|
Al-Mahdi Ahmad Bin Yahya
Al-Mahdī Aḥmad ibn Yaḥyā, or Aḥmad ibn Yaḥyā Ibn al-Murtaḍā () (1363/1374 – 1436), was a Muʿtazila scholar and imam of the Zaidī state in Yemen who briefly held the imamate in 1391–1392. He was an encyclopedist and a prolific writer on a range of subjects. Aḥmad ibn Yaḥyā was a 12th-generation descendant of the Zaidī imām ad-Da'i Yusuf (d. 1012). His full name was: al-Mahdī Aḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn al-Murtaḍā ibn Aḥmad al-Jawad ibn al-Murtaḍā ibn al-Mufaḍḍal ibn al-Manṣūr ibn al-Mufaḍḍal ibn al-Ḥajjāj ibn Alī ibn Yaḥyā ibn al-Qāsim ibn al-Da'ī Yūsuf. In 1391, when the elderly imām al-Nasir Muhammad Salah al-Din died, his sons were still minors. The qāḍī, ad-Dawwarī, took temporary administration of the Zaidī domains of highland Yemen, in their name. However, the Zaidi ulema assembled in the Jamal ad-Dīn Mosque in San'a and appointed Aḥmad ibn Yaḥyā imām under the title 'al-Mahdī Aḥmad'. The appointment was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muʿtazila
Mu'tazilism (, singular ) is an Islamic theological school that appeared in early Islamic history and flourished in Basra and Baghdad. Its adherents, the Mu'tazilites, were known for their neutrality in the dispute between Ali and his opponents after the death of the third caliph, Uthman. By the 10th century the term ''al-muʿtazilah'' had come to refer to a distinctive Islamic school of speculative theology ('' kalām'').Muʿtazilah ", ''''. This school of was founded by |
Salafi
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a fundamentalist revival movement within Sunni Islam, originating in the late 19th century and influential in the Islamic world to this day. The name "''Salafiyya''" is a self-designation, claiming a return to the traditions of the "pious predecessors" (), the first three generations of Muslims (the Islamic prophet Muhammad and the is companions then the , and the third generation, the ), who are believed to exemplify the pure form of Islam. In practice, Salafis claim that they rely on the Qur'an, the and the (consensus) of the , giving these writings precedence over what they claim as "later religious interpretations".Bin Ali Mohamed ''Roots Of Religious Extremism, The: Understanding The Salafi Doctrine Of Al-wala' Wal Bara'' World Scientific, 2015 p. 61 The Salafi movement aimed to achieve a renewal of Muslim life, and had a major influence on many Muslim thinkers and movements across the Islamic world. Salafi Muslims oppose ' (reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Yemeni People
The 14th century lasted from 1 January 1301 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCCI) to 31 December 1400 (MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of King Charles IV of France led to a claim to the French throne by King Edward III of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and the Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever established by a single conqueror. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Biographers
The 14th century lasted from 1 January 1301 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCCI) to 31 December 1400 (MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of King Charles IV of France led to a claim to the French throne by King Edward III of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and the Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever established by a single conqueror. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1436 Deaths
Year 1436 ( MCDXXXVI) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. Events January–March * January 11 – Eric of Pomerania is deposed from the Swedish throne for the second time, only three months after having been reinstated. Engelbrekt Engelbrektsson remains the leader of the land, in his capacity of ''rikshövitsman'', the military commander of the realm. * February 14 – In Yemen, the Imam Al-Mansur Ali bin Salah ad-Din of the Zaidi state, becomes of one of the victims of a plague sweeping the kingdom. His son, an-Nasir Muhammad, becomes the new Imam but dies four weeks later. * February – Karl Knutsson Bonde becomes the Rikshövitsman of the Swedish military jointly with Engelbrekt. The two will share the title until Engelbrekt's death two months later. * March 21 – Italian archaeologist Ciriaco Pizzecolli, exploring at the Greek village of Kastri) rediscovers the site of Delphi, eight centuries after it had been abandoned. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1363 Births
Year 1363 ( MCCCLXIII) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * April 9 – Haakon VI of Norway marries Margaret I of Denmark. * August – The Revolt of Saint Titus, against the rule of the Republic of Venice in the Kingdom of Candia (island of Crete), begins. * August 30–October 4 – Battle of Lake Poyang: The Dahan rebel forces of Chen Youliang are defeated by the Red Turban Rebel forces of Zhu Yuanzhang, during the final decade of Yuan dynasty control over China. Zhu's naval forces of 200,000 are pitted against Chen's naval forces of 650,000 troops, in what is not only the largest naval battle of the medieval age, but also one of the largest naval battles in history. Date unknown * Ottoman Turks seize Filibe (Philippopolis) in Thrace in the Byzantine–Ottoman wars. * Dmitry Donskoy, Prince of the Grand Duchy of Moscow, dethrones Dmitry of Suzdal to become Grand Prince of Vladimir. * Philip the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaydi
Zaydism () is a branch of Shia Islam that emerged in the eighth century following Zayd ibn Ali's unsuccessful rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate. Zaydism is one of the three main branches of Shi'ism, with the other two being Twelverism and Ismailism. Zaydism is typically considered the Shia branch that is closest to Sunni Islam, although the "classical" form of Zaydism (usually referred to as Hadawi) historically changed its stance on Sunni and Shia traditions multiple times, to the point where Zaydis' simply accepting Ali as a rightful successor to Muhammad was enough to consider them Shia. Twelver Shias sometimes consider Zaydism to be a "fifth school" of Sunni Islam. Zaydis regard rationalism as more important than Quranic literalism and historically were quite tolerant towards Sunni Shafi'ism, a religion of about half of the Yemenis. Most of the world's Zaydis are located in northern Yemen and Najran, Saudi Arabia. History In the 7th century some early Musli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
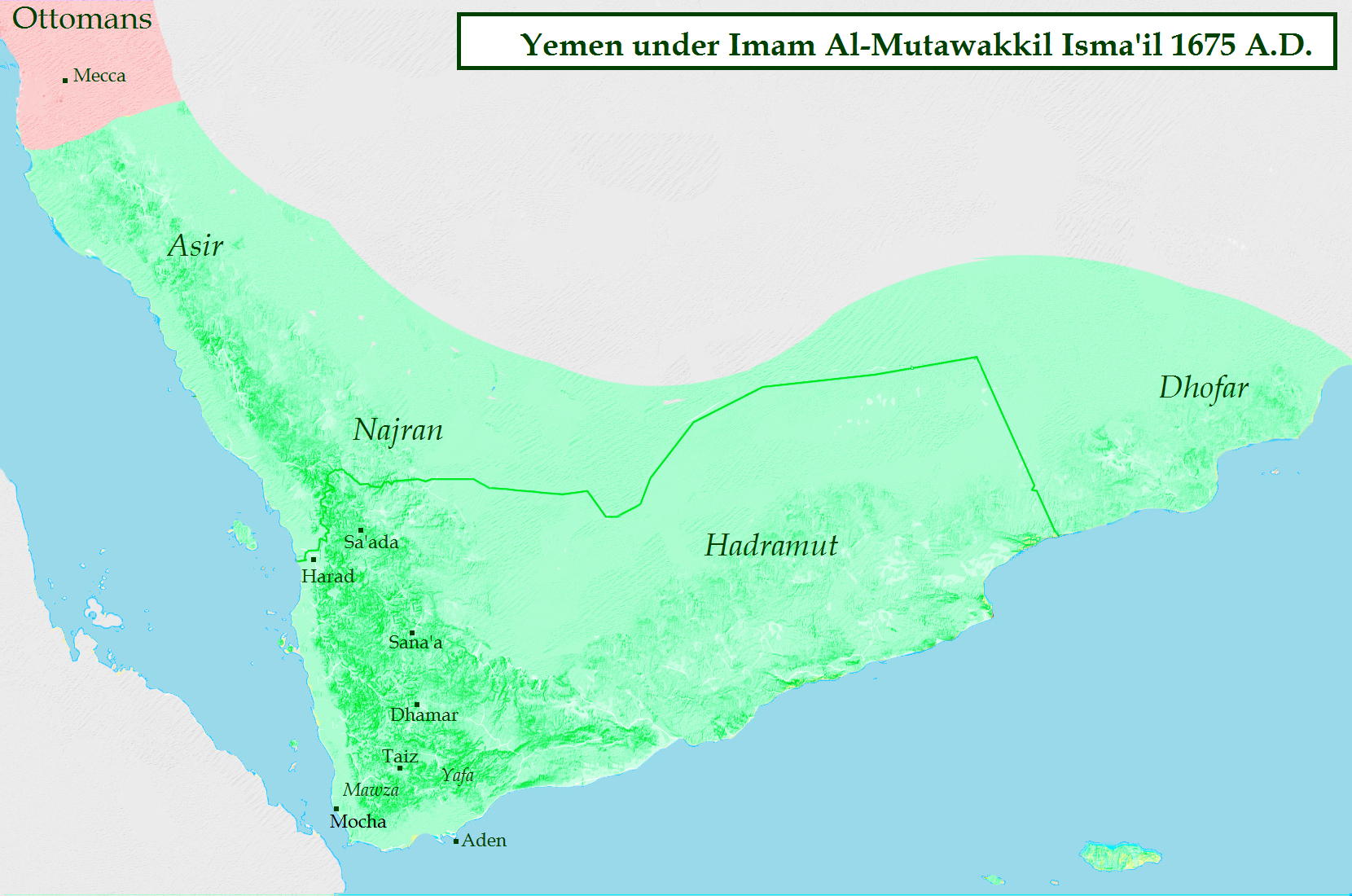
History Of Yemen
Yemen is one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Near East. Its relatively fertile land and adequate rainfall in a moister climate helped sustain a stable population, a feature recognized by the ancient Greek geographer Ptolemy, who described Yemen as ''Arabia Felix, Eudaimon Arabia'', meaning "''Fertile Arabia''" or "''Happy Arabia''". The South Arabian alphabet was developed at latest between the 12th century BC and the 6th century AD, when Yemen was successively dominated by six civilizations that controlled the lucrative spice trade: Minaeans, Ma'in, Qataban, Kingdom of Hadhramaut, Hadhramaut, Awsan, Sheba, Saba, and Himyarite Kingdom, Himyar. With the 630 AD Early Muslim conquests, arrival of Islam, Yemen became part of the wider Muslim world, where it has remained. Ancient history With its long sea border between early civilizations, Yemen has long existed at a crossroads of cultures with a strategic location in terms of trade on the west of the Arabian Peninsula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rassids
The Imams of Yemen and later also the Kings of Yemen were religiously consecrated leaders belonging to the Zaidiyyah branch of Shia Islam. They established a blend of religious and political rule in parts of Yemen from 897. Their imamate endured under varying circumstances until the republican revolution in 1962, then the formal abolition of the monarchy in 1970. Zaidiyyah theology differed from Ismailis or Twelver Shi'ites by stressing the presence of an active and visible imam as leader. The imam was expected to be knowledgeable in religious sciences, and to prove himself a worthy headman of the community, even in battle if this was necessary. A claimant of the imamate would proclaim a "call" ( da'wa), and there were not infrequently more than one claimant. The historian Ibn Khaldun (d. 1406) mentions the clan that usually provided the imams as the Banu Rassi or Rassids (). In the original Arab sources the term Rassids is otherwise hardly used; in Western literature it usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imams Of Yemen
The Imams of Yemen, later also titled the Kings of Yemen, were religiously consecrated leaders ( imams) belonging to the Zaidi branch of Shia Islam. They established a blend of religious and temporal-political rule in parts of Yemen from 897. Their imamate endured under varying circumstances until the end of the North Yemen civil war in 1970, following the republican revolution in 1962. Zaidi theology differs from Isma'ilism and Twelver Shi'ism by stressing the presence of an active and visible imam as leader. The imam was expected to be knowledgeable in religious scholarship, and to prove himself a worthy headman of the community, even in battle if this was necessary. A claimant of the imamate would proclaim a "call" (dawah), and there were not infrequently more than one claimant. History Establishment The imams based their legitimacy on descent from the Islamic prophet Muhammad, mostly via al-Qasim ar-Rassi (d. 860). After him, the medieval imams are sometimes known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |