|
Air Gunner
An air gunner or aerial gunner is a member of a military aircrew who operates flexible-mount or turret-mounted machine guns or autocannons in an aircraft. Modern aircraft weapons are usually operated automatically without the need for a dedicated air gunner, but older generation (World War II and earlier) bombers used to carry up to eight air gunners. Most modern air gunners are helicopter door gunners, who typically have other primary roles such as crew chief or observer in addition to their air gunner role. Others fly as members of aircrews on gunships, where their duties may include loading guns or manually firing them if computer systems fail. A modern gunner can be someone who operates armament on an aircraft besides the pilot or someone defending the aircraft with a machine gun or auto-cannon (more commonly in World War II) References See also * Aircrew (Flight crew) * Door gunner * Tail gunner * Nose gunner * Gunner Badge The Aerial Gunner Badge was a milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waist Gunner In Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress, 1943
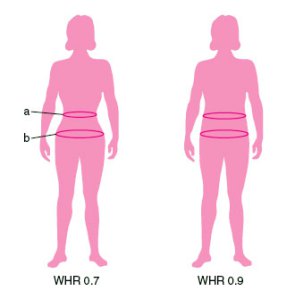
The waist is the part of the abdomen between the rib cage and hips. On people with slim bodies, the waist is the narrowest part of the torso. ''Waistline'' refers to the horizontal line where the waist is narrowest, or to the general appearance of the waist. Structure Because of this and because the waist is often synonymous with the stomach, one can become confused as to the exact location of the waist. Another confusing factor is that the waistline differs on different people. A study showed that self-reported measurements as opposed to measurement done by a technician, underestimated waist circumference and this underestimation increased with increased body size. In the study, waist circumference measured at the level of the umbilicus was larger than that measured at the natural waist. To locate the natural waistline, one need simply stand upright and then tilt over to the side keeping the legs and hips straight. Where the torso creases is the natural waistline. Waist me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
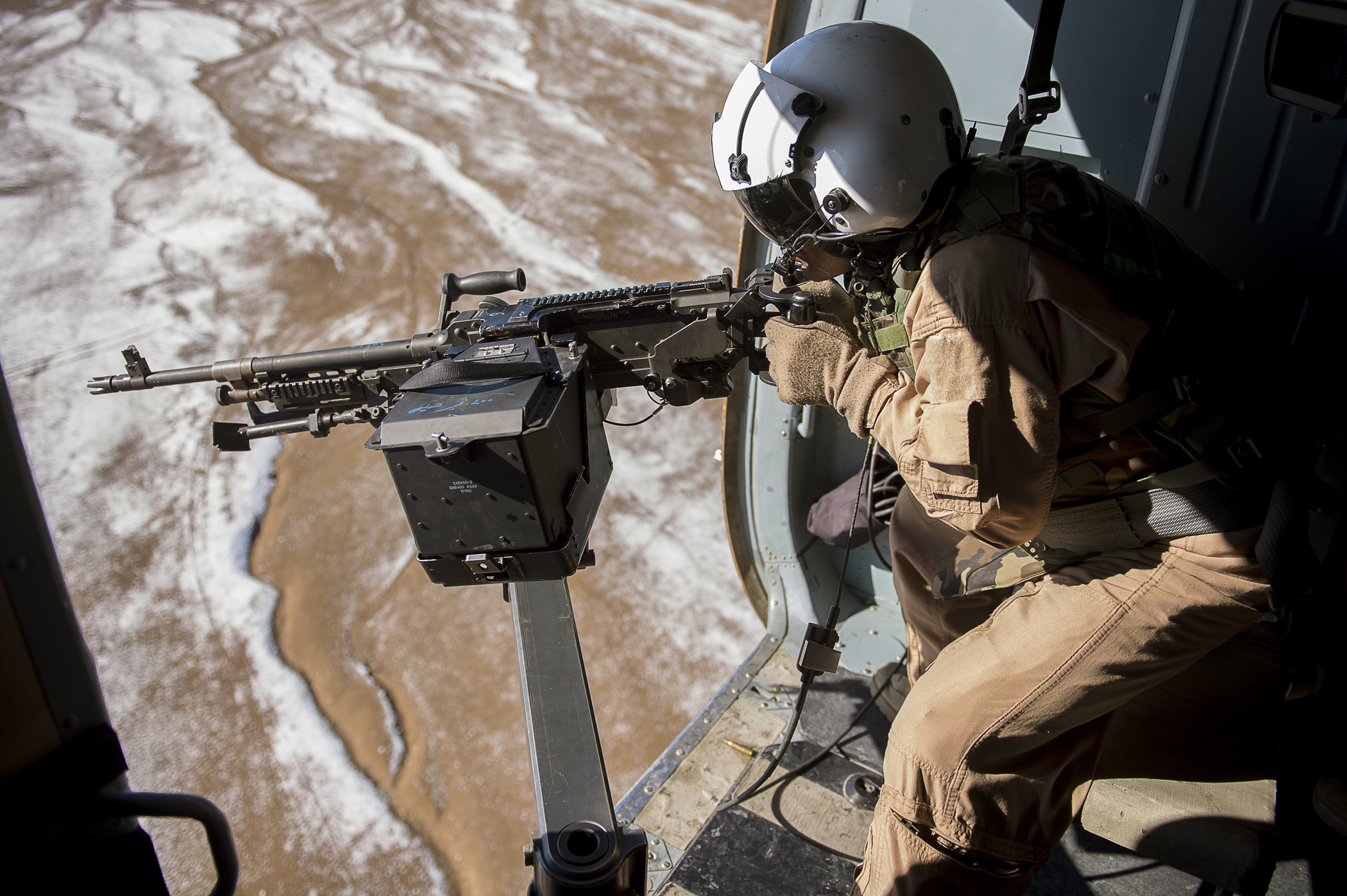
Door Gunner
A door gunner is a crewman tasked with firing and maintaining manually directed armament aboard a military helicopter. The actual role will vary depending on the task given on a particular mission. For certain aircraft a door gunner would use a fully automatic Gatling gun placement. On many larger aircraft such as military planes a turret is used along with heavy cannons. Origins The concept of the ''door gunner'' originated during the Vietnam War, when helicopters were first used in combat in large numbers. The original personnel who served as early door gunners aboard CH-21, UH-34, and UH-1 helicopters in Vietnam, were enlisted men, with a designated and specially trained '' crew chief'' serving as both the aircraft's maintenance manager and a door gunner. Normally, a second enlisted soldier served as a second door gunner (such as on a UH-1, and UH-34, which both used two gunners – one on each side of the aircraft). Later, as the war progressed, the door gunner posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunner Badge
The Aerial Gunner Badge was a military aeronautical badge of the United States Army Air Forces and was issued during the Second World War. The badge was first created and authorized on April 29, 1943 to recognize both the training and hazardous duty of aerial gunners, who manned defensive machineguns on board such aircraft as the B-17, B-24, B-25, B-26 and B-29 bombers. The Aerial Gunner Badge appeared as a standard observer badge, upon which was centered a winged bullet. It was primarily awarded to USAAF enlisted aircrewmen, but a small number of commissioned officers also qualified and were awarded this insignia, to include film actor Clark Gable. The Aerial Gunner Badge was issued until 1953, in the newly created United States Air Force (1947). The Aerial Gunner Badge was declared obsolete and phased out in favor of the Aircrew Badge. Those having received the Aerial Gunner Badge were permitted to wear the original badge until 1955, at which time the badge was no longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nose Gunner
A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passes through the pharynx, shared with the digestive system, and then into the rest of the respiratory system. In humans, the nose is located centrally on the face and serves as an alternative respiratory passage especially during suckling for infants. The protruding nose that completely separate from the mouth part is a characteristic found only in therian mammals. It has been theorized that this unique mammalian nose evolved from the anterior part of the upper jaw of the reptilian-like ancestors (synapsids). Air treatment Acting as the first interface between the external environment and an animal's delicate internal lungs, a nose conditions incoming air, both as a function of thermal regulation and filtration during respiration, as well as ena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tail Gunner
A tail gunner or rear gunner is a crewman on a military aircraft who functions as a gunner defending against enemy fighter or interceptor attacks from the rear, or "tail", of the plane. The tail gunner operates a flexible machine gun or autocannon emplacement in the tail end of the aircraft with an unobstructed view toward the rear of the aircraft. While the term ''tail gunner'' is usually associated with a crewman inside a gun turret, the first tail guns were operated from open apertures within the aircraft's fuselage, such as the Scarff ring mechanism used in the British Handley Page V/1500, which was introduced during latter months of the First World War. Increasingly capable tail gunner positions were developed during the interwar period and the Second World War, resulting in the emergence of the powered turret and fire control systems incorporating radar guidance. In particularly advanced tail gunner arrangements, the tail armament may be operated by remote cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Door Gunner
A door gunner is a crewman tasked with firing and maintaining manually directed armament aboard a military helicopter. The actual role will vary depending on the task given on a particular mission. For certain aircraft a door gunner would use a fully automatic Gatling gun placement. On many larger aircraft such as military planes a turret is used along with heavy cannons. Origins The concept of the ''door gunner'' originated during the Vietnam War, when helicopters were first used in combat in large numbers. The original personnel who served as early door gunners aboard CH-21, UH-34, and UH-1 helicopters in Vietnam, were enlisted men, with a designated and specially trained '' crew chief'' serving as both the aircraft's maintenance manager and a door gunner. Normally, a second enlisted soldier served as a second door gunner (such as on a UH-1, and UH-34, which both used two gunners – one on each side of the aircraft). Later, as the war progressed, the door gunner posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircrew
Aircrew, also called flight crew, are personnel who operate an aircraft while in flight. The composition of a flight's crew depends on the type of aircraft, plus the flight's duration and purpose. Commercial aviation Flight deck positions In commercial aviation, the aircrew are called ''flight crew''. Some flight crew position names are derived from nautical terms and indicate a rank or command structure similar to that on ocean-going vessels, allowing for quick executive decision making during normal operations or emergency situations. Historical flightdeck positions include: * Captain, the pilot highest-ranking member or members of a flight crew. * First officer (FO, also called a co-pilot), another pilot who is normally seated to the right of the captain. (On helicopters, an FO is normally seated to the left of the captain, who occupies the right-hand seat).Smith, PatrickPatrick Smith's Ask The Pilot: When a Pilot Dies in Flight AskThePilot.com website, 2013, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilot
An aircraft pilot or aviator is a person who controls the flight of an aircraft by operating its directional flight controls. Some other aircrew members, such as navigators or flight engineers, are also considered aviators, because they are involved in operating the aircraft's navigation and engine systems. Other aircrew members, such as drone operators, flight attendants, mechanics and ground crew, are not classified as aviators. In recognition of the pilots' qualifications and responsibilities, most militaries and many airlines worldwide award aviator badges to their pilots. History The first recorded use of the term ''aviator'' (''aviateur'' in French) was in 1887, as a variation of ''aviation'', from the Latin ''avis'' (meaning ''bird''), coined in 1863 by in ''Aviation Ou Navigation Aérienne'' ("Aviation or Air Navigation"). The term ''aviatrix'' (''aviatrice'' in French), now archaic, was formerly used for a female aviator. These terms were used more in the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunship
A gunship is a military aircraft armed with heavy aircraft guns, primarily intended for attacking ground targets either as airstrike or as close air support. In modern usage the term "gunship" refers to fixed-wing aircraft having laterally-mounted heavy armaments (i.e. firing to the side) to attack ground or sea targets. These gunships are configured to circle the target instead of performing strafing runs. Such aircraft have their armament on one side harmonized to fire at the apex of an imaginary cone formed by the aircraft and the ground when performing a pylon turn ( banking turn). The term "gunship" originated in the mid-19th century as a synonym for gunboat and also referred to the heavily armed ironclad steamships used during the American Civil War. The term helicopter gunship is commonly used to describe armed helicopters. World War II aviation Bomber escort During 1942 and 1943, the lack of a usable escort fighter for the United States Army Air Forces in the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of STOL (Short TakeOff and Landing) or STOVL (Short TakeOff and Vertical Landing) aircraft cannot perform without a runway. In 1942, the Sikorsky R-4 became the first helicopter to reach full-scale production.Munson 1968.Hirschberg, Michael J. and David K. Dailey"Sikorsky". ''US and Russian Helicopter Development in the 20th Century'', American Helicopter Society, International. 7 July 2000. Although most earlier designs used more than one main rotor, the configuration of a single main rotor accompanied by a vertical anti-torque tail rotor (i.e. unicopter, not to be confused with the single-blade monocopter) has become the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
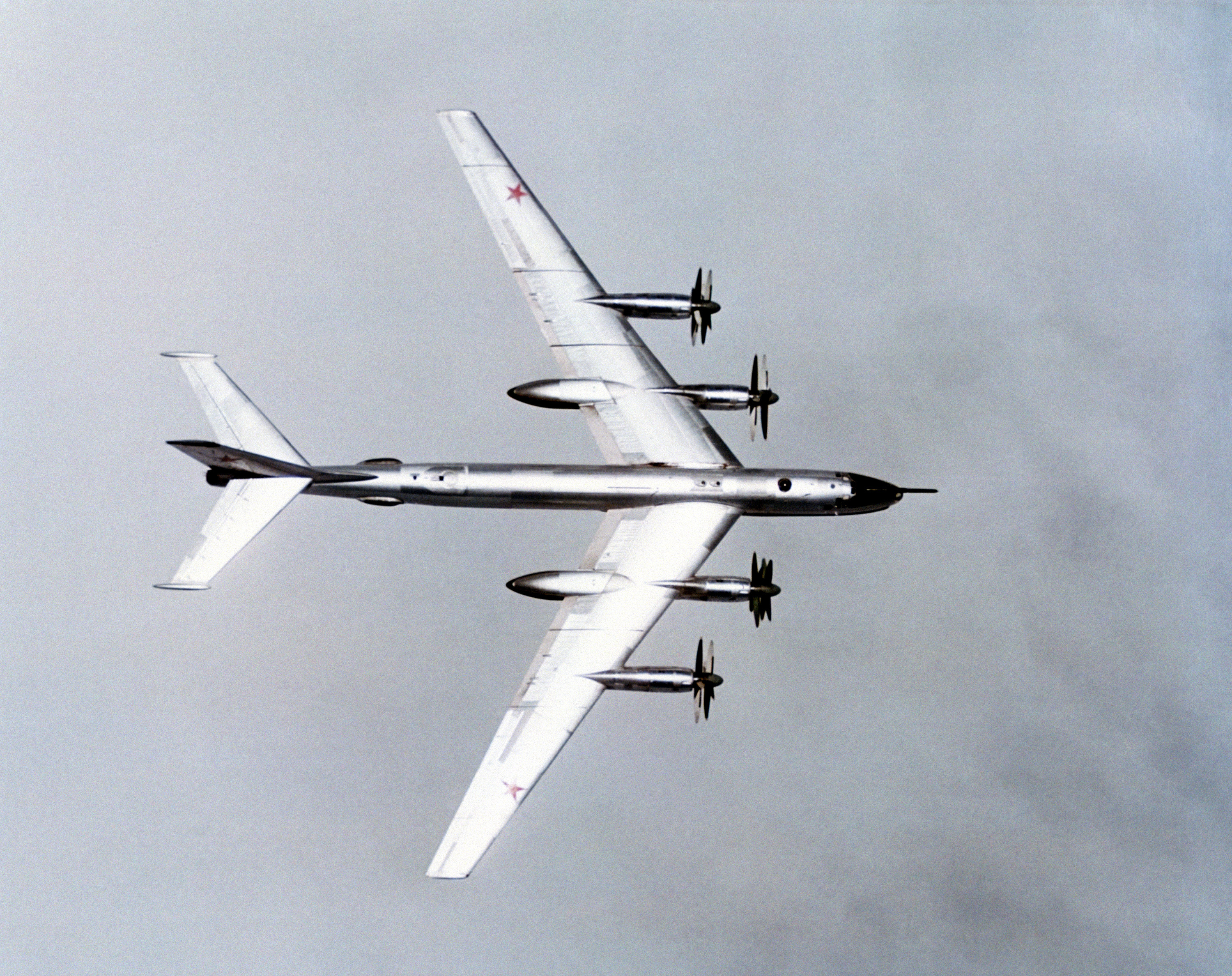
Tu-95 Tail
The Tupolev Tu-95 (russian: Туполев Ту-95; NATO reporting name: "Bear") is a large, four-engine turboprop-powered strategic bomber and missile platform. First flown in 1952, the Tu-95 entered service with the Long-Range Aviation of the Soviet Air Forces in 1956 and was first used in combat in 2015. It is expected to serve the Russian Aerospace Forces until at least 2040. A development of the bomber for maritime patrol is designated the Tu-142, while a passenger airliner derivative was called the Tu-114. The aircraft has four Kuznetsov NK-12 engines with contra-rotating propellers. It is the only propeller-powered strategic bomber still in operational use today. The Tu-95 is one of the loudest military aircraft, particularly because the tips of the propeller blades move faster than the speed of sound. Its distinctive swept-back wings are set at an angle of 35°. The Tu-95 is the only propeller-driven aircraft with swept wings that has been built in large numbers. Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an aircraft occurred in the Italo-Turkish War, with the first major deployments coming in the World War I, First World War and World War II, Second World War by all major airforces causing devastating damage to cities, towns, and rural areas. The first purpose built bombers were the Italy, Italian Caproni Ca 30 and United Kingdom, British Bristol T.B.8, both of 1913. Some bombers were decorated with nose art or victory markings. There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strategic bombing is done by heavy bombers primarily designed for long-range bombing missions against strategic targets to diminish the enemy's ability to wage war by limiting access to resources through crippling infrastructure or reduci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)




.jpg)