|
Agouti (coloration)
Agouti is a type of fur coloration in which each hair displays two or more bands of pigmentation. The overall appearance of agouti fur is usually gray or dull brown, although dull yellow is also possible. Agouti fur is characterized by an appearance of being composed of hairs of different colors, separate from definite markings (although agouti can appear in combination with other markings, such as spots, stripes or patches). This effect is caused by different ''portions'' of each hair being visible, such that different colors of the hair's banding are seen, despite hairs actually having similar coloration. This effect produces a very distinctive, finely "speckled" appearance similar to "salt and pepper" hair, as well as an iridescent effect very similar to shot silk which causes the overall color to appear to shift subtly depending on the angle of the light or when the animal moves. Agouti fur is the wild type pigmentation for many domesticated mammals. It is a highly re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodents
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/ricochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Once included with rodents, rabbits, hares, and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agouti-signaling Protein
Agouti-signaling protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASIP gene. It is responsible for the distribution of melanin pigment in mammals. Agouti interacts with the melanocortin 1 receptor to determine whether the melanocyte (pigment cell) produces phaeomelanin (a red to yellow pigment), or eumelanin (a brown to black pigment). This interaction is responsible for making distinct light and dark bands in the hairs of animals such as the agouti, which the gene is named after. In other species such as horses, agouti signalling is responsible for determining which parts of the body will be red or black. Mice with wildtype agouti will be grey-brown, with each hair being partly yellow and partly black. Loss of function mutations in mice and other species cause black fur coloration, while mutations causing expression throughout the whole body in mice cause yellow fur and obesity. The agouti-signaling protein (ASIP) is a competitive antagonist with alpha-Melanocyte-stimulati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodentia
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/ricochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Once included with rodents, rabbits, hares, and pik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agouti
The agouti (, ) or common agouti is any of several rodent species of the genus ''Dasyprocta''. They are native to Central America, northern and central South America, and the southern Lesser Antilles. Some species have also been introduced elsewhere in the West Indies. They are related to guinea pigs and look quite similar, but they are larger and have longer legs. The species vary considerably in colour, being brown, reddish, dull orange, greyish, or blackish, but typically with lighter underparts. Their bodies are covered with coarse hair, which is raised when alarmed. They weigh and are in length, with short, hairless tails. The related pacas were formerly included in genus ''Agouti'', but these animals were reclassified in 1998 as genus ''Cuniculus''. The Spanish term is ''agutí.'' In Mexico, the agouti is called the '. In Panama, it is known as the ' and in eastern Ecuador, as the '. Etymology The name "agouti" is derived from either Guarani or Tupi, both South Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fancy Mouse
A fancy mouse is a domesticated form of the house mouse (''Mus musculus''), one of many species of mouse , mice, usually kept as a type of pocket pet. Fancy mice have also been specially bred for Pet show, exhibiting, with shows being held internationally. A pet mouse is inexpensive compared to larger pets, and even many other pet rodents, but mice are comparatively short-lived: typically only 2 to 3 years. Description The term ''fancy mouse'' is used to describe a mouse that has been selectively bred for exhibition. Wild-caught specimens that become docile and are bred for many generations still fall under the ''fancy'' type. Fancy mice can vary greatly in size, from small pet mice that are approximately long from nose to the proximal start of the tail, to show mice that measure nose to tail. Pet mice weigh about . Varieties Artificial Selection, Artificial selection in fancy mice has created numerous available fur colours. These include colours like black, chocolate, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Kelpie
The Australian Kelpie, or simply Kelpie, is an Australia, Australian Herding dog, sheepdog capable of Muster (livestock), mustering and droving with little or no guidance. It is a medium-sized dog and comes in a variety of colours. The Kelpie has been exported throughout the world and is used to Muster (livestock), muster livestock, primarily sheep, cattle and goats. The breed has been separated into two distinct varieties: the Show (or Bench) Kelpie and the Working Kelpie. The Show Kelpie is seen at conformation dog shows in some countries and is selected for appearance rather than working instinct, while the Working Kelpie is bred for its working ability. History The ancestors of most Kelpies were British dogs known loosely as collies (sometimes spelled colleys). These were mostly black, or very dark brown, dogs – hence the name collie, which has the same root as coal. (The official collie breeds were not formed until about 10 or 15 years after the Kelpie was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberian Wolf
The Iberian wolf (''Canis lupus signatus'', or ''Canis lupus lupus'', Spanish: ''Lobo ibérico,'' Portuguese: ''Lobo-ibérico''), is a subspecies of grey wolf. It inhabits the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, which includes northwestern Spain and northern Portugal, housing 2,200 to 2,700 wolves. They form the largest wolf population in Western Europe. Due to population controls and damage to livestock, Iberian wolves were the only Western European subspecies of wolf whose hunting remained legal, until February 2021 when hunting was banned in Spain. The hunting permits given in Spain over the period 2019-21 were for a quota of 339 animals in total, strictly in the region north of the Douro river. Along with the difficulty of their hunt by virtue of their vigilant nature and the rarity of their sightings, they were strongly desired by many European hunters as a big-game trophy. Hunting in Spain became legal again in 2025 for the same region, due to growing population and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Carrier
A hereditary carrier (genetic carrier or just carrier), is a person or other organism that has inherited a recessive allele for a genetic trait or mutation but usually does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. Carriers are, however, able to pass the allele onto their offspring, who may then express the genetic trait. Carriers in autosomal inheritances Autosomal dominant-recessive inheritance is made possible by the fact that the individuals of most species (including all higher animals and plants) have two alleles of most hereditary predispositions because the chromosomes in the cell nucleus are usually present in pairs (diploid). Carriers can be female or male as the autosomes are homologous independently from the sex. In carriers the expression of a certain characteristic is recessive. The individual has both a genetic predisposition for the dominant trait and a genetic predisposition for the recessive trait, and the dominant expression prevails in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, and its behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code (its genotype) and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting the phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and again in his 1982 book '' The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as caddisfly larva cases and beaver dams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
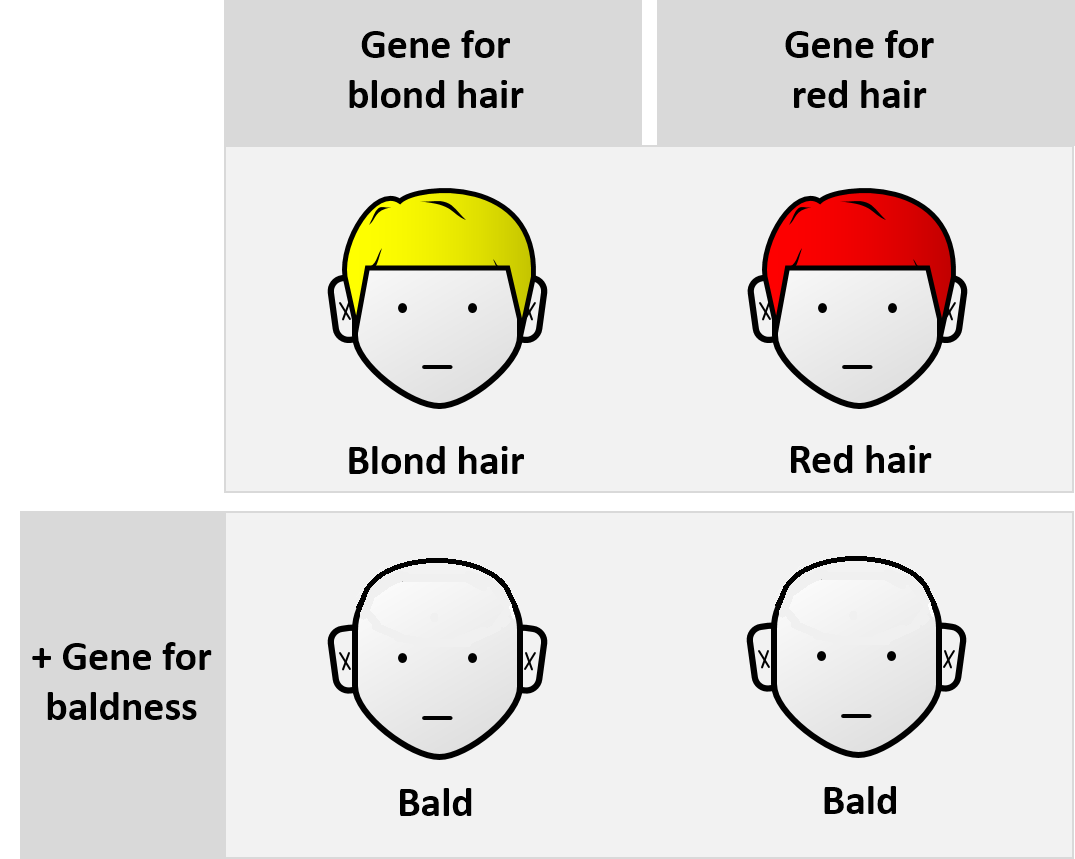
Epistasis
Epistasis is a phenomenon in genetics in which the effect of a gene mutation is dependent on the presence or absence of mutations in one or more other genes, respectively termed modifier genes. In other words, the effect of the mutation is dependent on the genetic background in which it appears. Epistatic mutations therefore have different effects on their own than when they occur together. Originally, the term ''epistasis'' specifically meant that the effect of a gene variant is masked by that of different gene. The concept of ''epistasis'' originated in genetics in 1907 but is now used in biochemistry, computational biology and evolutionary biology. The phenomenon arises due to interactions, either between genes (such as mutations also being needed in regulators of gene expression) or within them (multiple mutations being needed before the gene loses function), leading to non-linear effects. Epistasis has a great influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes, which leads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |