|
Adrenal Hemorrhage
Adrenal hemorrhage (AH) is acute blood loss from a ruptured vessel of the adrenal glands above the kidneys. It is a rare, yet potentially fatal event that could be caused by trauma and multiple non-traumatic conditions. Despite the unclear etiology, there are several risk factors of adrenal hemorrhage, including birth trauma, sepsis, and hemorrhagic disorders. Anoxia and sepsis are the most frequent causes at birth, while adrenal insufficiency often manifests in neonates. Adrenal haemorrhage has been reported during COVID-19 infection and following Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccination. According to the degree and rate of hemorrhage, its clinical manifestations can vary widely. The non-specific signs and symptoms in prominent underlying diseases often prevent prompt recognition and proper treatment of the condition, which may result in adrenal crisis, Shock (circulatory), shock, and death. Although the mortality rate varies with the severity of the underlying inductive disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Glands
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis. The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACTH
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and is often produced in response to biological stress (along with its precursor corticotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus). Its principal effects are increased production and release of cortisol and androgens by the zona fasiculata and zona reticularis, respectively. ACTH is also related to the circadian rhythm in many organisms. Deficiency of ACTH is an indicator of secondary adrenal insufficiency (suppressed production of ACTH due to an impairment of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, cf. hypopituitarism) or tertiary adrenal insufficiency (disease of the hypothalamus, with a decrease in the release of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)). Conversely, chronically ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet Aggregation
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activation''. Third, they connect to each other throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA), most typically a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine. Catechol can be either a free molecule or a substituent of a larger molecule, where it represents a 1,2-dihydroxybenzene group. Catecholamines are derived from the amino acid tyrosine, which is derived from dietary sources as well as synthesis from phenylalanine. Catecholamines are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins in circulation. Included among catecholamines are epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and dopamine. Release of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla of the adrenal glands is part of the fight-or-flight response. Tyrosine is created from phenylalanine by hydroxylation by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. Tyrosine is also ingested directly from dietary prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
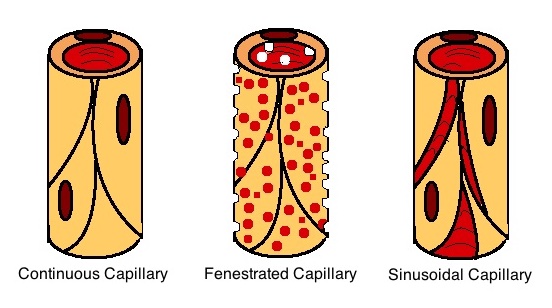
Sinusoids
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Cortex
The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of the adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones. It is also a secondary site of androgen synthesis. Layers The adrenal cortex comprises three main zones, or layers that are regulated by distinct hormones as noted below. This ''anatomic zonation'' can be appreciated at the microscopic level, where each zone can be recognized and distinguished from one another based on structural and anatomic characteristics. Zona glomerulosa The outermost layer, the zona glomerulosa is the main site for the production of aldosterone, a mineralocorticoid. The synthesis and secretion of aldosterone are mainly regulated by the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. The zona glomerulosa cells express a specific enzyme aldosterone synthase (also known as CYP11B2). Aldosterone is largely responsible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plexus
In anatomy, a plexus (from the Latin term for 'braid') is a branching network of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, or nerves. The nerves are typically axons outside the central nervous system. The standard plural form in English is plexuses. Alternatively, the Latin plural plexūs may be used. Types Nerve plexuses The four primary nerve plexuses are the cervical plexus, brachial plexus, lumbar plexus, and the sacral plexus. Cardiac plexus Celiac plexus Renal plexus Venous plexus Choroid plexus The choroid plexus is a part of the central nervous system in the brain and consists of capillaries, brain ventricles, and ependymal cells. Invertebrates The plexus is the characteristic form of nervous system in the coelenterates and persists with modifications in the flatworms. The nerves of the radially symmetric echinoderms also take this form, where a plexus underlies the ectoderm of these animals and deeper in the body other nerve cells form plexuses of limited extent. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Blood Flow
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis. The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
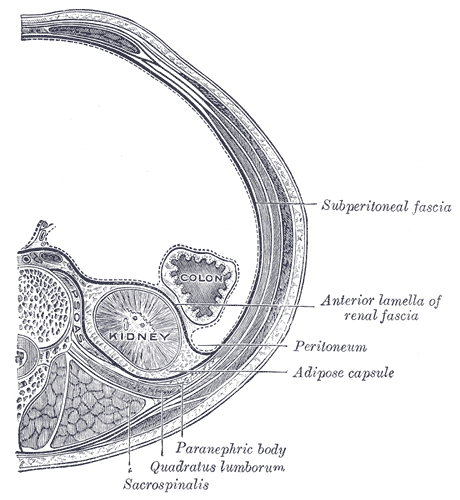
Retroperitoneum
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal. This is different from organs that are not retroperitoneal, which have peritoneum on their posterior side and are suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity. The retroperitoneum can be further subdivided into the following: *Perirenal (or perinephric) space *Anterior pararenal (or paranephric) space *Posterior pararenal (or paranephric) space Retroperitoneal structures Structures that lie behind the peritoneum are termed "retroperitoneal". Organs that were once suspended within the abdominal cavity by mesentery but migrated posterior to the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
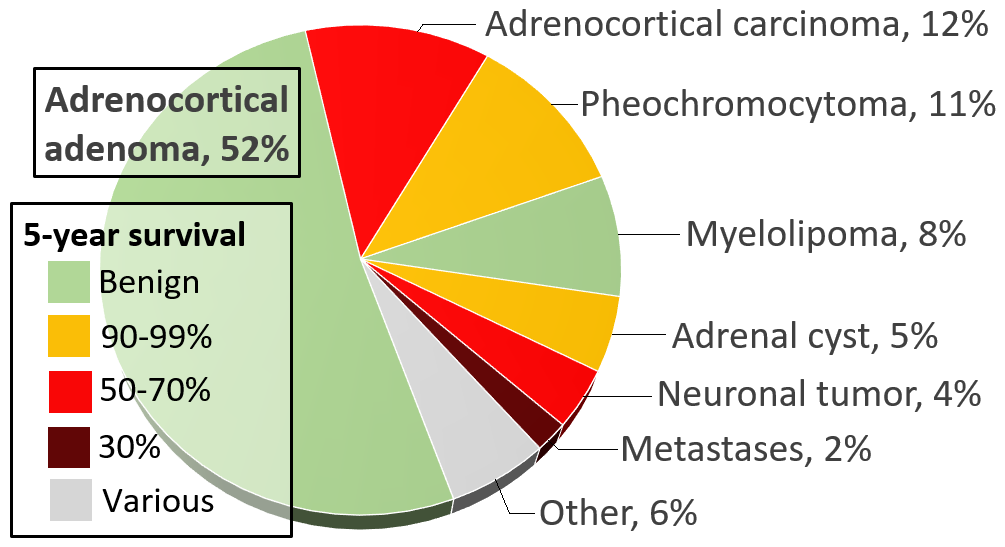
Myelolipoma
Myelolipoma (, from the Ancient Greek 'marrow'; , 'of, or pertaining to, ''fat'''; ''-oma'' 'tumor or mass'; also myolipoma) is a benign tumor-like lesion composed of mature adipose (fat) tissue and haematopoietic (blood-forming) elements in various proportions. Myelolipomas can present in the adrenal gland, or outside of the gland. Signs and symptoms The majority of myelolipomas are asymptomatic. Most do not produce any adrenal hormones. Most are only discovered as a result of investigation for another problem. When myelolipomas do produce symptoms, it is usually because they have become large, and are pressing on other organs or tissues nearby. Symptoms include pain in the abdomen or flank, blood in the urine, a palpable lump or high blood pressure. As they are benign tumors, myelolipomas do not spread to other body parts. Larger myelolipomas are at risk of localised tissue death and bleeding, which may cause a retroperitoneal haemorrhage. Causes Although several hypothes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has occurred, the affected cells divide incessantly and become cancerous, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Because lesions can occur anywhere in the body and their definition is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, sizes, locations, or causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called '' chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries, or "cavities". Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, "skin lesions" or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |