|
Akathisia
Akathisia (IPA: /æ.kə.ˈθɪ.si.ə/) is a movement disorder characterized by a subjective feeling of inner restlessness accompanied by mental distress and/or an inability to sit still. Usually, the legs are most prominently affected. Those affected may fidget, rock back and forth, or pace, while some may just have an uneasy feeling in their body. The most severe cases may result in poor adherence to medications, exacerbation of psychiatric symptoms, and, because of this, aggression, violence, and/or suicidal thoughts. Akathisia is also associated with threatening behaviour and physical aggression in mentally disordered patients. However, the attempts to find potential links between akathisia and emerging suicidal or homicidal behaviour were not systematic and were mostly based on a limited number of case reports and small case series. Apart from these few low-quality studies, there is another more recent and better quality study (a systematic review from 2021) that concludes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychomotor Agitation
Psychomotor agitation is a symptom in various disorders and health conditions. It is characterized by unintentional and purposeless motions and restlessness, often but not always accompanied by emotional distress and is always an indicative for admission. Typical manifestations include pacing around, wringing of the hands, uncontrolled tongue movement, pulling off clothing and putting it back on, and other similar actions. In more severe cases, the motions may become harmful to the individual, and may involve things such as ripping, tearing, or chewing at the skin around one's fingernails, lips, or other body parts to the point of bleeding. Psychomotor agitation is typically found in various mental disorders, especially in psychotic and mood disorders. It can be a result of drug intoxication or withdrawal. It can also be caused by severe hyponatremia. People with existing psychiatric disorders and men under the age of 40 are at a higher risk of developing psychomotor agitation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
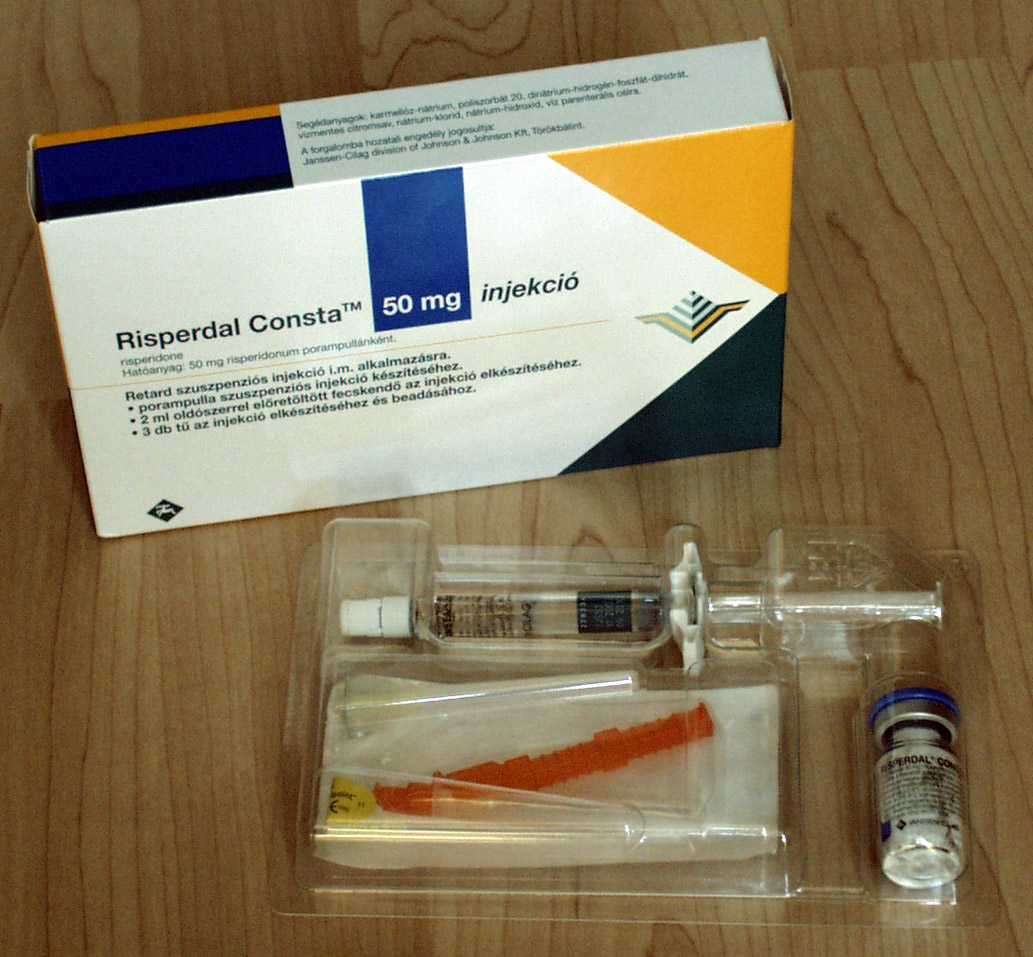
Antipsychotic
Antipsychotics, previously known as neuroleptics and major tranquilizers, are a class of Psychiatric medication, psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), principally in schizophrenia but also in a range of other psychotic disorders. They are also the mainstay, together with mood stabilizers, in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Moreover, they are also used as adjuncts in the treatment of Treatment-resistant depression, treatment-resistant major depressive disorder. The use of antipsychotics may result in many unwanted side effects such as Extrapyramidal symptoms, involuntary movement disorders, gynecomastia, impotence, weight gain and metabolic syndrome. Long-term use can produce List of long term side effects of antipsychotics, adverse effects such as tardive dyskinesia, tardive dystonia, Akathisia, tardive akathisia, and brain tissue volume reduction. The long term use of antipsychotics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirtazapine
Mirtazapine, sold under the brand name Remeron among others, is an atypical antidepressant, atypical tetracyclic antidepressant, and as such is used primarily to treat Depression (mood), depression. Its effects may take up to four weeks but can also manifest as early as one to two weeks. It is often used in cases of depression complicated by anxiety or insomnia. The effectiveness of mirtazapine is comparable to other commonly prescribed antidepressants. It is taken oral administration, by mouth. Common side effects include somnolence, sleepiness, vertigo, dizziness, hyperphagia, increased appetite, and weight gain. Serious side effects may include mania, neutropenia, low white blood cell count, and increased suicide among children. Drug withdrawal, Withdrawal symptoms may occur with stopping. It is not recommended together with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, although evidence supporting the danger of this combination has been challenged. It is unclear if use during pregnancy i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine) , medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the Human brain, brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system , peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system, using various techniques of neurotherapy. IEEE Brain (2019). "Neurotherapy: Treating Disorders by Retraining the Brain". ''The Future Neural Therapeutics White Paper''. Retrieved 23.01.2025 from: https://brain.ieee.org/topics/neurotherapy-treating-disorders-by-retraining-the-brain/#:~:text=Neurotherapy%20trains%20a%20patient's%20brain,wave%20activity%20through%20positive%20reinforcement International Neuromodulation Society, Retrieved 23 January 2025 from: https://www.neuromodulation.com/ Val Danilov I (2023). "The O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), colloquially known as "benzos", are a class of central nervous system (CNS) depressant, depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955, and was made available in 1960 by Roche, Hoffmann–La Roche, which followed with the development of diazepam (Valium) three years later, in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide. Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, GABAA receptor, resulting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenhydramine
Diphenhydramine, sold under the brand name Benadryl among others, is an antihistamine and sedative. Although generally considered sedating, diphenhydramine can cause paradoxical central nervous system stimulation in some individuals, particularly at higher doses. This may manifest as agitation, anxiety, or restlessness rather than sedation. It is a H1 antagonist#First-generation (non-selective, classical), first-generation H1-antihistamine and it works by blocking certain effects of histamine, which produces its antihistamine and sedative effects. Diphenhydramine is also a potent anticholinergic. It is mainly used to treat allergy, allergies, insomnia, and symptoms of the common cold. It is also less commonly used for tremors in parkinsonism, and nausea. It is taken oral administration, by mouth, injection into a vein, injected into a vein, injection into a muscle, injected into a muscle, or topical medication, applied to the skin. Maximal effect is typically around two hours af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction. Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathisia, sexual dysfunction, and emotional blunting. There is an increased risk of Suicidal ideation, suicidal thinking and Suicide, behavior when taken by children, adolescents, and young adults. Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome, Discontinuation syndrome, which resembles recurrent Depression (mood), depression in the case of the Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, SSRI class, may occur after stopping the intake of any antidepressant. Research regarding the effectiveness of antidepressants for depression in adults is controversial and has found both benefits and drawbacks. Meanwhile, evidence of benefit in children and adolescents is unclear, even though antidepressant use has considerably increased in children and adolescents in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipsychotic Switching
Antipsychotic switching refers to the process of switching out one antipsychotic for another antipsychotic. There are multiple Indication (medicine), indications for switching antipsychotics, including inadequate efficacy and drug intolerance. There are several strategies that have been theorized for antipsychotic switching, based upon the timing of discontinuation and tapering of the original antipsychotic and the timing of initiation and titration of the new antipsychotic. Major adverse effects from antipsychotic switching may include Supersensitivity psychosis, supersensitivity syndromes, Drug withdrawal, withdrawal, and Rebound effect, rebound syndromes. Rationale Antipsychotics may be switched due to inadequate efficacy, drug intolerance, patient/guardian preference, drug regimen simplification, or for economic reasons. # Inadequate efficacy: An inadequate treatment response to an antipsychotic, assuming that the lack of efficacy is due to an otherwise adequately dosed regime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Syndrome
In chemistry and biology, activation is the process whereby something is prepared or excited for a subsequent reaction. Chemistry In chemistry, "activation" refers to the reversible transition of a molecule into a nearly identical chemical or physical state, with the defining characteristic being that this resultant state exhibits an increased propensity to undergo a specified chemical reaction. Thus, activation is conceptually the opposite of protection, in which the resulting state exhibits a ''decreased'' propensity to undergo a certain reaction. The energy of activation specifies the amount of free energy the reactants must possess (in addition to their rest energy) in order to initiate their conversion into corresponding products—that is, in order to reach the transition state for the reaction. The energy needed for activation can be quite small, and often it is provided by the natural random thermal fluctuations of the molecules themselves (i.e. without any exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. The brain includes several distinct dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward-motivated behavior. The anticipation of most types of rewards increases the level of dopamine in the brain, and many addictive drugs increase dopamine release or block its reuptake into neurons following release. Other brain dopamine pathways are involved in motor control and in controllin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions. SSRIs primarily work by blocking serotonin reabsorption (reuptake) via the serotonin transporter, leading to gradual changes in brain signaling and receptor regulation, with some also interacting with sigma-1 receptors, particularly fluvoxamine, which may contribute to cognitive effects. Marketed SSRIs include six main antidepressants—citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, and sertraline—while dapoxetine is indicted for premature ejaculation. Fluoxetine has been approved for veterinary use in treatment of canine separation anxiety. SSRIs are the most widely prescribed antidepressants in many countries. Their effectiveness, especially for mild to moderate depression, remains debated due to mixed research findings and concerns abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Generation Antipsychotic
Typical antipsychotics (also known as major tranquilizers, and first generation antipsychotics) are a class of antipsychotic drugs first developed in the 1950s and used to treat psychosis (in particular, schizophrenia). Typical antipsychotics may also be used for the treatment of acute mania, agitation, and other conditions. The first typical antipsychotics to come into medical use were the phenothiazines, namely chlorpromazine which was discovered serendipitously. Another prominent grouping of antipsychotics are the butyrophenones, an example of which is haloperidol. The newer, second-generation antipsychotics, also known as atypical antipsychotics, have largely supplanted the use of typical antipsychotics as first-line agents due to the higher risk of movement disorders with typical antipsychotics. Both generations of medication tend to block receptors in the brain's dopamine pathways, but atypicals at the time of marketing were claimed to differ from typical antipsychotics in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |