|
Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy
Alcoholic cardiomyopathy (ACM) is a disease in which the long-term consumption of alcohol (drug), alcohol leads to heart failure. ACM is a type of dilated cardiomyopathy. The heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, leading to heart failure. It can affect other parts of the body if the heart failure is severe. It is most common in males between the ages of 35 and 50. Etiology The causal relationship between alcohol consumption and cardiomyopathy and heart failure is unclear. Per the American Heart Association (AHA), alcohol is one of the leading causes of dilated cardiomyopathy. However, multiple longitudinal studies have shown a paradoxical lowering of dilated cardiomyopathy with modest-to-moderate alcohol consumption. ACM is a type of heart disease that occurs due to chronic alcohol consumption. The etiology of ACM is multifactorial, with a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors playing a role. The direct toxic effects of alcohol on the heart muscle c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (drug)
Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ethanol, is the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits (hard liquor). Alcohol is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant, decreasing Action potential, electrical activity of neurons in the brain, which causes the characteristic effects of alcohol intoxication ("drunkenness"). Among other effects, alcohol produces euphoria, anxiolytic, decreased anxiety, increased sociability, sedation, and impairment of cognitive, memory, motor control, motor, and sense, sensory function. Alcohol has a variety of adverse effects. Short-term effects of alcohol consumption, Short-term adverse effects include generalized impairment of neurocognitive function, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and symptoms of hangover. Alcohol is addiction, addictive and can result in alcohol use disorder, Substance dependence, dependence, and Alcohol withdrawal syndrome, withdrawal upon cessation. The long-term effects of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilated Cardiomyopathy E00475 (CardioNetworks ECHOpedia)
Dilation (or dilatation) may refer to: Physiology or medicine * Cervical dilation, the widening of the cervix in childbirth, miscarriage etc. * Coronary dilation, or coronary reflex * Dilation and curettage, the opening of the cervix and surgical removal of the contents of the uterus * Dilation and evacuation, the dilation of the cervix and evacuation of the contents of the uterus * Esophageal dilation, a procedure for widening a narrowed esophagus * Pupillary dilation (also called mydriasis), the widening of the pupil of the eye * Vasodilation, the widening of luminal diameter in blood vessels Mathematics * Dilation (affine geometry), an affine transformation * Dilation (metric space), a function from a metric space into itself * Dilation (operator theory), a dilation of an operator on a Hilbert space * Dilation (morphology), an operation in mathematical morphology * Scaling (geometry), including: ** Homogeneous dilation (homothety), the scalar multiplication operator on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
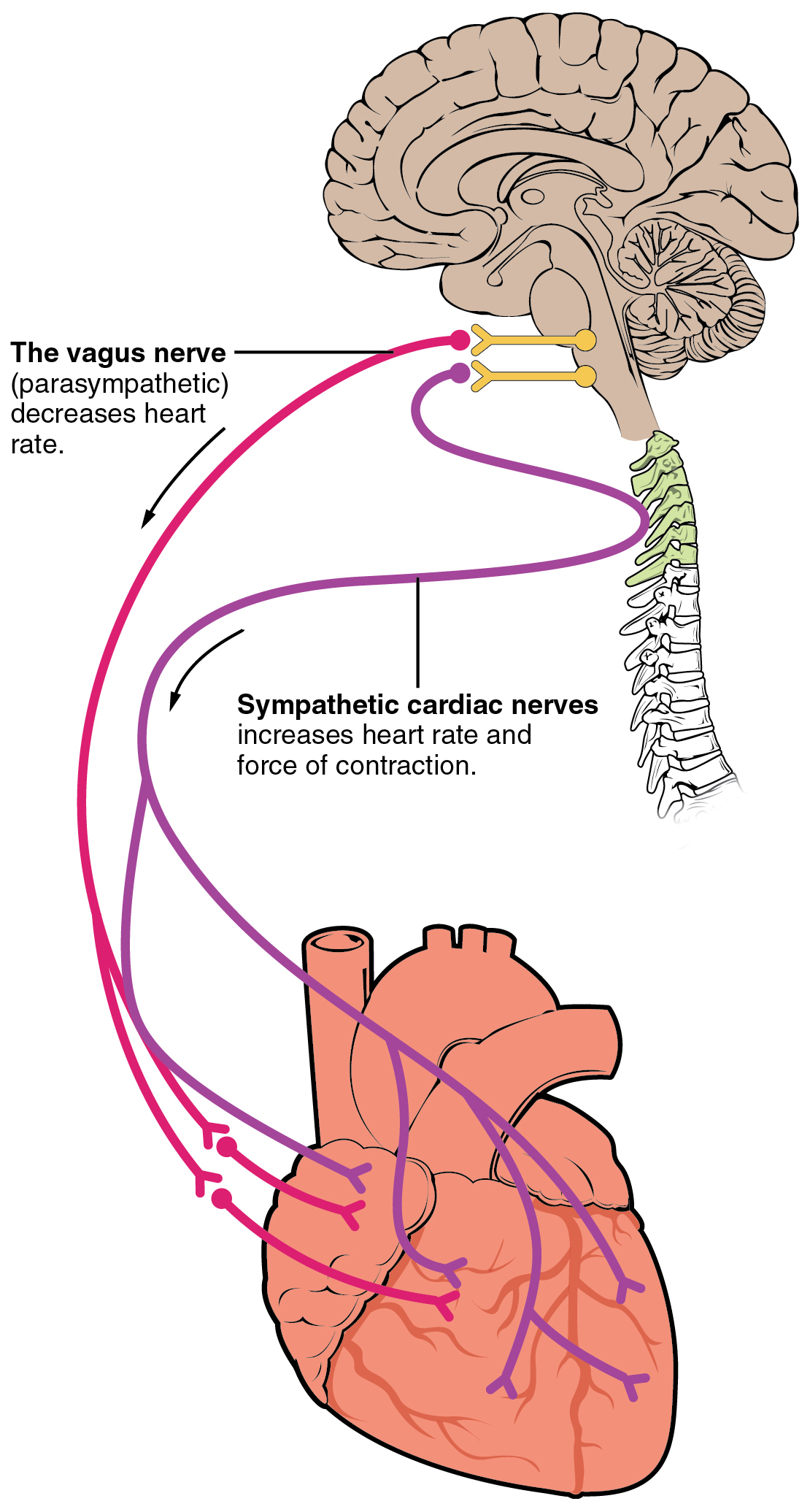
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of primary diseases of the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. An irregular heart beat and fainting may occur. Those affected are at an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. As of 2013, cardiomyopathies are defined as "disorders characterized by morphologically and functionally abnormal myocardium in the absence of any other disease that is sufficient, by itself, to cause the observed phenotype." Types of cardiomyopathy include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (broken heart syndrome). In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy the heart muscle enlarges and thickens. In dilated cardiomyopathy the ventricles enlarge and weaken. In restrictive cardiomyopathy the ventricle stiffens. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Transplant
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart from a recently deceased organ donor (brain death is the most common) and implant it into the patient. The patient's own heart is either removed and replaced with the donor heart ( orthotopic procedure) or, much less commonly, the recipient's diseased heart is left in place to support the donor heart (heterotopic, or "piggyback", transplant procedure). Approximately 5,000 heart transplants are performed each year worldwide, more than half of which are in the US. Post-operative survival periods average 15 years. Heart transplantation is not considered to be a cure for heart disease; rather it is a life-saving treatment intended to improve the quality and duration of life for a recipient. History American medical researcher Simon Fle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Pacemaker
A pacemaker, also known as an artificial cardiac pacemaker, is an Implant (medicine), implanted medical device that generates Pulse (signal processing), electrical pulses delivered by electrodes to one or more of the Heart chamber, chambers of the heart. Each pulse causes the targeted chamber(s) to muscle contraction, contract and pump blood, thus regulating the function of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The primary purpose of a pacemaker is to maintain an even heart rate, either because the heart's natural cardiac pacemaker provides an inadequate or irregular heartbeat, or because there is a heart block, block in the heart's electrical conduction system. Modern pacemakers are externally programmable and allow a cardiologist to select the optimal pacing modes for individual patients. Most pacemakers are on demand, in which the stimulation of the heart is based on the dynamic demand of the circulatory system. Others send out a fixed rate of impulses. A specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implantable Cardioverter-defibrillator
An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) or automated implantable cardioverter defibrillator (AICD) is a device implantable inside the body, able to perform defibrillation, and depending on the type, cardioversion and pacing of the heart. The ICD is the first-line treatment and prophylactic therapy for patients at risk for sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia. "AICD" was trademarked by the Boston Scientific corporation, so the more generic "ICD" is preferred terminology. On average ICD batteries last about six to ten years. Advances in technology, such as batteries with more capacity or rechargeable batteries, may allow batteries to last for more than ten years. The leads (electrical cable wires connecting the device to the heart) have much longer average longevity, but can malfunction in various ways, specifically insulation failure or fracture of the conductor; thus, ICDs and leads generally require replacement after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diuretics
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine. Medical uses In medicine, diuretics are used to treat heart failure, liver cirrhosis, hypertension, influenza, water poisoning, and certain kidney diseases. Some diuretics, such as acetazolamide, help to make the urine more alkaline, and are helpful in increasing excretion of substances such as aspirin in cases of overdose or poisoning. Diuretics are sometimes abused by people with an eating disorder, especially people with bulimia nervosa, with the goal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Blockers
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention). They are also widely used to treat high blood pressure, although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most people. Beta blockers are competitive antagonists that block the receptor sites for the endogenous catecholamines epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) on adrenergic beta receptors, of the sympathetic nervous system, which mediates the fight-or-flight response. Beta-adrenergic receptors are found on cells of the heart muscles, smooth muscles, airways, arteries, kidneys, and other tissues that are part of the sympathetic nervous system and lead to stress responses, especially when they are stimulated by epinephrine (adrenaline). Beta blockers interfere with the binding to the receptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACE Inhibitors
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of hypertension, high blood pressure and heart failure. This class of medicine works by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decrease in blood volume, which leads to lower blood pressure and decreased oxygen demand from the heart. ACE inhibitors Enzyme inhibitor, inhibit the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme, an important component of the renin–angiotensin system which converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II, and hydrolyses bradykinin. Therefore, ACE inhibitors decrease the formation of angiotensin II, a vasoconstrictor, and increase the level of bradykinin, a peptide vasodilator. This combination is synergistic in lowering blood pressure. As a result of inhibiting the ACE enzyme in the bradykinin system, the ACE inhibitor drugs allow for increased levels of bradykinin which would normally be degraded. Bradykinin produces prostaglandin. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QRS Complex
The QRS complex is the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles of the heart and contraction of the large ventricular muscles. In adults, the QRS complex normally lasts ; in children it may be shorter. The Q, R, and S waves occur in rapid succession, do not all appear in all leads, and reflect a single event and thus are usually considered together. A Q wave is any downward deflection immediately following the P wave. An R wave follows as an upward deflection, and the S wave is any downward deflection after the R wave. The T wave follows the S wave, and in some cases, an additional U wave follows the T wave. To measure the QRS interval start at the end of the PR interval (or beginning of the Q wave) to the end of the S wave. Normally this interval is 0.08 to 0.10 seconds. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods of abnormal cardiac cycle, beating, which become longer or continuous over time. It may also start as other forms of arrhythmia such as atrial flutter that then transform into AF. Episodes can be asymptomatic. Symptomatic episodes may involve heart palpitations, syncope (medicine), fainting, Presyncope, lightheadedness, Unconsciousness, loss of consciousness, or shortness of breath. Atrial fibrillation is associated with an increased risk of heart failure, dementia, and stroke. It is a type of supraventricular tachycardia. Atrial fibrillation frequently results from bursts of tachycardia that originate in muscle bundles extending from the Atrium (heart), atrium to the pulmonary veins. Pulmonary vein isolation by catheter ablation, trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilated Cardiomyopathy B-Mode
Dilation (or dilatation) may refer to: Physiology or medicine * Cervical dilation, the widening of the cervix in childbirth, miscarriage etc. * Coronary dilation, or coronary reflex * Dilation and curettage, the opening of the cervix and surgical removal of the contents of the uterus * Dilation and evacuation, the dilation of the cervix and evacuation of the contents of the uterus * Esophageal dilation, a procedure for widening a narrowed esophagus * Pupillary dilation (also called mydriasis), the widening of the pupil of the eye * Vasodilation, the widening of luminal diameter in blood vessels Mathematics * Dilation (affine geometry), an affine transformation * Dilation (metric space), a function from a metric space into itself * Dilation (operator theory), a dilation of an operator on a Hilbert space * Dilation (morphology), an operation in mathematical morphology * Scaling (geometry), including: ** Homogeneous dilation (homothety), the scalar multiplication operator on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |