlated equilibrium. Formal definition An N-player strategic game \displaystyle (N,\,\) is characterized by an action set A_i and utility function u_i for each player When player i chooses strategy a_i \in A_i and the remaining players choose a strategy profile described by the a_, then player i's utility is \displaystyle u_i(a_i,a_). A ''strategy modification'' for player i is a function \phi_i\colon A_i \to A_i. That is, \phi_i te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
PPAD
In computer science, PPAD ("Polynomial Parity Arguments on Directed graphs") is a complexity class introduced by Christos Papadimitriou in 1994. PPAD is a subclass of TFNP based on functions that can be shown to be total by a parity argument. The class attracted significant attention in the field of algorithmic game theory because it contains the problem of computing a Nash equilibrium: this problem was shown to be complete for PPAD by Daskalakis, Goldberg and Papadimitriou with at least 3 players and later extended by Chen and Deng to 2 players.*. Definition PPAD is a subset of the class TFNP, the class of function problems in FNP that are guaranteed to be total. The TFNP formal definition is given as follows: :A binary relation P(''x'',''y'') is in TFNP if and only if there is a deterministic polynomial time algorithm that can determine whether P(''x'',''y'') holds given both ''x'' and ''y'', and for every ''x'', there exists a ''y'' such that P(''x'',''y'') holds. Subclas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Complexity Class
In computational complexity theory, a complexity class is a set (mathematics), set of computational problems "of related resource-based computational complexity, complexity". The two most commonly analyzed resources are time complexity, time and space complexity, memory. In general, a complexity class is defined in terms of a type of computational problem, a model of computation, and a bounded resource like time complexity, time or space complexity, memory. In particular, most complexity classes consist of decision problems that are solvable with a Turing machine, and are differentiated by their time or space (memory) requirements. For instance, the class P (complexity), P is the set of decision problems solvable by a deterministic Turing machine in polynomial time. There are, however, many complexity classes defined in terms of other types of problems (e.g. Counting problem (complexity), counting problems and function problems) and using other models of computation (e.g. probabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fixed Point Theorem
In mathematics, a fixed-point theorem is a result saying that a function ''F'' will have at least one fixed point (a point ''x'' for which ''F''(''x'') = ''x''), under some conditions on ''F'' that can be stated in general terms. In mathematical analysis The Banach fixed-point theorem (1922) gives a general criterion guaranteeing that, if it is satisfied, the procedure of iterating a function yields a fixed point. By contrast, the Brouwer fixed-point theorem (1911) is a non- constructive result: it says that any continuous function from the closed unit ball in ''n''-dimensional Euclidean space to itself must have a fixed point, but it doesn't describe how to find the fixed point (see also Sperner's lemma). For example, the cosine function is continuous in ��1, 1and maps it into ��1, 1 and thus must have a fixed point. This is clear when examining a sketched graph of the cosine function; the fixed point occurs where the cosine curve ''y'' = cos(''x'') intersects the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Approximation Ratio
In computer science and operations research, approximation algorithms are efficient algorithms that find approximate solutions to optimization problems (in particular NP-hard problems) with provable guarantees on the distance of the returned solution to the optimal one. Approximation algorithms naturally arise in the field of theoretical computer science as a consequence of the widely believed P ≠ NP conjecture. Under this conjecture, a wide class of optimization problems cannot be solved exactly in polynomial time. The field of approximation algorithms, therefore, tries to understand how closely it is possible to approximate optimal solutions to such problems in polynomial time. In an overwhelming majority of the cases, the guarantee of such algorithms is a multiplicative one expressed as an approximation ratio or approximation factor i.e., the optimal solution is always guaranteed to be within a (predetermined) multiplicative factor of the returned solution. However, there a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
MIT Press
The MIT Press is the university press of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The MIT Press publishes a number of academic journals and has been a pioneer in the Open Access movement in academic publishing. History MIT Press traces its origins back to 1926 when MIT published a lecture series entitled ''Problems of Atomic Dynamics'' given by the visiting German physicist and later Nobel Prize winner, Max Born. In 1932, MIT's publishing operations were first formally instituted by the creation of an imprint called Technology Press. This imprint was founded by James R. Killian, Jr., at the time editor of MIT's alumni magazine and later to become MIT president. Technology Press published eight titles independently, then in 1937 entered into an arrangement with John Wiley & Sons in which Wiley took over marketing and editorial responsibilities. In 1961, the centennial of MIT's founding charter, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |