|
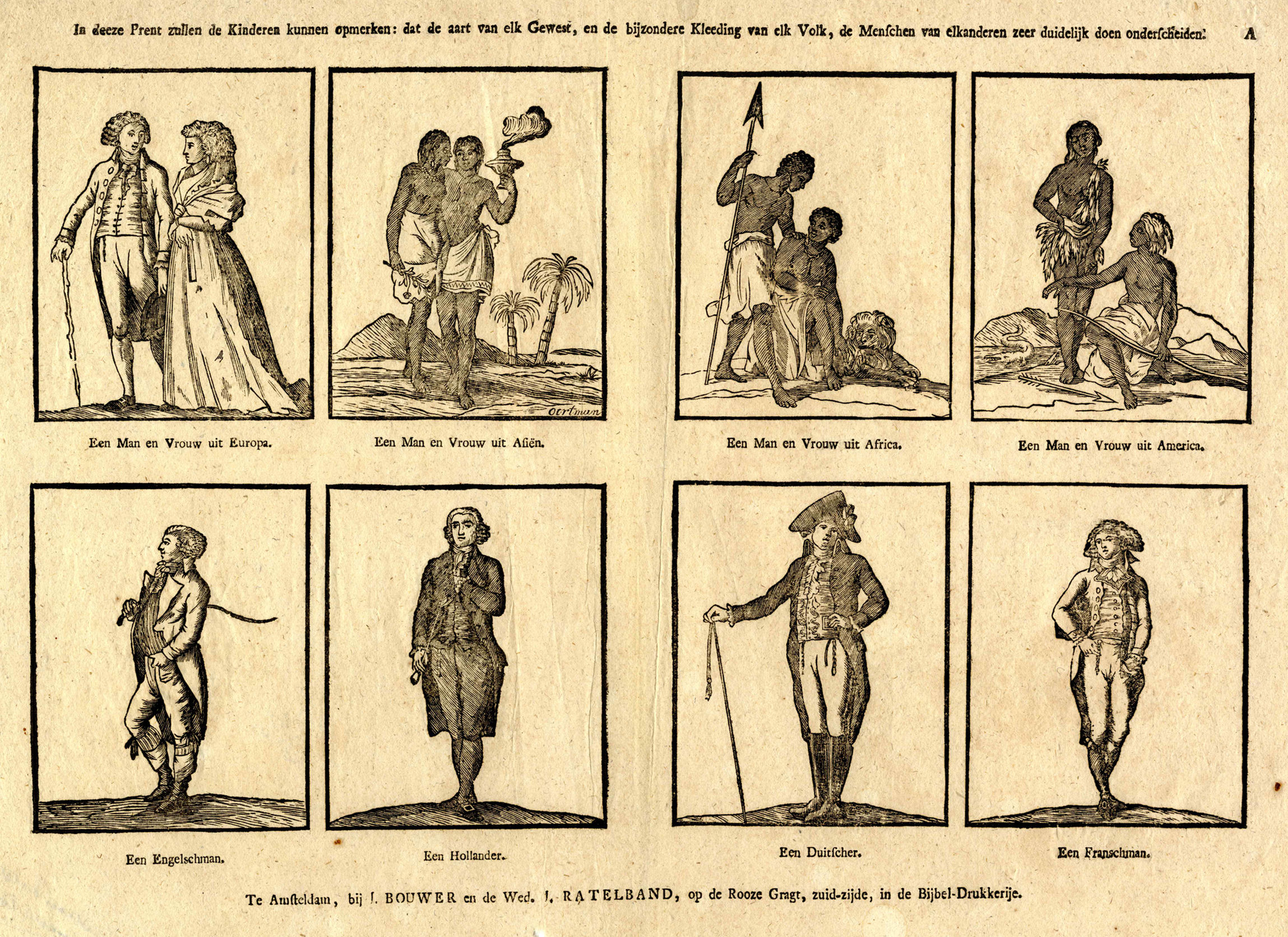
Ageism
Ageism, also called agism in American English, is a type of discrimination based on one's age, generally used to refer to age-based discrimination against Old age, elderly people. The term was coined in 1969 by Robert Neil Butler to describe this discrimination, building on the terminology of sexism and racism. Butler defined ageism as a combination of three connected elements: negative attitudes towards old age and the Ageing, ageing process, discriminatory practices against older people, and institutional practices and policies that perpetuate stereotypes about elderly people. The term "ageism" is also used to describe the oppression of younger people by older people. An example is a 1976 pamphlet published by Youth Liberation of Ann Arbor, Michigan. In the UK, at a meeting of the Bracknell Forest Council in June 1983, councillor Richard Thomas pointed out that age discrimination works against younger and older people. This includes the practice of denying younger people certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Becca Levy
Becca R. Levy is a professor of Epidemiology (Social and Behavioral Sciences) at Yale School of Public Health and Professor of Psychology at Yale University. She is a leading researcher in the fields of social gerontology and psychology of aging. She is credited with creating the field of how age stereotypes, which are assimilated from the culture, impact the health of older individuals.Appleby, J. (2019). From the CEO: Is ageism the "secondhand smoke" of healthy aging? ''Gerontological News'', ''47(7''), 2. The Dean of Columbia School of Public Health describes Levy as "a pioneer" in the "growing body of impressive research showing that our attitudes toward aging affect our health, our resilience in the face of adversity, and our very survival." Career Levy was born in Atlanta, Georgia. She studied psychology and Near Eastern studies at the University of Michigan, where she received a BA with Highest Distinction. Next she received her MA and PhD in psychology from Harvard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adultism
Adultism is a bias or prejudice against children or youth. It has been defined as "the power adults have over children", or the abuse thereof, as well as "prejudice and accompanying systematic discrimination against young people", and "bias towards adults... and the social addiction to adults, including their ideas, activities, and attitudes". It can be considered a subtype of ageism, or prejudice and discrimination due to age in general. This phenomenon is said to affect families, schools, justice systems and the economy, in addition to other areas of society. Its impacts are largely regarded as negative, except in cases related to child protection and the overriding social contract. Increased study of adultism has recently occurred in the fields of education, psychology, civic engagement, higher education and further, with contributions from Europe, North America and South America. Definitions and terminology Origin According to one writer, "the term 'adultism' has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrimination
Discrimination is the process of making unfair or prejudicial distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong, such as race, gender, age, class, religion, or sexual orientation. Discrimination typically leads to groups being unfairly treated on the basis of perceived statuses based on ethnic, racial, gender or religious categories. It involves depriving members of one group of opportunities or privileges that are available to members of another group. Discriminatory traditions, policies, ideas, practices and laws exist in many countries and institutions in all parts of the world, including some, where such discrimination is generally decried. In some places, countervailing measures such as quotas have been used to redress the balance in favor of those who are believed to be current or past victims of discrimination. These attempts have often been met with controversy, and sometimes been called re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Neil Butler
Robert Neil Butler (January 21, 1927 – July 4, 2010) was an American physician, gerontologist, psychiatrist, and author, who was the first director of the National Institute on Aging. Butler is known for his work on the social needs and the rights of the elderly and for his research on healthy aging and the dementias. Background Having grown up with his grandparents in Vineland, New Jersey, Butler was shocked by the dismissive and contemptuous attitude toward the elderly and their diseases by many of his teachers at medical school, an attitude he later characterized as "ageism". He graduated from Columbia College of Columbia University, where he was editor of the ''Columbia Daily Spectator'' and a member of the Philolexian Society. Career Butler was a principal investigator of one of the first interdisciplinary, comprehensive, longitudinal studies of healthy community-residing older persons, conducted at the National Institute of Mental Health (1955–1966), which resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephebiphobia
Ephebiphobia is the fear of youth. First coined as the "fear or loathing of teenagers",Astroth, K. (1994) Beyond ephebiphobia: problem adults or problem youths? (fear of adolescents). ''Phi Delta Kappan''. January 1, 1994. the phenomenon is recognized today as the "inaccurate, exaggerated and sensational characterization of young people" in a range of settings around the world. Studies of the fear of youth occur in sociology and youth studies. It is distinguished from pedophobia by being more focused on adolescents than prepubescent children. Lexicology Coinage The word ''ephebiphobia'' is formed from the Greek '' éphēbos'', meaning "youth" or "adolescent" and ''phóbos'', meaning "fear" or "phobia". The coinage of this term is attributed to a 1994 article by Kirk Astroth published in ''Phi Delta Kappan''. Today, common usage occurs internationally by sociologists, government agencies, and youth advocacy organizations that define ephebiphobia as an abnormal or irrational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Age
Old age is the range of ages for people nearing and surpassing life expectancy. People who are of old age are also referred to as: old people, elderly, elders, senior citizens, seniors or older adults. Old age is not a definite biological stage: the chronological age denoted as "old age" varies culturally and historically. Some disciplines and domains focus on the aging and the aged, such as the organic processes of aging (senescence), medical studies of the aging process (gerontology), diseases that afflict older adults (geriatrics), technology to support the aging society (gerontechnology), and leisure and sport activities adapted to older people (such as senior sport). Older people often have limited regenerative abilities and are more susceptible to illness and injury than younger adults. They face social problems related to retirement, loneliness, and ageism. In 2011, the United Nations proposed a human-rights convention to protect old people. History European The hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerontophobia
Gerontophobia is the hatred or fear of older adults, or a fear of age-related self-degeneration (similar to gerascophobia). The term comes from the Greek γέρων – ''gerōn'', "old man" and φόβος – ''phobos'', "fear". Gerontophobia that stems from a fear of aging has been linked to thanatophobia, as fear of old age can be a precursor to fear of death. Gerontophobia can be caused by stereotypes of older adults displayed in the media. Ageism Discriminatory aspects of ageism have been strongly linked to gerontophobia. This irrational fear or hatred of older adults can be associated with the expectation that someday all young people including oneself will be old inevitably and suffer from the irreversible health decline that comes with old age, which is associated with disability, disease, and death. The sight of aged people could be a possible reminder of death ('' memento mori'') and inevitable biological vulnerability. This unwillingness to accept these can manifest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotype
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalization, generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example, an expectation about the group's personality, preferences, appearance or ability. Stereotypes make information processing easier by allowing the perceiver to rely on previously stored knowledge in place of incoming information. Stereotypes are often faulty generalization, faulty, inaccurate, and Belief perseverance, resistant to new information. Although stereotypes generally have negative implications, they aren't necessarily negative. They may be positive, neutral, or negative. They can be broken down into two categories: explicit stereotypes, which are conscious, and implicit stereotypes, which are subconscious. Explicit stereotypes An explicit stereotype is a belief about a group that a person is consciously aware of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronocentrism
Chronocentrism is the assumption that certain time periods (typically the present) are better, more important, or a more significant frame of reference than other time periods, either past or future. The perception of more positive attributes such as morality, technology, and sophistication to one's own time could lead an individual as a member of a collectivity to impose their forms of time on others and impede the efforts towards more homogeneous temporal commons. History Chronocentrism (from the Greek '' chrono-'' meaning "time") was coined by sociologist Jib Fowles in an article in the journal ''Futures'' in February, 1974. Fowles described chronocentrism as "the belief that one's own times are paramount, that other periods pale in comparison". A critical view described it as the belief that only the present counts and that the past is irrelevant except to serve as a reference to a few basic assumptions about what went before. More recently, it has been defined as "the egotis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert N
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of ''Hrōþ, Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use Robert (surname), as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert (name), Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta (given name), Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto (given name), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT Press
The MIT Press is the university press of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The MIT Press publishes a number of academic journals and has been a pioneer in the Open Access movement in academic publishing. History MIT Press traces its origins back to 1926 when MIT published a lecture series entitled ''Problems of Atomic Dynamics'' given by the visiting German physicist and later Nobel Prize winner, Max Born. In 1932, MIT's publishing operations were first formally instituted by the creation of an imprint called Technology Press. This imprint was founded by James R. Killian, Jr., at the time editor of MIT's alumni magazine and later to become MIT president. Technology Press published eight titles independently, then in 1937 entered into an arrangement with John Wiley & Sons in which Wiley took over marketing and editorial responsibilities. In 1961, the centennial of MIT's founding charter, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, imagination, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem-solving and decision-making, comprehension and production of language. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge to discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from very different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) are synthesized in the developing field of cognitive science, a progressively autonomou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |